7 Steps to Do-It-Yourself Hydroponic Growing Systems
Creating your own hydroponic growing system involves precise management of nutrient solutions and environmental conditions to optimize plant growth without the need for soil. Key benefits include efficient water usage, accelerated growth rates, and the ability to control lighting, pH, and temperature parameters for year-round cultivation.
Essential components include a nutrient reservoir, air and water pumps, pH and EC meters, and suitable grow lights. Popular systems like Nutrient Film Technique (NFT) and Deep Water Culture (DWC) cater to various plant species, enhancing productivity.
By mastering these elements, you can greatly boost yields and streamline urban food production, uncovering advanced techniques and solutions.

Key Takeaways
- Optimized Nutrient Delivery: Hydroponic systems ensure precise nutrient uptake by dissolving nutrients directly in water.
- Efficient Water Usage: Recirculation techniques in hydroponic systems significantly reduce water consumption compared to traditional soil methods.
- Environmental Control: Hydroponics allows for the regulation of pH, light, and temperature, enabling year-round cultivation.
- System Types: Choose from Nutrient Film Technique, Deep Water Culture, Ebb and Flow, and Aeroponics based on your plant species and cultivation goals.
Benefits of Hydroponic Gardening

Hydroponic gardening offers numerous benefits, including optimized nutrient delivery, efficient water usage, and the ability to control environmental conditions to maximize plant growth and yield.
By dissolving essential nutrients directly into water, hydroponic systems guarantee precise nutrient uptake, preventing soil-borne diseases and nutrient deficiencies.
Water efficiency is enhanced through recirculation techniques, considerably reducing water usage compared to traditional soil-based methods.
Environmental control, through regulated pH levels, light intensity, and temperature, provides ideal growth conditions year-round.
This scientific approach eliminates variables associated with soil cultivation, leading to accelerated growth rates and higher yields.
For innovators, hydroponics represents a sustainable, scalable solution to food production challenges, particularly in urban settings with limited arable land.
Types of Hydroponic Systems
Among the various methodologies employed in soilless cultivation, several distinct hydroponic systems stand out for their unique mechanisms of nutrient delivery and plant support.
The Nutrient Film Technique (NFT) circulates a thin film of nutrient-rich solution over the plant roots, optimizing oxygenation and nutrient uptake.
Deep Water Culture (DWC) submerges roots in an oxygenated nutrient solution, promoting rapid growth through direct nutrient access.
The Ebb and Flow system operates on a cyclic flooding and draining mechanism, ensuring roots receive intermittent exposure to air and nutrients.
Aeroponics, the most advanced, mists roots with nutrient solution, ensuring maximum aeration and nutrient absorption.
Each system offers unique advantages, catering to different plant species and cultivation objectives, driving the evolution of innovative hydroponic practices.
Choosing the Right Plants

Selecting the appropriate plant species is paramount to maximizing the efficiency and productivity of your chosen hydroponic system.
For ideal growth, opt for crops with high transpiration rates, such as leafy greens like lettuce and spinach, which thrive in nutrient-rich, water-based environments.
Herbs, including basil and cilantro, also exhibit robust growth in hydroponic setups.
Fruit-bearing plants, such as tomatoes and strawberries, require more advanced systems with precise nutrient delivery and pH control.
Root vegetables, conversely, are generally less suited to hydroponic cultivation due to their spatial and substrate requirements.
Necessary Tools and Materials
Equipping a hydroponic system necessitates a precise selection of tools and materials, ensuring ideal functionality and plant health.
Essential components include a reservoir for nutrient solutions, an air pump with air stones for oxygenation, and appropriate grow media such as Rockwool or clay pellets.
Additionally, submersible water pumps facilitate nutrient distribution, while pH and EC (electrical conductivity) meters are indispensable for monitoring solution quality.
Lighting systems, preferably LED or high-intensity discharge (HID) lights, provide the necessary photosynthetically active radiation (PAR).
Timers automate light and pump cycles, optimizing energy use.
Moreover, nutrient solutions must be meticulously formulated to supply all essential macronutrients and micronutrients.
These elements collectively foster a controlled environment conducive to robust plant growth and innovation in hydroponic agriculture.
