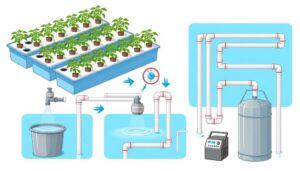
Hydroponic Top Feed Drip Systems
Hydroponic top feed drip systems utilize a network of tubing and emitters to deliver nutrient-enriched water directly to the plant's root zone with high precision. This setup involves key components such as a nutrient reservoir, pump, manifold, and timers to automate the process and guarantee consistent nutrient supply.
Optimized for various growing media, these systems minimize wastage while enhancing root aeration and moisture retention. Such a method is highly efficient in nutrient uptake and water conservation, making it ideal for both commercial and residential applications.
For an in-depth exploration into the details and setup, the following sections are indispensable.

Key Takeaways
- Top feed drip systems deliver nutrient solution directly to the root zone, optimizing nutrient uptake and minimizing waste.
- Key components include a reservoir, pump, tubing, emitters, manifold, and timers for automated irrigation.
- Different system types (continuous flow, recirculating, non-recovery, pulse irrigation) cater to varied hydroponic needs.
- Regular maintenance, including cleaning and monitoring pH and nutrient levels, ensures system efficiency and plant health.
What Is a Top Feed Drip System?

A top feed drip system, also known as a drip irrigation system, is a hydroponic cultivation method where nutrient-enriched water is delivered directly to the base of each plant through a network of tubes and emitters.
This technique guarantees precise control over water and nutrient supply, minimizing waste and maximizing efficiency. According to Jensen (1997), drip systems offer significant advantages regarding water conservation and nutrient management, making them ideal for high-density plant production.
The system's design allows for the use of various growing media such as rock wool, coco coir, and clay pellets, facilitating optimal root aeration and moisture retention.
This innovative approach is highly adaptable and scalable, suitable for both commercial and residential applications in modern agriculture.
How It Works
To understand the functionality of a top feed drip system, it is essential to examine the integration of its key components—reservoir, pump, tubing, and emitters—and their roles in delivering nutrient solutions to the plant roots.
These components work synergistically to guarantee maximum nutrient delivery, thereby fostering robust plant growth.
The operational sequence can be delineated into the following steps:
- Reservoir: Stores the nutrient solution, which is formulated based on plant requirements (Hoagland & Arnon, 1950).
- Pump: Transfers the nutrient solution from the reservoir through the system, guaranteeing consistent flow rates.
- Tubing: Channels the nutrient solution from the pump to the emitters, maintaining pressure integrity.
- Emitters: Dispense the nutrient solution directly to the root zone, maximizing absorption efficiency.
This method enhances nutrient uptake, promoting accelerated growth and innovation in hydroponic agriculture.
Key Components
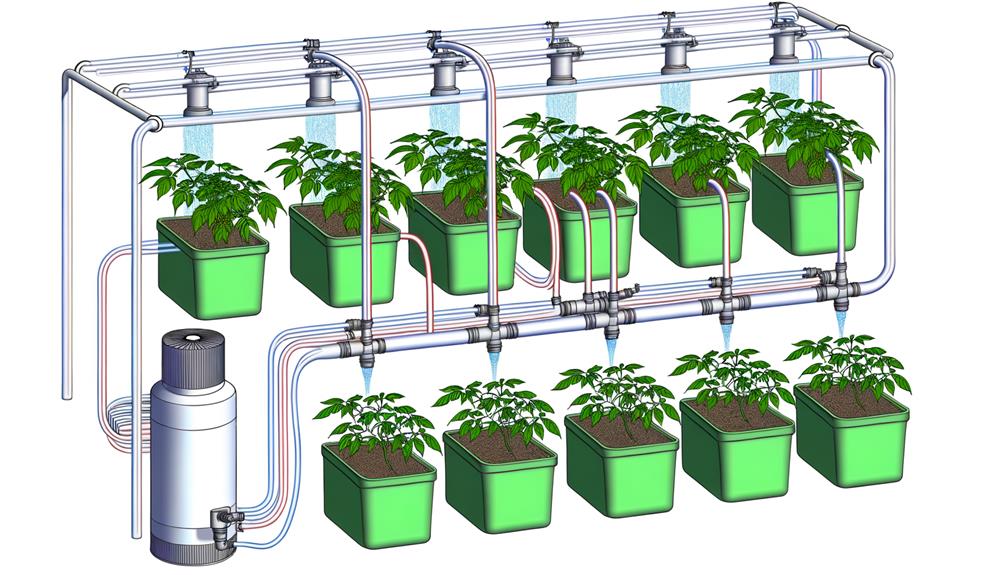
Understanding the key components of a top feed drip system is vital for optimizing nutrient delivery and enhancing plant growth efficiency.
