How Much Electricity Does Your Hydroponic System Use?
The electricity usage of a hydroponic system varies widely based on factors such as the type of system, grow lights, pumps, aerators, and climate control equipment. LEDs for lighting can range from 50 to 300 watts, while water pumps consume 20 to 100 watts and aerators use 2 to 30 watts.
Climate control adds another 300 to 1500 watts for air conditioning and 300 to 700 watts for dehumidifiers. Efficiently managed, this can optimize energy consumption.
Understanding the nuances of each component offers a pathway to reducing overall electricity costs, making it essential to explore further.

Key Takeaways
- LED grow lights, the most energy-efficient option, consume between 50-300 watts.
- Water pumps in hydroponic systems typically use 20-100 watts.
- Aerators for oxygenating nutrient solutions operate between 2-30 watts.
- Climate control equipment like dehumidifiers, fans, and air conditioners use 50-1500 watts.
Types of Hydroponic Systems
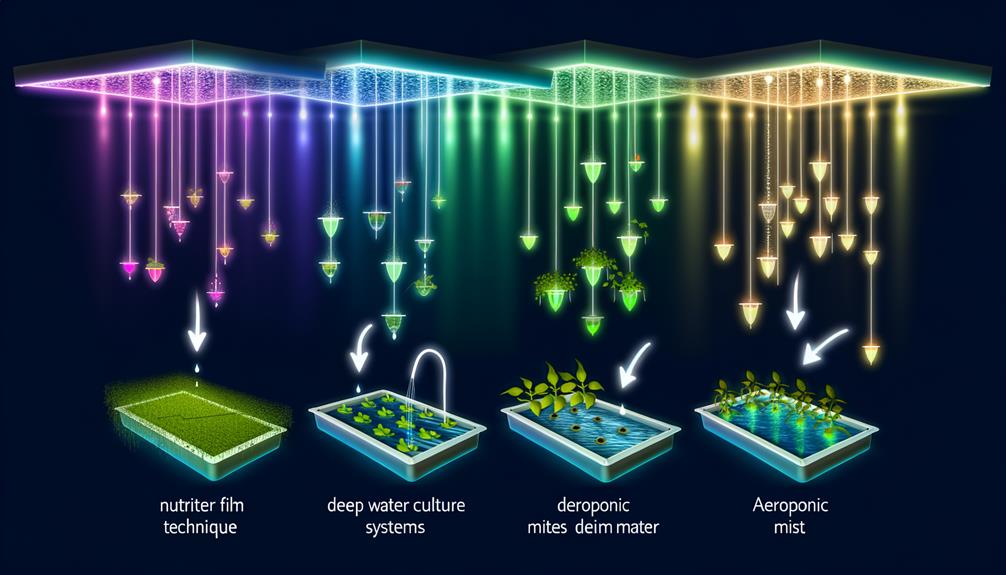
Hydroponic systems, each with unique operational requirements and efficiencies, can be broadly categorized into nutrient film technique (NFT), deep water culture (DWC), aeroponics, drip systems, and ebb and flow systems.
NFT systems utilize thin films of nutrient solutions delivered continuously to plant roots, optimizing nutrient uptake.
DWC systems submerge roots in oxygenated nutrient solutions, enhancing growth rates.
Aeroponics suspends roots in air, misting them with nutrient solutions, maximizing oxygen exposure.
Drip systems deliver precise amounts of nutrients directly to plant roots, conserving resources.
Ebb and flow systems flood and drain the grow bed, providing intermittent nutrient exposure.
Each system's energy consumption varies, influenced by pumps, aeration, and control mechanisms, necessitating careful design and optimization to guarantee sustainable and efficient operation.
Role of Grow Lights
The role of grow lights in hydroponic systems is critical, as they greatly influence light intensity requirements for ideal plant growth.
Energy efficiency options, such as LED lights, can mitigate the high electricity usage commonly associated with traditional lighting systems.
Analyzing the balance between light intensity and energy consumption is essential for enhancing both plant health and operational cost-efficiency.