Setting Up Your System
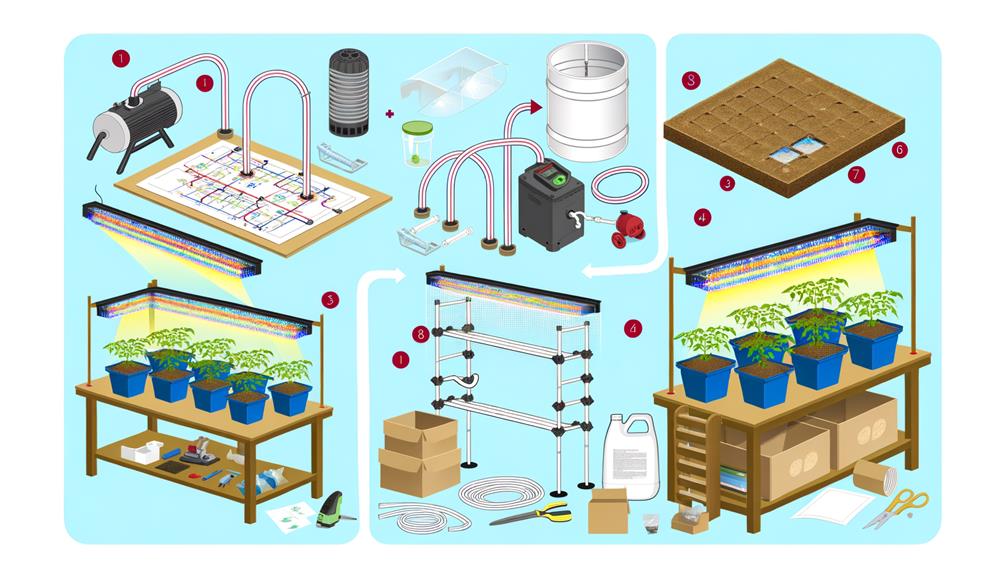
To effectively establish a hydroponic system, it is vital to select appropriate equipment that meets the specific needs of the plant species being cultivated.
Preparing a balanced nutrient solution tailored to the growth stage of the plants guarantees ideal nutrient uptake and overall plant health.
Additionally, installing suitable grow lights is fundamental for providing the necessary light spectrum and intensity to promote photosynthesis and robust plant development.
Choosing Proper Equipment
Essential to the success of any hydroponic system is the careful selection of equipment that meets the specific requirements of your chosen growing method.
Vital components include grow lights, which should provide the ideal light spectrum for photosynthesis, and high-efficiency pumps that guarantee consistent nutrient delivery.
The choice of grow medium, whether rockwool, perlite, or clay pellets, must support root aeration and moisture retention.
Advanced pH and EC meters are indispensable for monitoring nutrient solution parameters.
Additionally, temperature and humidity controllers are essential for maintaining an ideal growing environment.
Selecting a robust reservoir and an appropriate irrigation system, such as drip emitters or nutrient film technique (NFT) channels, will further streamline operations and enhance plant growth potential.
Preparing Nutrient Solution
Properly preparing the nutrient solution is essential for enhancing plant health and ensuring vigorous growth in any hydroponic system.
Begin by selecting a high-quality hydroponic nutrient blend, ensuring it contains macronutrients (N, P, K) and essential micronutrients (Fe, Mn, Zn).
Dissolve the nutrients in dechlorinated water, maintaining a pH range of 5.5-6.5 for ideal nutrient uptake.
Utilize a reliable pH meter and EC (electrical conductivity) meter to monitor and adjust the solution's parameters accurately.
Regularly check and replenish the nutrient solution to sustain consistent nutrient availability.
Ensuring the solution is well-aerated can enhance root oxygenation, promoting healthier plant growth.
Adhering to these guidelines will foster a robust, productive hydroponic environment.
Installing Grow Lights
Installing grow lights in your hydroponic system is crucial for providing the ideal spectrum and intensity of light necessary for vigorous plant growth and development.
High-Intensity Discharge (HID) lights, including Metal Halide (MH) and High-Pressure Sodium (HPS), are frequently used due to their proven efficacy in promoting photosynthesis.
