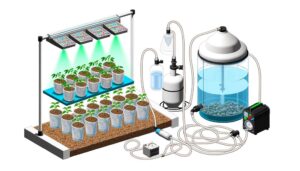
Building an Aquaponics System Involves Combining Aquaculture and Hydroponics in 3 Steps
Building an aquaponics system involves integrating aquaculture and hydroponics to establish a symbiotic, sustainable food production environment. Fish waste provides organic nutrients for plants, while plants purify the water, creating a closed-loop ecosystem.
Key components include fish tanks, grow beds, biofilters, and water pumps. Selecting appropriate fish species and plant varieties is essential for maintaining balance and efficiency.
Effective water management, advanced lighting, and temperature control further enhance system performance. Mastery of these fundamentals guarantees a robust and sustainable operation, and for a thorough understanding of each component's role, further exploration is beneficial.
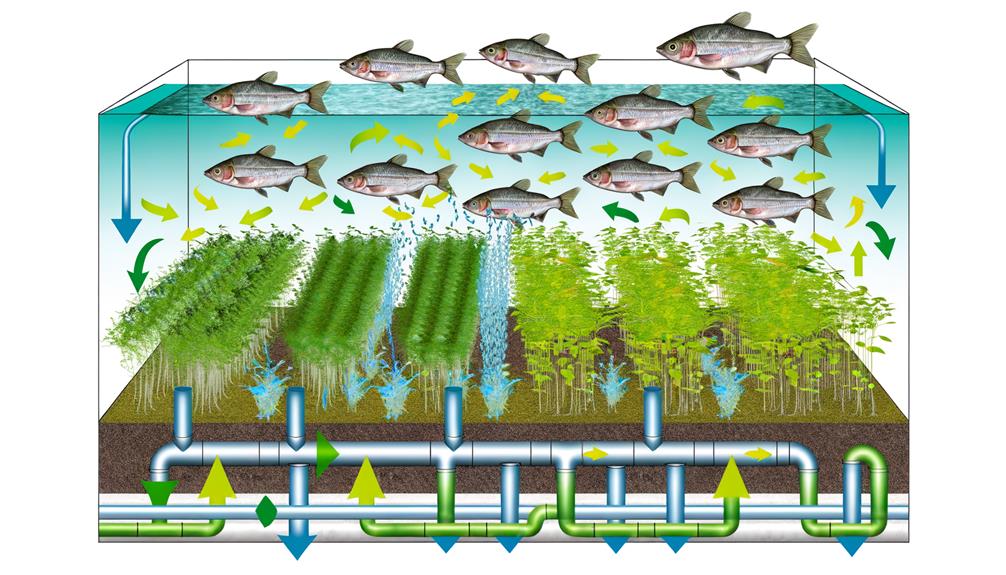
Key Takeaways
- Aquaponics integrates fish farming (aquaculture) and soilless plant cultivation (hydroponics) in a closed-loop system.
- Fish waste provides organic nutrients for plant growth, eliminating the need for chemical fertilizers.
- Plants filter and purify water, creating a sustainable and minimal-waste environment.
- Key components include fish tanks, grow beds, biofilters, and water pumps for system efficiency.
