What Is the Best Water Temperature for Hydroponics
The ideal water temperature for hydroponics is between 65°F to 75°F (18°C to 24°C). This range optimizes dissolved oxygen levels and nutrient uptake while preventing thermal stress and microbial imbalance that can compromise root integrity.
High temperatures elevate microbial growth and pathogenic risks, whereas low temperatures impede metabolic processes and enzyme activities. Advanced hydroponic systems utilize chillers and heaters for precise temperature regulation to guarantee a stable growing environment.
Maintaining this range is essential for plant health and preventing diseases like Pythium. Further insights into effective hydroponic practices await your exploration.

Key Takeaways
- The ideal water temperature range for hydroponics is 65°F to 75°F.
- Optimal temperatures ensure efficient nutrient uptake and root health.
- Maintaining water temperature between 65°F and 70°F prevents diseases like Pythium.
- Consistent temperature control enhances oxygen levels, promoting root respiration.
Importance of Water Temperature

Maintaining the ideal water temperature in hydroponic systems is vital for maximizing nutrient uptake efficiency and overall plant health.
Preferred temperature ranges, typically between 65°F to 75°F (18°C to 24°C), guarantee that dissolved oxygen levels are maintained at optimal concentrations, essential for root respiration and metabolic functions.
Water temperatures outside this range can precipitate thermal stress, potentially compromising root integrity and microbial balance. High temperatures accelerate microbial growth, increasing the likelihood of pathogenic infestations, while cooler temperatures slow down root metabolism.
Advanced hydroponic systems often incorporate temperature control mechanisms such as chillers and heaters to maintain this significant parameter.
Research underscores the importance of continuous monitoring and precise regulation to foster an environment conducive to robust plant development and innovative agricultural outcomes.
Effects on Nutrient Uptake
How does water temperature influence the efficiency of nutrient uptake in hydroponic systems?
Ideal water temperature is vital for maximizing nutrient absorption. Water temperature directly impacts root metabolism and enzymatic activities, essential for nutrient uptake. Deviations from the perfect temperature range can lead to nutrient imbalances and diminished plant health.
- Enzyme Activity: Enzymes involved in nutrient absorption operate efficiently within a specific temperature range, typically 65-75°F (18-24°C). Temperatures outside this range can reduce their effectiveness.
- Solubility: Higher water temperatures can decrease the solubility of essential nutrients, leading to nutrient precipitation and potential deficiencies.
- Root Health: Excessively high or low temperatures can cause root stress, reducing their ability to absorb nutrients effectively and leading to stunted growth.
Maintaining ideal water temperature guarantees robust nutrient uptake and overall plant vigor.
Impact on Oxygen Levels
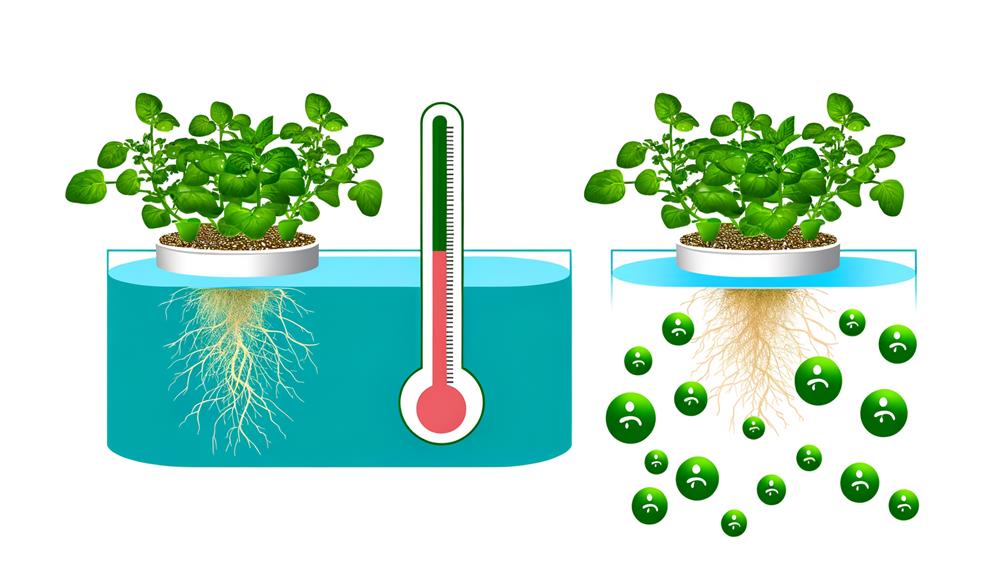
Ideal water temperature is essential for maintaining adequate dissolved oxygen levels in hydroponic systems, as temperature inversely affects oxygen solubility.