Light Intensity Requirements
Understanding the ideal light intensity requirements is essential for maximizing plant growth and efficiency in hydroponic systems. Different plants require varying levels of light to thrive, making it crucial to tailor the lighting setup to specific crop needs. In addition to light intensity, factors such as nutrient concentration and how much fertilizer to use play a significant role in optimizing plant health. By carefully balancing these elements, growers can enhance yields and ensure robust plant development in hydroponic systems.
Research indicates that optimal light intensity for most hydroponically-grown crops ranges between 300-800 μmol/m²/s of Photosynthetically Active Radiation (PAR). This guarantees sufficient photon flux density, promoting robust photosynthesis and growth.
Utilizing LED grow lights with adjustable spectra allows for precise control, matching the specific needs of different plant stages.
Additionally, implementing photoperiod management—adjusting light duration—can enhance energy utilization and crop yield.
Monitoring and adjusting light intensity using quantum sensors guarantees data-driven decisions, leading to improved plant performance.
Energy Efficiency Options
Maximizing energy efficiency in hydroponic systems hinges on the strategic utilization of advanced grow lights, particularly LEDs, which offer precise spectral control and reduced power consumption. LEDs outperform traditional lighting options by providing targeted wavelengths essential for photosynthesis, greatly lowering energy expenditure. When selecting grow lights, understanding key metrics such as energy consumption, light output, and lifespan is vital.
| Light Type | Average Wattage | Lifespan (hours) |
|---|---|---|
| LED | 50-300 | 50,000 |
| HPS | 600-1000 | 24,000 |
| Fluorescent | 200-400 | 20,000 |
Water Pumps and Aerators

Water pumps and aerators are critical components in hydroponic systems, contributing greatly to overall electricity usage.
Understanding pump power consumption and aerator energy usage allows for precise calculation and optimization of operational costs.
Implementing efficiency optimization tips can lead to reduced energy expenditure and enhanced system performance.
Pump Power Consumption
Accurately calculating the power consumption of water pumps and aerators is essential for maximizing the energy efficiency of a hydroponic system.
Water pumps typically consume between 20 to 100 watts, depending on their size and duty cycle. High-efficiency pumps that feature advanced motor technologies can further minimize power usage.
Aerators, though generally consuming less power, still require careful assessment to guarantee ideal integration with the system's energy profile.
By monitoring real-time wattage and operational hours, hydroponic growers can identify opportunities to reduce energy costs. Implementing timers and variable speed controllers can also enhance pump operation, improving overall energy efficiency.
This data-driven approach promotes sustainable practices and drives innovation in hydroponic system design.
Aerator Energy Usage
Analyzing the energy consumption patterns of aerators is essential for enhancing the overall efficiency of hydroponic systems.
Aerators typically operate at power ratings between 2 to 30 watts, depending on the type and capacity. Their function is to oxygenate the nutrient solution, thereby improving root respiration and nutrient uptake.
Data indicates that continuous operation can amount to approximately 0.048 to 0.72 kWh per day. Integrating energy-efficient models or employing intermittent aeration strategies can greatly reduce this consumption.
Investing in aerators with variable speed functions offers an adaptive approach to managing energy use, aligning oxygenation needs with diurnal plant cycles.
Hence, precise selection and operation of aerators are pivotal in achieving both energy efficiency and maximum crop yield in hydroponic systems.
Efficiency Optimization Tips
Enhancing the efficiency of water pumps and aerators involves strategic selection, proper maintenance, and the implementation of advanced control systems to minimize energy usage while maintaining peak performance.
Selecting energy-efficient models with variable-speed capabilities allows for precise adjustment based on real-time needs, reducing unnecessary power consumption.
Regular maintenance, including cleaning filters and checking for leaks, guarantees optimal operation and longevity.
Advanced control systems, such as timers and sensors, enable automated adjustments to pump and aerator activity, aligning with plant requirements and reducing operational hours.
Implementing these strategies can lead to energy savings of up to 30%, according to industry studies, thereby offering a sustainable approach to hydroponic farming while maintaining high productivity levels.