Understanding Aquaponics Basics
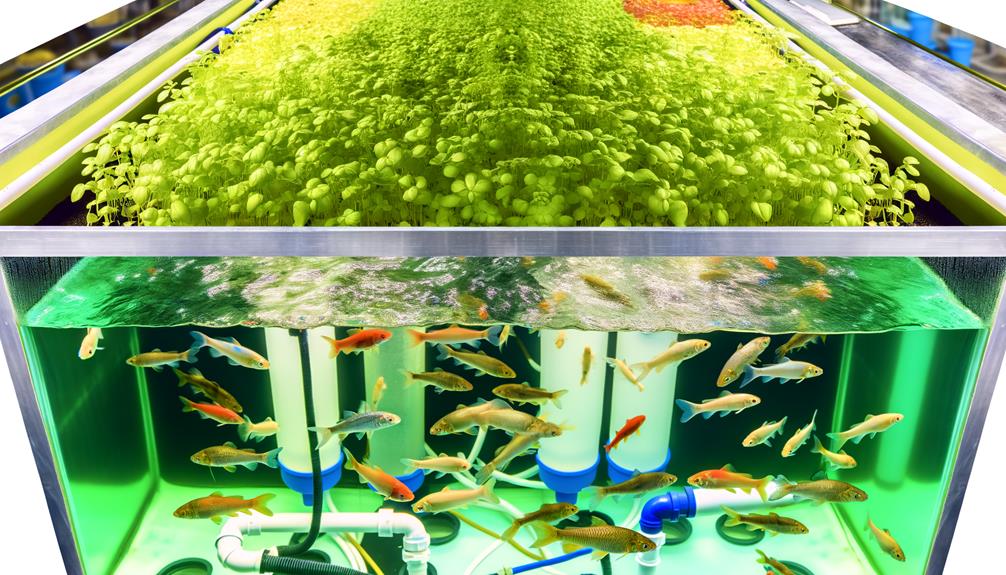

Understanding the fundamentals of aquaponics is essential for implementing a system that effectively integrates aquaculture and hydroponics to create a sustainable, symbiotic environment.
At its core, aquaponics involves cultivating fish and plants together in a recirculating system where fish waste provides organic nutrients for plant growth, while plants naturally filter and purify the water. This closed-loop system prioritizes resource efficiency and minimizes waste.
Key components include a fish tank, grow beds, biofilter, and water pump, each playing a critical role in maintaining balance. By leveraging natural biological processes, aquaponics fosters an innovative method for producing food sustainably.
Mastery of these basics lays the groundwork for optimizing system performance and achieving long-term ecological and economic benefits.
Choosing the Right Fish
Selecting the appropriate fish species is fundamental for enhancing the balance and efficiency of an aquaponics system, as it directly influences water quality, nutrient availability, and overall system health.
Species such as Tilapia, Barramundi, and Catfish are favored due to their robustness, fast growth rates, and tolerance to varying water conditions.
Additionally, choosing fish that can thrive in a recirculating system guarantees a consistent nutrient supply for the plants.
Temperature compatibility between fish and plant species is also critical to maintain ideal growth conditions.
Selecting Plant Varieties
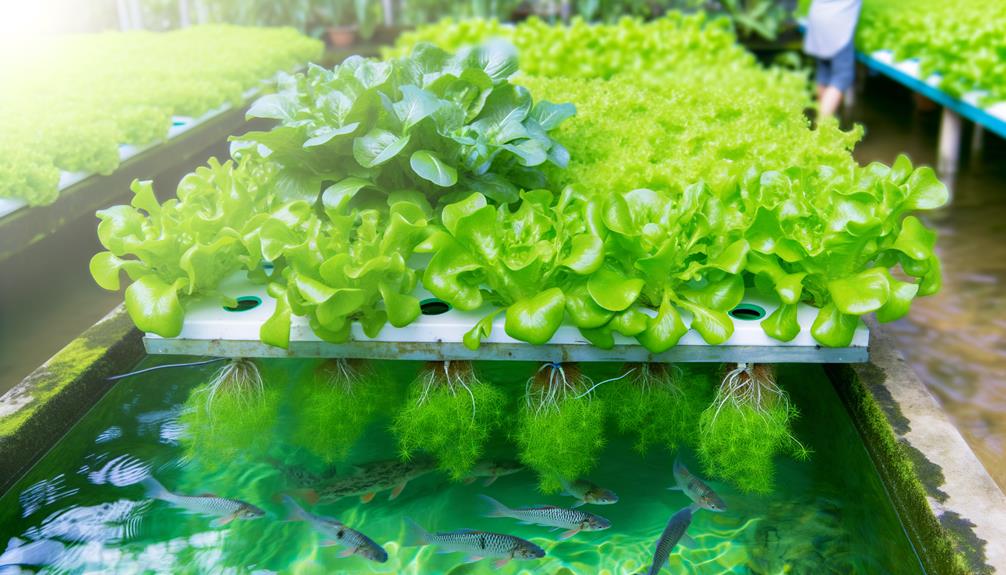

Incorporating diverse plant varieties that are well-suited to aquaponic conditions enhances system efficiency and sustainability, while promoting innovative cultivation methods.
