5 Essential Steps to Grow Strawberries Hydroponically
To grow strawberries hydroponically, select a suitable system such as Nutrient Film Technique (NFT) or Deep Water Culture (DWC). Opt for everbearing varieties like 'Albion' for continuous fruiting.
Ascertain proper plant spacing, and use high-efficiency LED lighting to mimic sunlight. Nutrient solutions must be carefully balanced with essential macro and micronutrients, maintaining a pH range of 5.5-6.5 and an electrical conductivity (EC) of 1.4-2.0 mS/cm.
Monitor and adjust these parameters regularly. Post-harvest, strawberries should be stored at 0-2°C with 90-95% relative humidity.
By following these steps, one can optimize growth and yield. Explore further to master the complete process.
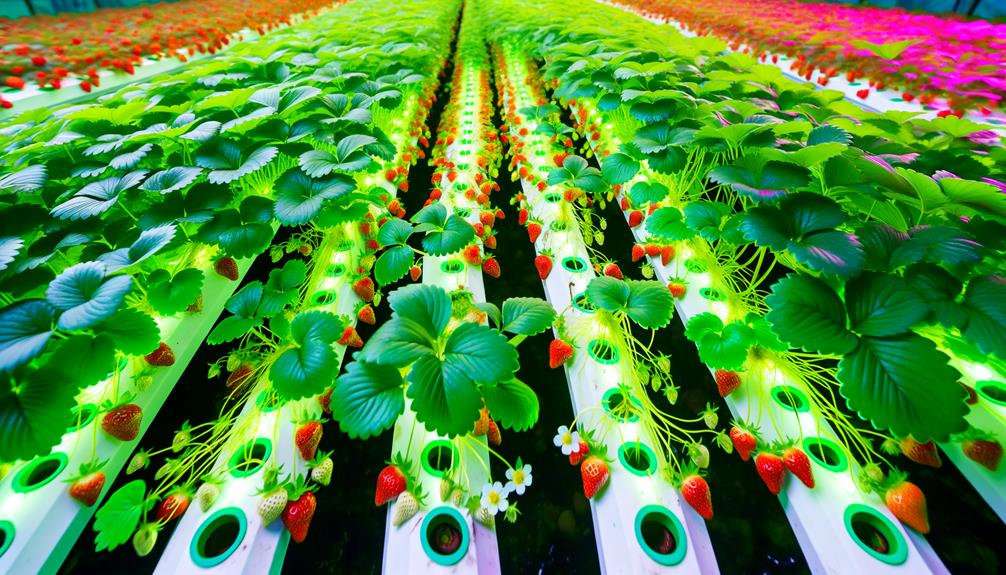

Key Takeaways
- Choose a hydroponic system like NFT or DWC for strawberry cultivation.
- Select everbearing or day-neutral varieties for continuous fruiting and disease resistance.
- Maintain nutrient solution pH between 5.5 and 6.5 for optimal nutrient uptake.
- Use high-efficiency LED lighting to supplement natural sunlight if growing indoors.
Choosing the Right System
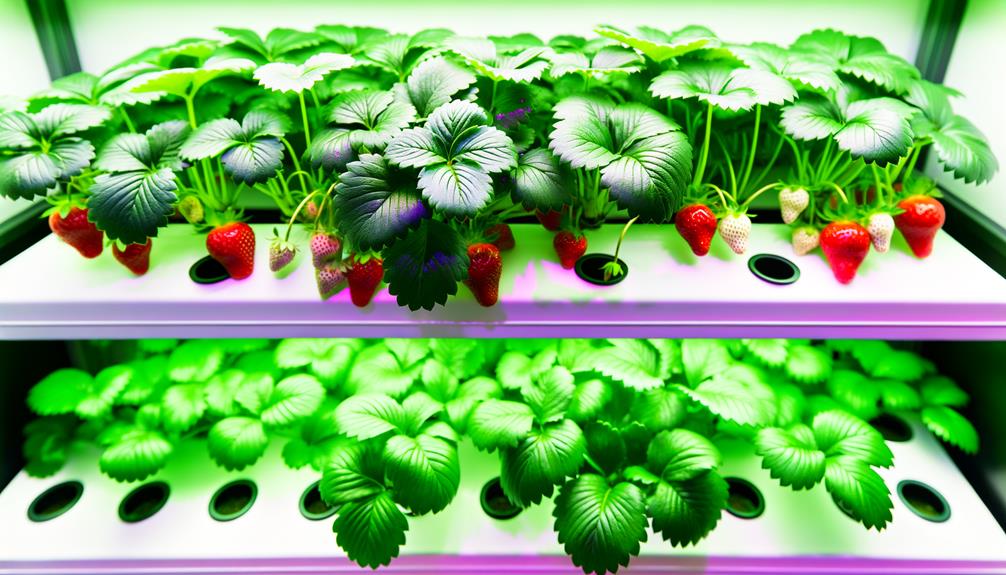
Selecting an appropriate hydroponic system is essential for enhancing the growth and yield of hydroponically cultivated strawberries. Critical systems include Nutrient Film Technique (NFT), Deep Water Culture (DWC), and Aeroponics.
