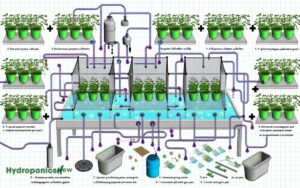
7 Essential Tips for Watering Hydroponic Plants: A Complete Guide
You need to manage water levels for hydroponic plants precisely. Water needs vary by plant type, growth stage, and environmental factors. Seedlings need minimal water, but requirements peak during flowering and fruiting phases.
Monitor daily water uptake and adjust flow rates accordingly. Maintain water pH between 5.5 and 6.5 and guarantee nutrient solution concentration stays within 1.2 to 2.5 mS/cm.
Factors like temperature, humidity, and light intensity will also impact water needs. Utilizing digital sensors for tracking helps maintain ideal water levels.
Effective water management is crucial for optimal plant health and growth. Dive deeper for advanced insights into maintaining perfect hydroponic conditions. This involves carefully monitoring nutrient levels, pH balance, and oxygenation to ensure plants receive the ideal growing environment. Proper water circulation and filtration help prevent root diseases and algae buildup, which can compromise plant health. To keep hydroponic plants alive, growers must consistently check water quality and adjust conditions as needed for sustained growth.

Key Takeaways
Understanding Hydroponic Water Needs
To understand hydroponic water needs, you must consider factors such as plant type, growth stage, and environmental conditions. Hydroponic systems rely on precise water management to maximize plant growth.
Start by identifying the specific water requirements for each plant species you’re cultivating. Seedlings typically need a higher moisture level, whereas mature plants might require less frequent watering. Utilize sensors and timers to monitor and adjust water delivery accurately.
Measure humidity, temperature, and light exposure regularly, as these environmental variables directly impact water uptake. Maintaining water pH between 5.5 and 6.5 is essential for nutrient absorption.
Frequent testing and adjustments ensure ideal conditions, preventing issues like root rot or nutrient deficiencies. This meticulous approach maximizes yield and plant health.
Factors Affecting Water Requirements
You need to take into account several key factors when determining the water requirements for hydroponic plants.
Plant growth stage, nutrient solution concentration, and environmental conditions all greatly impact water uptake.
Plant Growth Stage
The water requirements for hydroponic plants vary considerably depending on their growth stage. Seedlings need less water than mature, fruit-bearing plants. Initially, seedlings require minimal hydration to establish roots. Aim for 60-70% humidity to prevent desiccation.
As plants shift to the vegetative stage, increase water delivery to support rapid leaf and stem growth.
During flowering and fruiting phases, water needs peak due to higher transpiration rates and the energy demands of fruit production. Monitor daily water uptake rates and adjust flow rates accordingly.
Employ data loggers to track consumption patterns, ensuring precise adjustments. Consistent monitoring and adaptation are essential for ideal hydroponic plant health, maximizing yield, and maintaining resource efficiency.
Nutrient Solution Concentration
Accurately managing the concentration of your nutrient solution directly influences the water requirements of hydroponic plants. When you increase nutrient concentration, plants absorb more nutrients per unit of water, potentially reducing overall water consumption.
Conversely, a diluted solution can lead to higher water uptake to meet nutrient needs. It’s essential to monitor Electrical Conductivity (EC) levels, which measure nutrient concentration. Ideal EC ranges vary by plant type but generally fall between 1.2 to 2.5 mS/cm.
Deviations from these ranges can lead to either nutrient deficiencies or toxicities, impacting water uptake efficiency.
Regularly calibrate your EC meter and adjust your nutrient solution accordingly to maintain precise control over your hydroponic system’s water requirements.
Environmental Conditions
Environmental conditions like temperature, humidity, and light intensity have a significant impact on the water requirements of hydroponic plants.
You need to monitor these factors closely to guarantee ideal growth. Higher temperatures increase water uptake due to enhanced transpiration rates.
Conversely, low humidity levels can lead to faster evaporation, necessitating frequent water replenishment. Light intensity influences photosynthesis rates, thereby affecting water consumption.
Here’s a quick reference table:
| Condition | Impact on Water Needs | Ideal Range |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Increases with higher temps | 18-24°C (65-75°F) |
| Humidity | Low humidity increases needs | 50-70% |
| Light Intensity | Higher light increases needs | 400-700 µmol/m²/s |
Types of Hydroponic Systems
Several distinct hydroponic systems exist, each with unique methods for delivering nutrients and water to plants. You’ll find that these systems vary in complexity and efficiency.
Here are four primary types:
- Deep Water Culture (DWC): Roots are submerged in nutrient-rich water, providing consistent hydration.
- Nutrient Film Technique (NFT): A thin film of water flows over the roots, ensuring continuous nutrient delivery.
- Ebb and Flow (Flood and Drain): Periodically floods the grow tray with nutrient solution, then drains, allowing roots to oxygenate.
- Drip System: Delivers water and nutrients directly to the plant roots through a network of tubes and emitters.
Each system’s water usage efficiency varies, impacting overall water management strategies. Understanding these types helps optimize plant growth and resource use.
Monitoring Water Levels
To guarantee ideal plant growth, you must continuously monitor water levels in your hydroponic system to prevent over- or under-watering. Use digital sensors to track water levels accurately. These sensors provide real-time data, ensuring you can make timely adjustments.