When water temperature rises, its capacity to hold dissolved oxygen diminishes, potentially jeopardizing plant root health and growth. Oxygen-depleted environments can lead to hypoxic conditions, which impair root respiration and nutrient uptake efficiency.
Conversely, lower water temperatures enhance oxygen solubility, promoting robust root development and metabolic functions. Research indicates that optimizing oxygen levels is critical for maximizing plant growth rates, preventing root diseases, and increasing overall system efficiency.
Accordingly, precise control of water temperature is imperative to achieve a balanced hydroponic ecosystem, ensuring sustainable and innovative agricultural practices.
Ideal Temperature Range
The ideal temperature range for hydroponic systems typically falls between 65°F and 75°F, as this promotes superior growth conditions for most plant species.
Maintaining this range is essential for preventing root diseases such as Pythium, which thrive in warmer water.
Additionally, this temperature range enhances nutrient uptake efficiency, facilitating robust plant development.
Optimal Growth Conditions
Maintaining a water temperature range between 65°F and 75°F is critical for ideal hydroponic plant growth, as it guarantees efficient nutrient absorption and root health. Research indicates that this temperature range enhances dissolved oxygen levels, which are pivotal for root respiration and metabolic activities.
To achieve peak growth conditions, consider the following:
- Temperature Consistency: Fluctuations outside the 65°F-75°F range can stress plants, hindering their growth and development.
- Water Quality Monitoring: Regularly check and maintain water quality parameters such as pH and electrical conductivity (EC) alongside temperature.
- Cooling Systems: Implementing cooling systems like chillers can help maintain the desired temperature, especially in warmer climates.
These measures provide a stable environment conducive to robust hydroponic plant growth.
Preventing Root Diseases
How can hydroponic systems mitigate root diseases effectively through precise water temperature management?
Maintaining water temperatures within the ideal range of 65-70°F (18-21°C) is essential. Elevated temperatures above 75°F (24°C) foster the proliferation of pathogenic organisms such as Pythium, which can devastate root systems. Conversely, temperatures below 60°F (16°C) can induce root shock and inhibit metabolic processes.
Utilizing water chillers and heaters allows for precise control, ensuring consistency within this prime range. Additionally, continuous monitoring using digital thermometers and automated alerts can preemptively address temperature deviations.
Consequently, maintaining this temperature range not only curbs pathogen growth but also sustains a robust root environment, integral for plant health and productivity in hydroponic systems.
Enhancing Nutrient Uptake
Ideal water temperature directly influences nutrient uptake efficiency in hydroponic systems. Research indicates that the best temperature range for nutrient absorption lies between 65°F and 75°F (18°C to 24°C). This range guarantees balanced metabolic activity and nutrient solubility, facilitating robust plant growth. Deviations from this range can impair nutrient availability and uptake, leading to less-than-ideal plant health and yield.
Key benefits of maintaining the ideal temperature include:
- Best Enzyme Activity: Enzymatic processes critical for nutrient absorption function best within this temperature range.
- Enhanced Oxygen Solubility: Adequate oxygen levels in the nutrient solution are crucial for root respiration and nutrient uptake.
- Prevention of Thermal Stress: Maintaining ideal temperatures minimizes thermal stress, thereby promoting consistent nutrient assimilation.
Adhering to this temperature range fosters a productive hydroponic environment.
Consequences of High Temperatures

Elevated water temperatures in hydroponic systems can greatly disrupt nutrient uptake efficiency, leading to stunted plant growth and increased susceptibility to pathogens.
High temperatures, typically above 75°F (24°C), decrease dissolved oxygen levels, which are critical for root respiration and nutrient absorption. This creates anaerobic conditions that favor the proliferation of harmful microorganisms such as Pythium, a notorious root rot pathogen.
Additionally, elevated temperatures expedite the decomposition of organic matter, releasing toxins detrimental to plant health. The enzymatic activities essential for nutrient assimilation are also hindered, causing nutrient imbalances and deficiencies.