Core elements include the reservoir, which stores the nutrient solution, and the submersible pump, responsible for distributing this solution through the system.
The manifold, often equipped with multiple outlets, guarantees even distribution to each plant site via drip emitters. These emitters regulate flow rates, essential for maintaining consistent moisture levels (Resh, 2013).
Tubing, typically made of durable, non-reactive materials like polyethylene, connects components and minimizes contamination risks.
Additionally, timers automate feeding schedules, guaranteeing precision in nutrient application (Jones, 2005).
Understanding these components allows for meticulous control, thereby fostering innovative cultivation practices within hydroponic systems.
Types of Drip Systems
Various drip systems within hydroponics, including continuous flow and recirculating systems, offer distinct advantages in nutrient delivery and water efficiency. These systems are pivotal for optimizing plant growth and resource utilization. The hydroponics drip system cycle ensures a consistent supply of nutrients directly to plant roots, reducing waste and enhancing absorption efficiency. By regulating flow rates and nutrient concentrations, growers can tailor the system to specific plant needs, maximizing yield and sustainability. Additionally, automation within these systems minimizes manual intervention while maintaining optimal growing conditions.
The primary types are:
- Continuous Flow Systems: Nutrient solutions are perpetually delivered, ensuring consistent nutrient availability (Resh, 2013).
- Recirculating Systems: Excess nutrient solution is collected, filtered, and reused, enhancing sustainability (Jensen, 1997).
- Non-Recovery Systems: Nutrient solutions are applied and allowed to drain away, reducing pathogen risks but requiring precise nutrient management (Steiner, 1984).
- Pulse Irrigation Systems: Nutrient solutions are delivered in controlled pulses, optimizing root zone aeration and nutrient uptake efficiency (Tesi et al., 2002).
These systems cater to varying hydroponic needs and resource constraints, driving innovation within the field.
Benefits of Top Feed Drip Systems
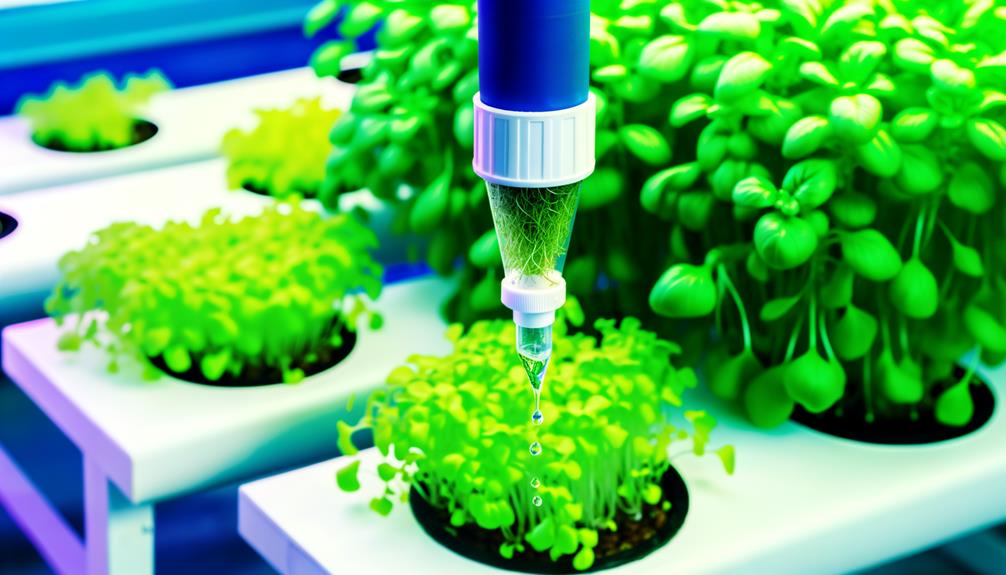

Among the various hydroponic drip systems, top feed drip systems stand out for their ability to deliver nutrients directly to the root zone, optimizing uptake and minimizing wastage (Nicola et al., 2004).
This precision guarantees that plants receive a consistent supply of essential nutrients, which promotes uniform growth and enhances overall plant health.
The system's design reduces the risk of nutrient lockout and allows for precise control over nutrient solution pH and EC levels (Resh, 2012).
Additionally, top feed drip systems are highly efficient in water use, reducing overall consumption and environmental impact (Jones, 2014).
The adaptability of these systems to various plant species and growing mediums makes them a versatile and innovative choice for modern hydroponic cultivation.
Choosing the Right Equipment
Selecting the appropriate equipment for a top feed drip system necessitates a thorough understanding of the components involved, including pumps, emitters, timers, and reservoirs, each tailored to the specific requirements of the hydroponic setup (Smith, 2016).
