3 Easy Steps to Build Your Own DIY Drip DTW Hydroponics System
Building a DIY drip drain-to-waste (DTW) hydroponics system requires precise planning and specialized materials to enhance plant growth. Start with a food-grade, light-proof reservoir to prevent algae growth, and use durable nutrient delivery tubes for a consistent flow.
Guarantee high-quality nutrient solutions tailored to your plants and inert growing media like perlite or rock wool. Incorporate an air pump and stones to oxygenate the nutrient solution, preventing root rot.
Design the system with adequate root space, ideal plant spacing, and high-quality drip emitters. Precise measurements and secure connections are essential for a stable framework.
For further insights, continue on the structured guidelines provided.

Key Takeaways
- Use food-grade, light-proof reservoirs to prevent algae growth and ensure safe nutrient storage.
- Position high-quality drip emitters directly above plant roots for consistent nutrient delivery.
- Install air pumps and stones to oxygenate nutrient solution and prevent root rot.
- Monitor pH and EC levels in real-time to maintain optimal nutrient balance.
Materials Needed
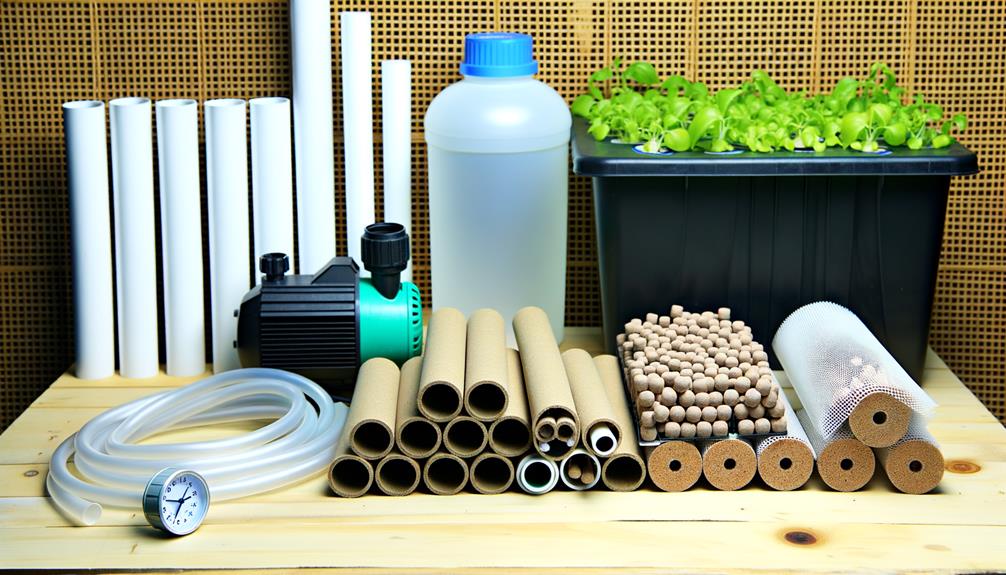