Consequently, precise temperature regulation is paramount to maintaining ideal hydroponic conditions, ensuring robust plant growth, and maximizing yield potential.
Risks of Low Temperatures
Low water temperatures in hydroponic systems can considerably impede plant growth by slowing metabolic processes.
Additionally, suboptimal temperatures reduce nutrient uptake efficiency, leading to nutrient deficiencies and stunted development.
Maintaining an appropriate temperature range is consequently critical for optimizing plant health and maximizing yield.
Slowed Plant Growth
Suboptimal water temperatures greatly impede enzymatic activities and metabolic processes in hydroponic plants, leading to slowed growth and stunted development.
Research indicates that enzymatic reactions, which are essential for cellular functions, are highly temperature-dependent. When water temperatures drop below the ideal range (generally 18-24°C), several adverse effects ensue:
- Enzyme Inactivation: Low temperatures reduce the kinetic energy available for enzymatic reactions, hindering important biochemical pathways.
- Respiratory Suppression: Cold conditions diminish respiration rates, leading to energy deficits within plant cells.
- Photosynthetic Decline: Reduced enzyme activity and metabolic slowdown compromise chlorophyll formation and photosynthetic efficiency.
Understanding these physiological constraints is critical for enhancing hydroponic systems, ensuring robust plant growth and maximizing yield potential. By addressing factors such as nutrient availability, pH balance, and oxygen levels, growers can optimize conditions for plant development. One key aspect is to perfectly prepare hydroponic water, ensuring it meets the specific needs of different crops and promotes efficient nutrient uptake. This careful management helps prevent deficiencies and imbalances, leading to healthier plants and higher productivity.
Reduced Nutrient Uptake
Hydroponic systems operating at suboptimal water temperatures face significant challenges in nutrient absorption, directly affecting plant health and productivity.
Research indicates that water temperatures below the ideal range of 65-75°F (18-24°C) can lead to reduced solubility of essential nutrients, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. This decrease in nutrient availability impedes the root system's ability to uptake these crucial elements efficiently.
Additionally, cold water can slow down the metabolic processes within the plant, exacerbating the nutrient deficiency. The cumulative effect is stunted growth, chlorosis, and diminished yield quality.
To optimize nutrient uptake and guarantee robust plant development, it is essential to maintain water temperatures within the recommended range, leveraging advanced temperature control systems where necessary.
Measuring Water Temperature

Accurate measurement of water temperature is essential for maintaining an ideal hydroponic environment and guaranteeing plant health. Consistent monitoring allows for the identification of thermal fluctuations that can adversely impact nutrient absorption and root development. Employing precise instruments for temperature measurement guarantees data accuracy and facilitates the implementation of corrective measures.
To achieve peak temperature control in hydroponic systems, consider:
- Digital Thermometers: Offer high precision and instant readings, ideal for dynamic environments.
- Thermocouples: Suitable for continuous monitoring, providing reliable data over extended periods.
- Infrared Thermometers: Allow non-contact temperature measurements, reducing contamination risks.
Utilizing these tools enables hydroponic enthusiasts to maintain the delicate thermal balance necessary for maximizing plant growth and health.
Choosing the Right Equipment
Selecting the appropriate equipment is essential for maintaining ideal water temperature in hydroponic systems.
Key tools include advanced temperature control devices such as thermostatic heaters and chillers, as well as high-precision water quality monitors that guarantee consistent environmental conditions.
Employing reliable hydroponic instruments will enhance plant health and maximize growth potential.
Essential Hydroponic Tools
Choosing the right equipment for your hydroponic system is vital for maximizing plant health, growth efficiency, and overall yield. Utilizing advanced tools guarantees precise control over environmental variables, essential for innovative agriculture.
Key equipment includes:
- pH and EC Meters: Accurate monitoring of pH and electrical conductivity (EC) levels is important to maintaining a suitable nutrient solution balance, directly impacting plant nutrient uptake.
- Grow Lights: High-efficiency LED grow lights provide the necessary spectrum for photosynthesis, promoting robust growth and maximizing energy efficiency.
- Air Pumps and Stones: Guaranteeing adequate oxygenation in nutrient solutions, air pumps and stones prevent root rot and enhance nutrient absorption.
Employing these tools empowers growers to create an ideal hydroponic environment, fostering superior plant performance and productivity.