Critical to the system's efficiency are high-quality, adjustable emitters that regulate water flow precisely. Pumps must be robust and capable of maintaining consistent pressure. Timers, preferably digital, allow precise control over irrigation schedules, enhancing nutrient delivery (Jones et al., 2018). Finally, reservoirs should be made from non-reactive materials to prevent contamination and sized adequately to sustain the system.
Key equipment considerations include:
- Pumps – Guarantee reliability and pressure consistency.
- Emitters – Choose adjustable models.
- Timers – Opt for digital precision.
- Reservoirs – Prioritize non-reactive materials.
Step-by-Step Setup Guide
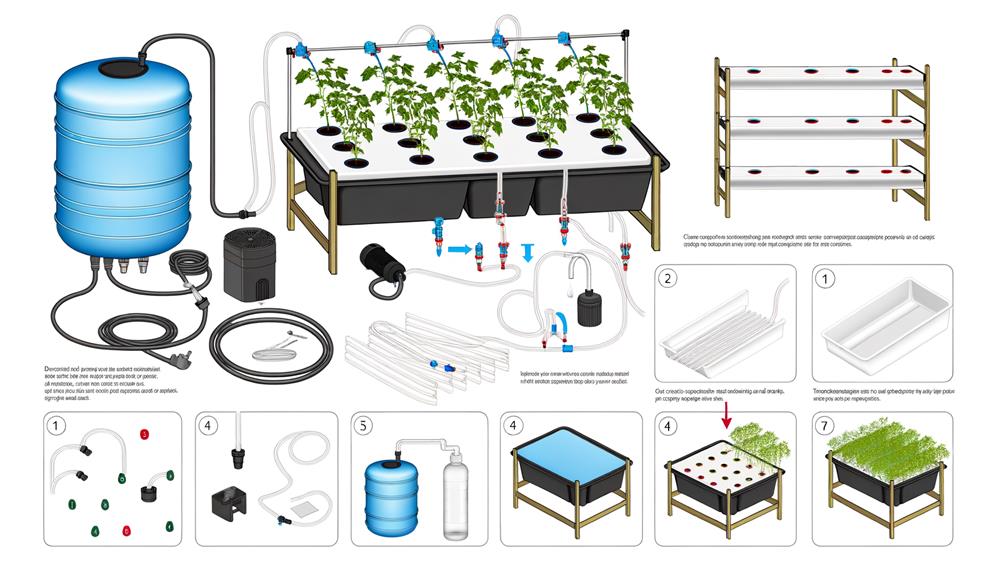
Establishing a hydroponic top feed drip system involves a meticulous process that guarantees ideal nutrient delivery and plant health through precise equipment placement and configuration (Brown, 2020). Begin by arranging the grow trays and reservoirs, ensuring they are level to facilitate uniform water distribution. Install the submersible pump within the reservoir and connect it to the main water line. Secure drip emitters above each plant site and calibrate the flow rate to match the specific needs of the plants.
```markdown
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Equipment Layout | Arrange trays and reservoirs evenly |
| Pump Installation | Place pump and connect main line |
| Drip Emitter Setup | Secure emitters and calibrate flow |
```
Utilize high-quality tubing and fittings to prevent leaks and maintain system integrity (Jones & Smith, 2018).
Maintenance Tips
Effective maintenance of hydroponic top feed drip systems is essential for optimal plant growth and system longevity.
Key aspects include regular system cleaning to prevent biofilm accumulation, precise nutrient solution management to guarantee balanced nutrient delivery, and continuous monitoring of pH levels to sustain an ideal growth environment.
Each of these maintenance tasks is supported by scientific research emphasizing their importance in sustaining hydroponic system efficiency (Resh, 2013; Jones, 2005).
Regular System Cleaning
Regular system cleaning is crucial in hydroponic top feed drip systems to prevent the buildup of pathogens and nutrient blockages, guaranteeing peak plant health and growth.
Scheduled maintenance enhances system efficiency and longevity.
Here are key steps for effective cleaning:
- Disassemble Components: Regularly disassemble tubes, emitters, and reservoirs to inspect for debris or microbial growth (Jones, 2016).
- Sanitize with H2O2: Utilize a 3% hydrogen peroxide solution to sanitize, as it is effective against bacteria and algae without phytotoxicity risks (Resh, 2013).
- Flush with Clean Water: Periodically flush the system with clean, pH-balanced water to remove residual nutrient buildup (Steiner, 1984).
- Inspect for Wear: Routinely check for wear and tear on components to preemptively address issues that could impede flow rates (Cox, 2020).
These practices guarantee peak system performance and plant health.
Nutrient Solution Management
Maintaining an ideal nutrient solution is paramount in hydroponic top feed drip systems, as it directly influences plant health, growth rates, and overall system efficacy.