Leafy greens such as lettuce, kale, and spinach thrive in aquaponic systems due to their rapid growth rates and nutrient uptake efficiency.
Herbs like basil, mint, and parsley also demonstrate robust performance, benefiting from the nutrient-rich aquaponic water.
Additionally, fruiting plants such as tomatoes, peppers, and cucumbers can be successfully cultivated, provided they receive adequate light and space.
Selecting plant varieties that have compatible nutrient requirements and growth cycles guarantees balanced nutrient levels, optimizing both plant and fish health.
This strategic selection fosters a resilient, productive system, contributing to the overall success of aquaponic farming.
Designing Your System
Designing an efficient aquaponics system requires careful consideration of several key factors, including the selection of system components, optimizing water flow, and implementing effective lighting and temperature control.
Each element plays a critical role in maintaining a balanced ecosystem and ensuring sustainable plant and fish growth.
Choosing System Components
Determining the essential components for your aquaponics system involves a strategic understanding of sustainable practices, innovative methods, and the technical intricacies required for peak functionality.
Central to this design are fish tanks, grow beds, and biofilters. Fish tanks should be selected based on material durability and suitability for aquatic life.
Grow beds, where plants thrive, require careful consideration of media types, including gravel or expanded clay.
Biofilters are critical for converting fish waste into nutrients, enhancing water quality and plant health.
Additionally, choosing efficient air and water pumps guarantees reliable oxygenation and circulation.
Lighting systems, preferably energy-efficient LEDs, are fundamental for plant photosynthesis.
Each component must be chosen with precision to foster a symbiotic, sustainable ecosystem.
Determining Water Flow
Effective water flow management is essential for maintaining the balance and health of your aquaponics system, ensuring that both aquatic and plant life receive ideal conditions for growth. To achieve the best water flow, consider the following key elements:
- Pump Selection: Choose a high-efficiency pump that meets the system's flow rate requirements, ensuring continuous circulation without excessive energy consumption.
- Plumbing Design: Implement a well-planned plumbing layout that minimizes resistance and potential blockages, facilitating smooth water movement.
- Flow Rate Calibration: Regularly calibrate flow rates to match the specific needs of different plant species and fish, promoting balanced nutrient distribution.
- Aeration Integration: Incorporate aeration techniques, such as air stones or venturi systems, to enhance oxygen levels, supporting both fish health and microbial activity.
Lighting and Temperature Control
Optimizing lighting and temperature control is essential for maximizing the efficiency and productivity of your aquaponics system.
Advanced LED grow lights, which offer customizable spectra, are pivotal for promoting photosynthesis while minimizing energy consumption.
Integrating intelligent climate control systems allows real-time monitoring and adjustments to maintain ideal temperature ranges for both aquatic and plant species.
Employing sustainable practices, such as utilizing renewable energy sources and precision environmental sensors, guarantees an eco-friendly approach.
Innovatively designed, automated shading systems can further regulate light exposure, preventing plant stress.