NFT involves a shallow stream of nutrient-rich solution flowing over the roots, ensuring constant nutrient and oxygen availability.
DWC immerses roots in an oxygenated nutrient solution, promoting rapid growth and robust root systems.
Aeroponics, the most advanced method, suspends roots in air while periodically misting them with a nutrient solution, maximizing oxygen exposure and nutrient uptake.
Each system requires rigorous monitoring of pH levels, Electrical Conductivity (EC), and dissolved oxygen to maintain ideal conditions.
Innovators should select a system based on space, resource availability, and desired yield outcomes.
Selecting Strawberry Varieties
When cultivating strawberries hydroponically, it's crucial to identify varieties that exhibit robust growth, high yield potential, and resistance to common diseases.
Everbearing varieties such as 'Albion' and 'Seascape' are particularly well-suited for hydroponic systems due to their continuous fruiting cycle and adaptability to controlled environments. These cultivars demonstrate superior vigor and are less susceptible to pests like spider mites and diseases like powdery mildew.
Additionally, the day-neutral variety 'Mara des Bois' offers an aromatic profile and consistent production regardless of photoperiod. Selecting these specific cultivars guarantees optimized nutrient uptake, efficient root system development, and maximal fruit quality.
Consequently, strategic selection based on these criteria can greatly improve productivity and sustainability in hydroponic strawberry cultivation.
Setting Up the System
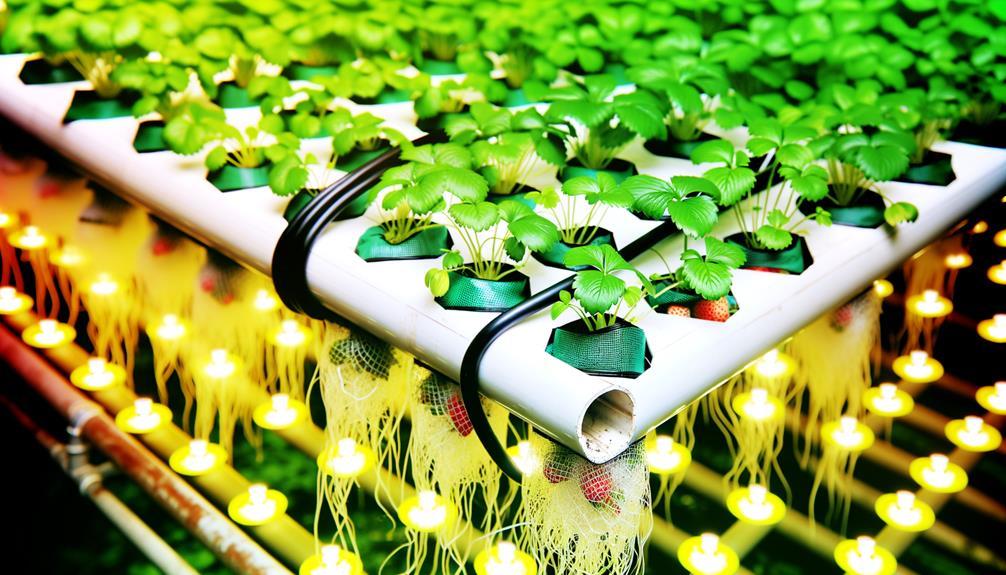

Establishing a hydroponic system for strawberry cultivation necessitates meticulous planning and precise assembly to confirm excellent growth conditions and nutrient delivery. Begin by selecting a suitable hydroponic method such as nutrient film technique (NFT) or deep water culture (DWC). Ascertain adequate spacing between plants to allow for maximum air circulation and light penetration. Integrate a high-efficiency LED lighting system to simulate natural sunlight. Install a pH and EC meter to continuously monitor water quality.