Alternatively, Light Emitting Diode (LED) grow lights offer energy efficiency, longevity, and customizable light spectra, making them an innovative choice for modern hydroponic setups.
Position the lights approximately 12-24 inches above the plant canopy to guarantee the best light distribution without causing photobleaching or heat stress.
Implementing a timer system is advisable to regulate photoperiods, mimicking natural sunlight cycles.
Proper installation and maintenance of grow lights are critical for maximizing yield and plant health.
Nutrient Solutions Explained
Understanding the complexities of nutrient solutions is fundamental to enhancing plant growth in hydroponic systems. Nutrient solutions are aqueous mixtures containing essential macro and micronutrients important for plant development. The precise formulation of these solutions can dramatically impact plant health and yield.
Key components include:
- Macronutrients: Nitrogen (N), Phosphorus (P), and Potassium (K) are critical for growth, energy transfer, and disease resistance.
- Micronutrients: Elements such as Iron (Fe), Manganese (Mn), and Zinc (Zn) are required in trace amounts but are essential for enzymatic functions and overall plant metabolism.
- pH Balancing: Maintaining an ideal pH range (typically 5.5-6.5) guarantees nutrient availability and prevents deficiencies or toxicities.
Mastering these elements is necessary for any hydroponic grower's success.
Monitoring and Maintenance
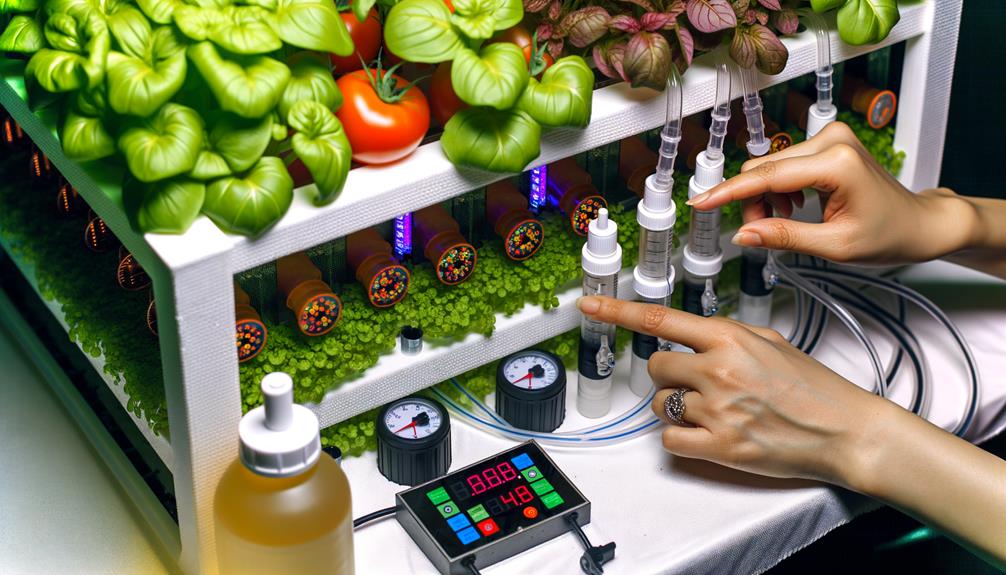

To guarantee ideal plant health and maximize yields in hydroponic systems, rigorous monitoring and maintenance of nutrient solutions, pH levels, and system components are indispensable. Employing precise instrumentation to measure electrical conductivity (EC) and pH guarantees peak nutrient uptake. Consistent inspection of system components, such as pumps and tubing, prevents malfunctions and nutrient imbalances. The following table outlines critical monitoring parameters:
| Parameter | Peak Range | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| pH Level | 5.5 – 6.5 | Daily |
| Electrical Conductivity (EC) | 1.2 – 2.2 mS/cm | Weekly |
| Water Temperature | 18°C – 22°C | Daily |
| Nutrient Solution | Fresh, balanced | Bi-weekly |
| System Cleanliness | No algae or debris | Weekly |
Maintaining these parameters guarantees a robust, high-yield hydroponic environment, leveraging advanced monitoring for superior growth outcomes.