Setting Up Tanks and Beds
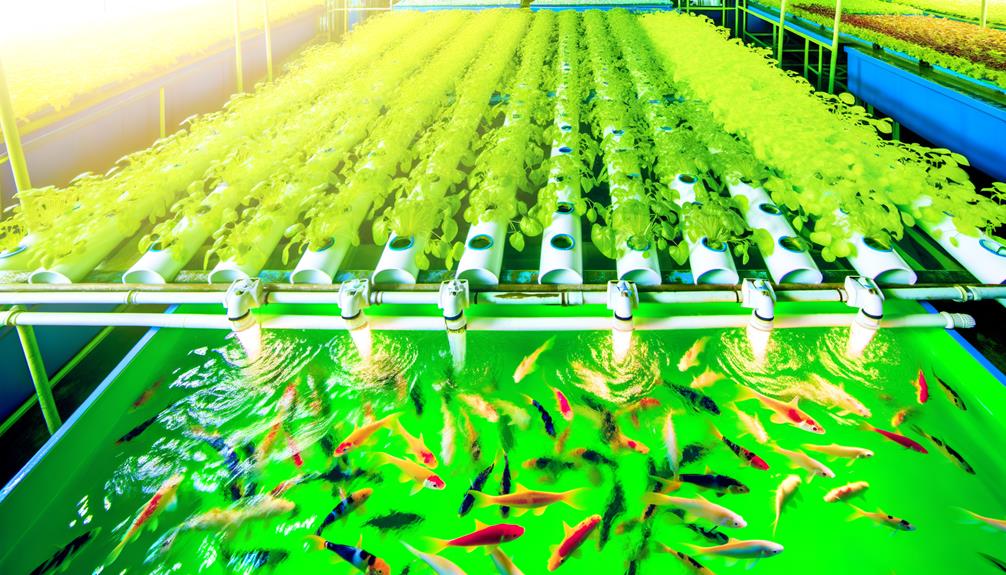

In establishing a successful aquaponics system, selecting appropriate tank materials and bed media is essential for system efficiency and sustainability. The choice of tank materials should ensure durability, resistance to corrosion, and safety for aquatic life, with food-grade plastic and fiberglass being popular options. Similarly, selecting the right bed media, such as expanded clay pebbles or gravel, promotes effective plant root support and biofiltration. Integrating a ship crate hydroponic setup can also be a cost-effective and sustainable way to repurpose materials while maintaining optimal growing conditions.
Opt for durable, non-toxic materials for tanks to guarantee the health of aquatic life, while considering light and temperature control.
Similarly, choosing the right grow bed media, such as expanded clay or gravel, optimizes plant growth and nutrient absorption.
Choosing Tank Materials
Selecting the appropriate tank materials is essential for guaranteeing the durability, safety, and efficiency of your aquaponics system. The choice of materials impacts the system's longevity, water quality, and ecological footprint.
Here are four key considerations:
- Material Composition: Opt for food-grade plastics (HDPE) or fiberglass to prevent chemical leaching and guarantee safety.
- Durability: Choose materials resistant to UV degradation and corrosion to enhance longevity and reduce maintenance.
- Thermal Stability: Guarantee the material can withstand temperature fluctuations to maintain a stable environment for aquatic life.
- Sustainability: Consider recycled or repurposed materials to minimize environmental impact and promote sustainable practices.
Bed Media Options
Choosing the right bed media is essential for ensuring efficient nutrient absorption, robust plant growth, and overall system stability in your aquaponics setup.
Among the most effective options are expanded clay pebbles, gravel, and lava rock.
Expanded clay pebbles offer excellent aeration and pH neutrality, promoting sustainable plant health.
Gravel is a cost-effective alternative, although it may require thorough cleaning to prevent clogging.
Lava rock, known for its porous structure, enhances microbial colonization, facilitating nutrient cycling.
When selecting your bed media, consider factors such as water retention, aeration, and ease of maintenance.
Each medium has unique properties that can be optimized for innovative, sustainable aquaponics practices, driving both system efficiency and environmental stewardship.
Balancing Water Chemistry
Achieving ideal water chemistry in an aquaponics system is essential for maintaining a harmonious environment where plants and fish can thrive. Guaranteeing the correct balance involves continuous monitoring and adjustment of various parameters.
Key factors to take into account include:
- pH Levels: Maintain a pH range between 6.8 and 7.2 to support both plant and fish health.
- Ammonia and Nitrite Levels: Regularly test to keep these toxic compounds at minimal concentrations, preferably below 0.5 ppm.
- Nitrate Levels: Ascertain nitrates are within 20-40 ppm to provide sufficient nutrients for plants without harming fish.
- Dissolved Oxygen: Enhance aeration to maintain dissolved oxygen levels above 5 ppm for maximal respiration of aquatic life.