| Component | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Grow Trays | Hold strawberry plants |
| Water Reservoir | Stores nutrient solution |
| Pumps | Circulate nutrient solution to plants |
| Air Stone | Oxygenates water to promote root health |
Properly calibrate each component to maintain a consistent and healthy growth environment.
Nutrient Solution Preparation
The preparation of a nutrient solution for hydroponic strawberries necessitates a precise blend of essential macro and micronutrients, including nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium, and trace elements.
Achieving an ideal nutrient balance is vital for plant health; hence, regular monitoring and adjustment of pH levels are imperative to guarantee nutrient availability.
Maintaining the solution within a pH range of 5.5 to 6.5 promotes ideal nutrient uptake, fostering robust growth and fruit production.
Essential Nutrient Components
A meticulously balanced nutrient solution is essential for the hydroponic cultivation of strawberries, ensuring ideal growth and fruit production. This solution must include macro-nutrients such as nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K) at specific ratios, typically 10-10-20 during the fruiting stage.
Additionally, micro-nutrients like calcium (Ca), magnesium (Mg), and iron (Fe) play critical roles in enzymatic functions and chlorophyll synthesis. To prepare an effective nutrient solution, dissolve these elements in deionized water, adhering to precise concentrations (ppm) and ensuring complete solubility.
Employing chelated forms of micro-nutrients can enhance bioavailability. Regularly monitor and adjust the electrical conductivity (EC) to maintain an effective range of 1.4-2.0 mS/cm, fostering robust plant health and maximizing fruit yield.
Balancing Ph Levels
Maintaining an ideal pH range of 5.5-6.5 in the nutrient solution is fundamental to maximizing nutrient uptake and ensuring vigorous strawberry plant growth in a hydroponic system.
Achieving this balance requires the regular use of a calibrated pH meter, ensuring precise measurements. Adjustments are made using pH adjusters, such as phosphoric acid to lower pH or potassium hydroxide to raise it.
Frequent monitoring and adjustments are essential, as fluctuations can impair nutrient absorption, leading to deficiencies or toxicities. Integrating a buffer solution can stabilize pH levels, promoting a favorable environment for root health and nutrient assimilation.
Planting and Maintenance
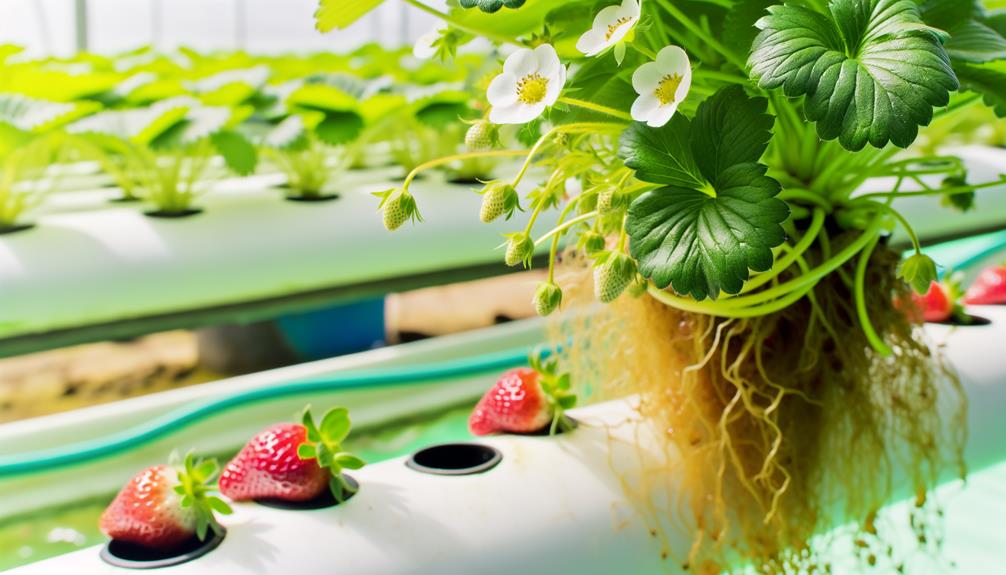

In the planting phase, selecting robust strawberry seedlings with well-developed root systems is paramount for ensuring ideal growth in a hydroponic environment.