To build your own hydroponics system, it is essential to gather specific materials that guarantee peak plant growth and system functionality.
Key components include a reservoir for nutrient solutions, which should be food-grade and light-proof to prevent algae growth.
Nutrient delivery tubes and emitters must be durable and precisely sized to ascertain consistent flow rates.
A high-quality hydroponic nutrient solution tailored to your plant species is critical for ideal growth.
Use inert growing media such as perlite or rock wool to support plant roots and facilitate nutrient uptake.
Additionally, an air pump and air stones are necessary to oxygenate the nutrient solution, thereby preventing root rot.
System Design
Designing an effective hydroponics system requires meticulous planning and an understanding of plant-specific requirements to guarantee ideal growth conditions. This involves selecting the appropriate nutrient solution, maintaining optimal water pH levels, and ensuring adequate light exposure. One popular approach is to build a flood and drain system, which periodically submerges plant roots in nutrient-rich water before draining to provide oxygen. Proper aeration and monitoring are essential to prevent root rot and promote healthy development.
The system must accommodate root space, nutrient delivery, and best light penetration. Precision in spacing between plants ensures adequate airflow and prevents overcrowding, which can lead to disease.
Utilizing high-quality drip emitters guarantees consistent nutrient and water delivery, critical for maintaining uniform growth. Selecting appropriate reservoir size based on plant water consumption is paramount, avoiding nutrient imbalances.
Employing sensors for real-time monitoring of pH and electrical conductivity (EC) levels enhances control over nutrient solutions. Integrating automated timers for drip intervals improves resource use and reduces manual intervention, fostering an environment conducive to robust plant development.
Building the Framework
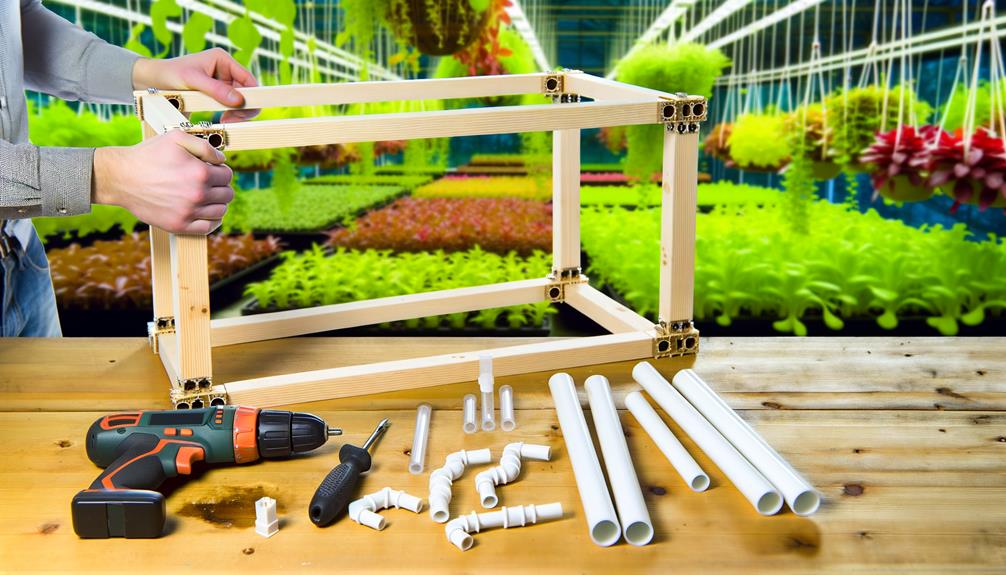

Constructing the framework of a hydroponics system requires precise assembly of structural components to support plant growth and nutrient delivery mechanisms efficiently.
Begin by selecting durable, non-reactive materials such as PVC or food-grade plastic to guarantee longevity and safety for plants.
Use accurate measurements to cut and assemble these materials into a stable structure, capable of holding the weight of growing plants and nutrient solution.
Securely fasten joints and connections to prevent leaks and maintain system integrity.
Incorporate adjustable shelving or support brackets to accommodate different plant sizes and growth stages.
Implement a design that allows for easy access to plants and maintenance tasks.
This foundational setup is essential for peak system performance and future scalability.
Installing the Drip System
After securing the structural framework, the next step involves installing the drip system to guarantee efficient nutrient delivery to the plants.
Begin by strategically positioning the main irrigation tubing along the framework to ascertain even distribution. Attach emitters to the tubing, ensuring they are precisely aligned with each plant's root zone for ideal hydration. Finally, connect the tubing to a nutrient reservoir equipped with a submersible pump.
- Tubing layout: Ascertain the tubing runs parallel to the plant rows for consistent coverage.
- Emitter placement: Position emitters directly above the plant roots to maximize nutrient uptake.
This precision-oriented installation will foster healthy growth and maximize system efficiency, meeting the needs of innovative horticulturists.
Maintenance Tips

Regular maintenance is essential to guarantee the long-term efficiency and productivity of your hydroponic system. Key tasks include monitoring nutrient levels, inspecting pump functionality, and making sure drip emitters are free from blockages. Precision in these tasks prevents plant stress and supports ideal growth.
| Maintenance Task | Frequency | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Nutrient Solution Check | Weekly | Measure and adjust pH and EC levels |
| Pump Inspection | Bi-weekly | Confirm the pump is operational and not clogged |
| Drip Emitter Cleaning | Monthly | Remove and clean emitters to prevent blockages |
| System Flush | Bi-monthly | Flush the entire system to remove salt build-up |
Adhering to this schedule fosters a resilient and productive hydroponic environment.
Conclusion
In summary, constructing a DIY drip DTW hydroponics system requires precise coordination of materials, design, and assembly.
The intricate process, akin to assembling a complex puzzle, demands meticulous attention to detail to guarantee ideal plant growth and system efficiency.
Proper maintenance further enhances the system's longevity, ensuring it continues to deliver nutrients effectively.
By adhering to these guidelines, one can cultivate a thriving hydroponic environment, fostering robust plant development and maximizing agricultural productivity.