Check water levels daily, as fluctuations can impact root health and nutrient uptake. Aim to maintain a consistent water level that aligns with your system type and plant requirements. Keep a log of water usage patterns to identify trends and predict future needs.
Monitoring is essential: too much water can lead to root rot, while too little can cause dehydration. Precision in water management ensures excellent plant growth and maximizes yield.
Nutrient Solution Balance
You need to maintain precise nutrient ratios to optimize plant health and growth in hydroponics. Monitor the pH levels regularly, as they directly affect nutrient absorption. Ensuring the correct balance will maximize yield and prevent nutrient deficiencies.
Essential Nutrient Ratios
Maintaining ideal nutrient ratios in a hydroponic solution is crucial for maximizing plant growth and ensuring a consistent supply of necessary minerals. To achieve this balance, you need to carefully monitor the concentration of each essential nutrient.
Here are the key ratios to maintain:
- Nitrogen (N): Promotes leaf growth. Ideal range: 150-250 ppm.
- Phosphorus (P): Supports root development and flowering. Ideal range: 30-50 ppm.
- Potassium (K): Enhances overall plant health and disease resistance. Ideal range: 150-200 ppm.
- Calcium (Ca): Strengthens cell walls and aids nutrient uptake. Ideal range: 100-150 ppm.
Ph Level Importance
Understanding the importance of pH levels in your nutrient solution is essential for optimizing nutrient uptake and plant health in hydroponic systems. You need to maintain a pH range of 5.5 to 6.5, as this range guarantees maximum nutrient availability.
Deviations outside this range can lead to nutrient lockout, where essential elements become inaccessible to plants. Use a reliable pH meter for precise monitoring. Regularly check and adjust the pH using pH up or pH down solutions.
Data shows that even minor pH fluctuations can greatly impact plant growth. By maintaining the correct pH, you’ll enhance nutrient absorption, leading to healthier, more vigorous plants. Remember, consistent pH management is key to a successful hydroponic setup.
Effects of Overwatering
Overwatering in hydroponic systems often leads to root rot, nutrient imbalances, and decreased oxygen availability, ultimately harming plant health.
When you overwater, roots become waterlogged, creating an anaerobic environment conducive to pathogenic fungi. This disrupts nutrient uptake and can cause deficiencies or toxicities.
Key indicators of overwatering include:
- Root Rot: Brown, mushy roots indicate oxygen deprivation and fungal infection.
- Nutrient Imbalances: Excess water dilutes nutrient concentrations, disrupting plant growth.
- Stunted Growth: Poor oxygenation inhibits root respiration, slowing down overall plant development.
- Wilting: Despite abundant water, lack of oxygen causes leaves to wilt and yellow.
Effects of Underwatering
Underwatering in hydroponic systems leads to nutrient deficiencies and impaired plant growth due to insufficient water for nutrient uptake.
When plants don’t receive enough water, they can’t absorb essential minerals, resulting in stunted growth and yellowing leaves. You’ll notice that plants suffer from stress, making them more susceptible to diseases and pests.
| Symptom | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Stunted Growth | Insufficient Nutrient Absorption | Increase Water Supply |
| Yellowing Leaves | Lack of Nitrogen Uptake | Adjust Nutrient Solution |
| Wilted Appearance | Dehydration | Monitor Water Levels |
| Increased Susceptibility | Plant Stress | Ensure Consistent Water Flow |
To maintain top-notch plant health, guarantee a consistent and adequate water supply. Accurate monitoring of hydroponic systems is critical to prevent underwatering and its detrimental effects.
Tips for Water Management
Effective water management in hydroponic systems hinges on precise control of water levels, flow rates, and nutrient concentrations to guarantee ideal plant growth. You need to consistently monitor and adjust these variables to maintain ideal plant health.
Here are four critical tips:
- Monitor pH Levels: Keep the pH between 5.5 and 6.5 for most plants.
- Check Electrical Conductivity (EC): Maintain nutrient concentration is within the recommended range, usually 1.2-2.0 mS/cm.
- Maintain Water Temperature: Ideal water temperature is between 65°F to 75°F to prevent root diseases.
- Regularly Replace Water: Change the water every two weeks to avoid nutrient imbalances and algae growth.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
While managing a hydroponic system, it is vital to avoid common mistakes that can compromise plant health and productivity. Overwatering, underestimating nutrient requirements, and neglecting pH levels are frequent errors. Precise monitoring is key for ideal growth.
Utilize the table below to understand the key areas to focus on:
| Mistake | Consequence | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Overwatering | Root rot, reduced oxygen | Adjust water flow, increase aeration |
| pH Neglect | Nutrient lockout | Regular pH testing, adjust as needed |
| Poor Nutrient Mix | Stunted growth, deficiency | Use balanced nutrient solutions |
| Inconsistent Light | Irregular growth, stress | Maintain consistent light cycles |
| Ignoring Temperature | Slow growth, disease | Monitor and regulate temperature |
Conclusion
You’ve now got a crystal-clear picture of how to quench your hydroponic plants’ thirst. Balancing water needs is like walking a tightrope, requiring precision and a keen eye on details.
By understanding your system and diligently monitoring water levels, you’ll strike the perfect harmony. Remember, overwatering and underwatering are pitfalls you can avoid with the right know-how.
Keep these tips in your back pocket, and you’ll master hydroponic water management like a seasoned pro.