Consistent monitoring and adjustment of the nutrient solution's pH and electrical conductivity levels are critical to meet the specific nutritional demands of the plants.
Regular maintenance, including the inspection for pests and diseases, is essential to promote healthy development and maximize fruit yield.
Seedling Selection Process
Selecting the appropriate strawberry seedlings for hydroponic cultivation requires careful consideration of factors such as cultivar suitability, disease resistance, and growth characteristics.
Start by choosing day-neutral or everbearing varieties, which are ideal for continuous fruiting under controlled environments.
Examine seedlings for vigor, confirming they exhibit robust root systems and healthy foliage.
Opt for disease-resistant cultivars to mitigate potential pathogen issues, particularly those resistant to common afflictions like Verticillium wilt and powdery mildew.
Prioritize seedlings with uniform growth patterns to guarantee consistent development and yield.
Before planting, acclimate seedlings to the hydroponic system by gradually introducing them to the nutrient solution, securing peak absorption and minimizing transplant shock.
This meticulous selection process enhances productivity and sustainability in hydroponic strawberry cultivation.
Nutrient Solution Management
Once the seedlings are acclimated, attention must be directed towards formulating and maintaining an ideal nutrient solution to support hydroponic strawberry growth. This involves carefully balancing essential minerals such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium to promote healthy root development and fruit production. When comparing Miracle Grow vs hydroponic nutrients, it’s important to note that traditional fertilizers may not provide the precise nutrient ratios required for optimal hydroponic growth. Regular monitoring of pH and electrical conductivity (EC) levels ensures that the nutrient solution remains within the ideal range for strawberry plants.
Essential macronutrients—nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K)—must be precisely balanced, typically in a ratio of 8-15-36, to promote vigorous vegetative and fruit development.
Micronutrients such as calcium, magnesium, and iron are equally crucial and should be included in trace amounts.
The pH level of the nutrient solution should be maintained between 5.8 and 6.2 to optimize nutrient uptake.
Regularly monitor electrical conductivity (EC) levels, aiming for a range of 1.8-2.2 mS/cm, to guarantee nutrient availability.
Consistent solution aeration and temperature control, ideally between 18-22°C, will further enhance root health and overall plant vitality.
Harvesting and Storage
To achieve ideal fruit quality, strawberries should be harvested when they are fully ripe, characterized by their uniform red color and firm texture. Harvesting should occur during the cooler parts of the day to minimize post-harvest heat stress. Use sterilized scissors to cut the stems, avoiding damage to the fruit and plant. Immediately place the harvested strawberries in a cool environment to retard respiration rates and prevent spoilage.
| Parameter | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Harvest Timing | Early morning or late evening |
| Harvest Tool | Sterilized scissors |
| Immediate Storage | 0-2°C |
| Humidity Control | 90-95% RH |
| Shelf Life | Up to 7 days |
For ideal storage, maintain high humidity and low temperatures to extend shelf life while preserving flavor and nutritional quality.
Conclusion
In summation, the hydroponic cultivation of strawberries, akin to a masterful symphony, harmonizes the selection of appropriate systems and varieties, meticulous system setup, precise nutrient solution preparation, diligent planting, and vigilant maintenance.
This method, offering a controlled environment, optimizes growth and yield, ensuring a bountiful harvest.
Consequently, the hydroponic approach transforms the cultivation process into a seamless dance of science and nature, culminating in the production of succulent, high-quality strawberries.