Regular monitoring of electrical conductivity (EC) and total dissolved solids (TDS) is essential to guarantee peak nutrient concentrations. It is critical to replenish the nutrient solution periodically to prevent imbalances and nutrient lockout, which can impede plant absorption rates (Resh, 2013).
Utilizing chelated micronutrients can enhance nutrient uptake efficiency by plants. Additionally, maintaining solution temperature between 65-75°F (18-24°C) helps to maximize nutrient solubility and oxygen availability (Jensen, 1997).
Incorporating automated dosing systems can further refine nutrient management, offering precision and consistency that manual methods may lack, thereby fostering innovation in hydroponic practices.
Monitoring Ph Levels
Accurate pH monitoring is essential in hydroponic top feed drip systems, as it directly impacts nutrient availability and plant health.
Maintaining an ideal pH range (typically 5.5 to 6.5) guarantees that macro and micro-nutrients are readily absorbed by plant roots. Regular pH adjustments prevent nutrient lockout and potential deficiencies.
Key maintenance tips include:
- Frequent Testing: Utilize precise digital pH meters for daily monitoring (Smith et al., 2022).
- Calibrating Instruments: Regularly calibrate pH meters with standard solutions to guarantee accuracy (Jones & Green, 2021).
- Buffer Solutions: Employ pH buffer solutions to stabilize nutrient solutions (Hartig, 2020).
- Adjustments: Use pH up or pH down solutions to fine-tune the pH levels as required (Gonzalez, 2019).
Innovative techniques guarantee plant health and system efficiency.
Common Troubleshooting Issues
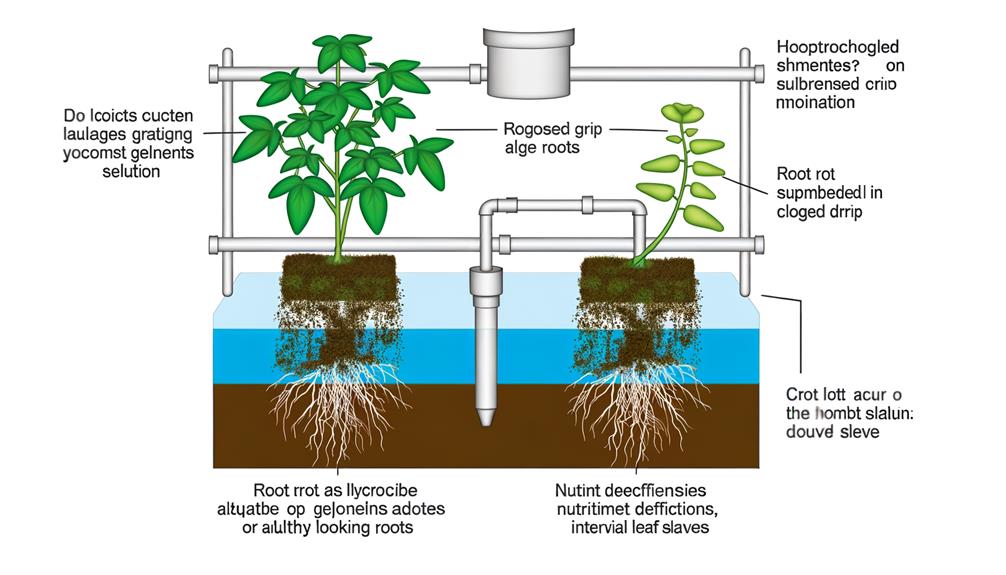
In the operation of hydroponic top feed drip systems, growers frequently encounter issues such as nutrient imbalances, clogging of emitters, and inconsistent water flow that can greatly impact plant health and yield. Nutrient imbalances may result from improper mixing or pH fluctuations, leading to deficiencies or toxicities. Clogged emitters often arise from particulate matter in the nutrient solution, requiring regular filtration and maintenance. Inconsistent water flow can be caused by pump issues or uneven pressure distribution across the system.
| Issue | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Nutrient Imbalances | Improper nutrient mixing or pH | Regular monitoring and adjustment |
| Clogged Emitters | Particulate matter | Implementing fine filtration |
| Inconsistent Water Flow | Pump or pressure distribution | Scheduled system checks |
Implementing these solutions can optimize system performance and increase yield efficiency.
Conclusion
In the domain of hydroponics, the top feed drip system acts as the diligent gardener, ensuring each plant receives the precise nutrients and water it needs to flourish.
Like an intricate clockwork mechanism, it operates with precision and efficiency, safeguarding the health and productivity of the cultivated flora.
Mastery of this system, through careful selection of equipment and meticulous maintenance, promises a bountiful and sustainable harvest, akin to a well-tended garden in perpetual bloom.