Mastering these elements fosters a sustainable, innovative aquaponics system.
Managing System Maintenance
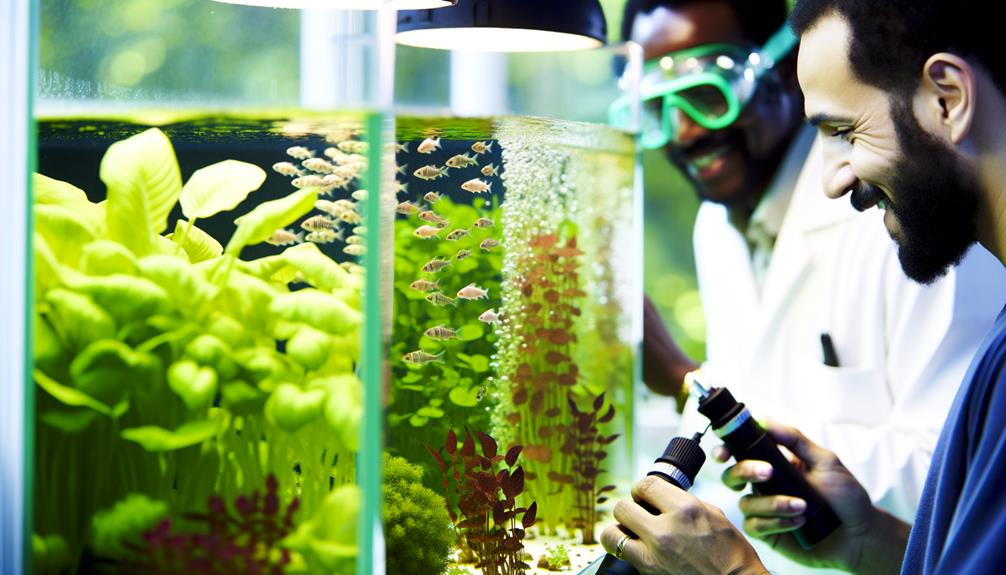

Maintaining an aquaponics system's operational integrity requires regular inspection and upkeep of all components to secure long-term sustainability and efficiency.
Key maintenance tasks include monitoring and cleaning water pumps, guaranteeing ideal flow rates, and preventing blockages. Regularly examine fish tanks and grow beds for debris accumulation, which can hinder system performance.
Utilize innovative filtration methods to maintain water clarity and quality. Implement sustainable practices such as periodic water testing to secure balanced nutrient levels and pH.
Additionally, inspect plumbing connections and aeration systems to prevent leaks and biofilm buildup. Employ proactive measures for pest and disease management, integrating biological controls when necessary.
This holistic approach guarantees the aquaponics system remains efficient, productive, and resilient.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Addressing common issues in an aquaponics system requires a systematic approach to diagnose and rectify problems effectively. Understanding that even minor imbalances can lead to significant disruptions, it is essential to employ technical expertise and sustainable practices.
Common issues include pH imbalances, nutrient deficiencies, and mechanical failures. Here are four steps to troubleshoot these problems:
- Monitor Water Quality: Regularly test pH levels, ammonia, nitrate, and nitrite concentrations to guarantee ideal conditions for both fish and plants.
- Inspect Equipment: Frequently check pumps, filters, and aeration systems for any signs of malfunction or wear and tear.
- Evaluate Plant Health: Look for symptoms such as yellowing leaves or stunted growth, which may indicate nutrient deficiencies.
- Observe Fish Behavior: Unusual fish behavior can signal water quality issues or diseases needing immediate attention.
Conclusion
The synthesis of aquaculture and hydroponics within an aquaponics system represents an innovative approach to sustainable agricultural practices.
By selecting appropriate fish species and plant varieties, designing an efficient system, and meticulously balancing water chemistry, one can achieve a harmonious ecosystem.
Constant vigilance in system maintenance and adept troubleshooting can mitigate potential complications.
Consequently, the intricate dance of aquatic life and plant cultivation emerges as a demonstration of advanced technical expertise and environmental stewardship.