Temperature Control Devices
Maintaining ideal water temperature in hydroponic systems necessitates the use of advanced temperature control devices to guarantee consistent thermal conditions conducive to plant growth. Precision equipment such as submersible water heaters, chillers, and thermostats enable exact temperature regulation. Submersible heaters make certain that the water remains at an ideal warmth, essential for nutrient uptake. Conversely, water chillers are indispensable in preventing overheating, which can lead to root damage. Thermostats provide real-time monitoring and automatic adjustment, making certain a stable environment.
| Device Type | Function | Key Feature |
|---|---|---|
| Submersible Heater | Maintains ideal warmth | Automatic shut-off |
| Water Chiller | Prevents overheating | Adjustable cooling settings |
| Thermostat | Real-time monitoring and control | Digital display and alerts |
These devices collectively make certain the hydroponic system remains within the ideal temperature range, promoting healthy plant growth.
Water Quality Monitors
Ensuring ideal water quality in hydroponic systems necessitates the use of precise water quality monitors to measure parameters such as pH, electrical conductivity (EC), and dissolved oxygen levels.
Accurate monitoring is vital for maximizing plant growth and nutrient uptake. Selecting the appropriate equipment involves evaluating the following:
- pH Meters: These devices should offer high accuracy and easy calibration to guarantee the pH stays within the ideal range of 5.5 to 6.5.
- EC Meters: Essential for measuring nutrient concentration, EC meters must provide reliable readings to maintain proper nutrient balance.
- Dissolved Oxygen Meters: Important for root health, these monitors should deliver precise measurements to prevent hypoxic conditions.
Investing in high-quality monitors guarantees sustained productivity and innovation in hydroponic cultivation.
Temperature Control Tips

Effectively managing water temperature in hydroponic systems is essential for enhancing plant health and growth.
Utilizing precision temperature control mechanisms, such as digital thermostats and aquarium heaters, can maintain water temperatures within the ideal range of 65-75°F (18-24°C).
Insulated reservoirs and reflective materials can mitigate temperature fluctuations by reducing thermal exchange.
Additionally, incorporating water chillers or cooling coils is instrumental in preventing overheating, particularly in high-intensity light setups.
For real-time monitoring, advanced sensors linked to automated control systems provide immediate adjustments, ensuring stability.
Data-driven approaches, supplemented by environmental control software, facilitate the fine-tuning of these parameters, fostering an innovative and efficient hydroponic environment.
These methods collectively enhance nutrient uptake and root health, driving superior plant performance.
Seasonal Adjustments
Adapting hydroponic water temperatures to seasonal variations is essential for optimizing plant growth and preventing thermal stress. During different seasons, water temperature management requires precision to maintain nutrient uptake and root health.
- Winter Adjustments: Utilize water heaters to keep temperatures within the ideal range of 68-72°F (20-22°C) to prevent root shock and slow growth rates.
- Summer Adjustments: Implement cooling systems or chillers to maintain water temperatures below 75°F (24°C), as higher temperatures can reduce dissolved oxygen levels and encourage pathogen proliferation.
- Transitional Seasons: Employ thermostatically controlled systems to seamlessly adjust water temperatures during spring and autumn, ensuring consistent conditions.
These seasonal adjustments are crucial for maintaining a stable growing environment, thereby enhancing hydroponic efficiency and plant health.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
One common mistake in hydroponics is neglecting to regularly monitor and adjust water temperature, leading to suboptimal plant growth and increased susceptibility to diseases. Elevated temperatures can decrease dissolved oxygen levels, promoting root rot and pathogenic proliferation. Conversely, excessively low temperatures can hinder nutrient uptake and stymie metabolic processes.
Utilizing precise temperature control systems, such as thermostatic heaters and chillers, can mitigate these risks.
Another error involves inadequate circulation, allowing thermal stratification and temperature gradients within the reservoir. Employing water pumps and aerators guarantees uniform temperature distribution.
Conclusion
Maintaining optimal water temperature in hydroponic systems is vital for maximizing nutrient uptake and dissolved oxygen levels.
Research indicates that the ideal temperature range is between 65°F and 75°F.
Significantly, temperatures exceeding 80°F can reduce oxygen solubility by approximately 50%, impairing plant growth.
Effective temperature management, utilizing appropriate equipment and seasonal adjustments, is necessary for preventing detrimental effects.
Adhering to these guidelines guarantees robust hydroponic plant health and productivity.