Climate Control Equipment
Effective climate control equipment is essential in a hydroponic system to maintain ideal growing conditions and greatly influences overall electricity usage. The necessity for precision in temperature, humidity, and airflow management drives the need for efficient devices.
Critical components include:
- Dehumidifiers: These regulate humidity levels, preventing mold and mildew, and typically consume between 300-700 watts depending on capacity and runtime.
- Fans and Ventilation Systems: Proper air circulation is crucial for plant health, with usage varying from 50 to 200 watts for each fan, contingent on size and operational duration.
- Air Conditioners: Essential for cooling, especially in warmer climates, these units can draw between 500-1500 watts, depending on the system's size and efficiency.
Innovative, energy-efficient models considerably reduce overall electrical consumption.
Energy Consumption of Heaters

In addition to climate control equipment, heaters play a significant role in managing energy consumption within hydroponic systems, particularly in colder environments.
The energy demand of heaters varies based on their wattage and operational duration. Typically, heaters consume between 150 to 1500 watts per hour, making them one of the more energy-intensive components.
Advanced systems often employ programmable thermostats and energy-efficient heaters to optimize usage. For instance, ceramic and infrared heaters can provide targeted warmth, reducing overall consumption.
Data-driven approaches, such as real-time monitoring, can further enhance efficiency by adjusting heater operation based on ambient temperature fluctuations.
Implementing smart energy solutions therefore guarantees the sustainable and cost-effective operation of hydroponic systems, fostering innovation in agricultural environments.
Impact of Ventilation Systems
Ventilation systems are essential for regulating air quality and temperature, directly impacting the energy efficiency and overall health of hydroponic environments. The power consumption of ventilation systems can be significant, but optimizing their operation is vital for a sustainable setup.
Key considerations include:
- Fan Efficiency: Modern, energy-efficient fans, typically rated at 0.5 to 1.5 kWh per day, can drastically reduce electricity usage.
- Climate Control Integration: Automated systems that adjust fan speed and operation based on temperature and humidity sensors can minimize unnecessary energy consumption.
- Air Circulation Design: Properly designed air circulation minimizes the need for high-power fans, reducing electrical load by ensuring even distribution of CO₂ and temperature.
Electrical Usage of Monitoring Devices

Monitoring devices in hydroponic systems, such as pH meters, EC sensors, and automated nutrient delivery controls, contribute to overall electricity usage by ensuring ideal growing conditions through continuous data collection and regulation. These devices, while essential for peak plant growth, can vary considerably in their power consumption. Below is a comparison of typical power consumption rates for common monitoring devices in hydroponic systems:
| Device | Average Power Consumption (W) |
|---|---|
| pH Meter | 1-3 |
| EC Sensor | 2-4 |
| Automated Nutrient Controller | 5-10 |
| Environmental Sensor Array | 7-15 |
| Data Logging System | 3-6 |
Tips for Reducing Electricity
To minimize electricity consumption in hydroponic systems, maximizing the efficiency of lighting, pumps, and climate control mechanisms is paramount. Implementing energy-efficient technologies and strategic operational adjustments can greatly reduce power usage.
Consider the following tips:
- LED Lighting: Replace traditional HID lights with high-efficiency LED grow lights. LEDs consume up to 60% less energy and produce less heat, reducing the need for cooling systems.
- Variable Speed Pumps: Utilize variable speed pumps for nutrient delivery. These pumps adjust flow rates based on demand, leading to considerable energy savings.
- Automation and Sensors: Employ advanced automation systems with sensors to monitor and adjust environmental conditions. This guarantees ideal resource use, thereby curbing unnecessary electricity consumption.
Conclusion
The electricity consumption of hydroponic systems is a multifaceted issue, influenced by grow lights, water pumps, climate control equipment, heaters, ventilation systems, and monitoring devices. Each component's energy usage contributes to the overall efficiency of the system.
While hydroponics may seem like a beacon of sustainable agriculture, its electrical demands suggest otherwise. To mitigate this, adopting energy-efficient technologies and strategic planning is essential.
Consequently, hydroponics, the supposed paragon of green farming, must still contend with its not-so-green energy footprint.