Common Issues and Solutions
Hydroponic systems, while highly efficient, are susceptible to various issues such as nutrient imbalances, pest infestations, and equipment failures, each requiring targeted solutions to maintain ideal plant health.
Addressing these concerns involves a systematic approach:
- Nutrient Imbalances: Regularly monitor and adjust nutrient solutions using an EC meter to verify ideal concentrations, preventing deficiencies and toxicities.
- Pest Infestations: Implement integrated pest management (IPM) practices, including biological controls and organic pesticides, to manage and prevent outbreaks.
- Equipment Failures: Conduct routine maintenance checks on pumps, lights, and timers to identify and replace faulty components, verifying uninterrupted system operation.
Optimizing Plant Growth

To achieve ideal plant growth in hydroponic systems, it is essential to meticulously balance light intensity and spectral quality with precise nutrient formulations tailored to specific plant needs.
Effective temperature and humidity control, maintaining parameters within optimal ranges, further guarantees robust physiological development and maximizes yield potential.
Implementing advanced monitoring and automation technologies can considerably enhance system efficiency and plant health.
Light and Nutrient Balance
Achieving ideal plant growth in hydroponic systems necessitates a meticulous balance of light intensity and spectral quality, coupled with precise nutrient management.
Optimal light conditions are critical for photosynthesis and can be controlled using LED grow lights that offer customizable spectral output. Proper nutrient solutions must be tailored to specific plant requirements, ensuring the correct concentration of essential macro and micronutrients.
To enhance light and nutrient balance, consider the following:
- Light Intensity: Adjust LED lights to maintain a Photosynthetically Active Radiation (PAR) range of 200-400 µmol/m²/s for vegetative growth.
- Spectral Quality: Utilize full-spectrum lights, emphasizing blue light (400-500 nm) for vegetative stages and red light (600-700 nm) for flowering stages.
- Nutrient Solution: Maintain Electrical Conductivity (EC) between 1.0-2.5 mS/cm, depending on plant type and growth stage.
Temperature and Humidity Control
Maintaining ideal temperature and humidity levels is paramount for regulating plant physiology and maximizing growth efficiency in hydroponic systems. Temperature affects enzymatic activities, nutrient uptake, and metabolic rates, while humidity influences transpiration and water absorption. An ideal range must be sustained to prevent plant stress and pathogen proliferation.
| Parameter | Ideal Range |
|---|---|
| Temperature | 68-75°F (20-24°C) |
| Humidity | 50-70% RH |
| Night Temp | 60-68°F (16-20°C) |
| Day Temp | 70-80°F (21-27°C) |
Advanced environmental controls, such as automated climate systems, promote precision. Innovations in sensor technology and IoT integration allow for real-time monitoring and adjustments, fostering consistent plant health and enhanced yields in hydroponic setups.
Harvesting and Enjoying Your Produce
Harvesting hydroponic produce requires keen attention to the ideal maturation indicators specific to each plant species, ensuring peak nutritional value and flavor. Mastery over this aspect involves understanding three critical factors:
- Visual Cues: Observe color changes, leaf texture, and fruit firmness. For instance, tomatoes should exhibit a deep red hue, while lettuce leaves should be crisp and vibrant.
- Timing: Harvesting should align with the diurnal cycle, preferably in the morning, to capture prime moisture content and nutrient density.
- Tools and Techniques: Utilize sterilized scissors or knives to prevent plant tissue damage and pathogen transmission.
Conclusion
Hydroponic gardening, akin to a finely-tuned symphony, requires precise orchestration of various elements to achieve ideal plant growth.
Just as a maestro harmonizes different instruments to create a masterpiece, the careful management of nutrient solutions, pH levels, and light conditions guarantees a thriving hydroponic ecosystem.
Data show that hydroponic systems can yield crops up to 30% faster than traditional soil-based methods, underscoring the system’s efficiency and potential for sustainable agriculture. This accelerated growth is primarily due to the direct delivery of nutrients to the plant roots, eliminating the need for extensive root systems to search for nourishment. As a result, hydroponics grows faster than soil, making it an ideal solution for regions with limited arable land or harsh climates. Additionally, the controlled environment reduces water usage and minimizes pesticide reliance, further enhancing its role in sustainable agriculture.






