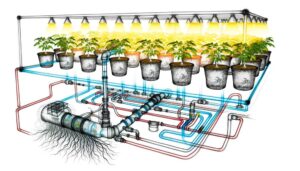
Does a Vertical Hydroponic System Work?
A vertical hydroponic system functions by stacking grow towers to maximize spatial efficiency and deliver nutrient-rich water to plant roots without the need for soil. Utilizing pumps, the system circulates this nutrient solution, guaranteeing even distribution and optimal root zone conditions.
LED lighting systems provide necessary spectrums for photosynthesis, while controlled environment agriculture (CEA) manages temperature and humidity. Precise pH and electrical conductivity levels are maintained for ideal nutrient uptake.
Automated dosing and frequent system checks guarantee consistent plant growth and prevent diseases. This integrated approach considerably enhances plant yield and efficiency while minimizing resource use.
For further insights, important details follow.
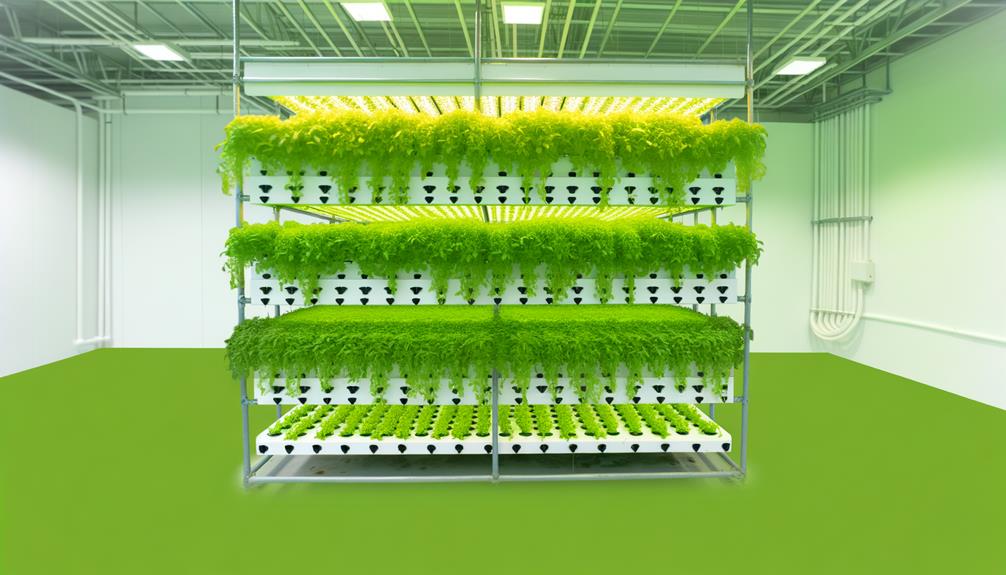

Key Takeaways
- Vertical hydroponic systems use stacked layers to maximize space and grow plants without soil.
- Nutrient-rich water solutions are delivered directly to plant roots via nutrient delivery systems and pumps.
- LED lighting systems provide the necessary light spectrum for photosynthesis and plant growth.
- Effective water circulation ensures even distribution of nutrients and oxygen to all plant levels.
Basic Concept
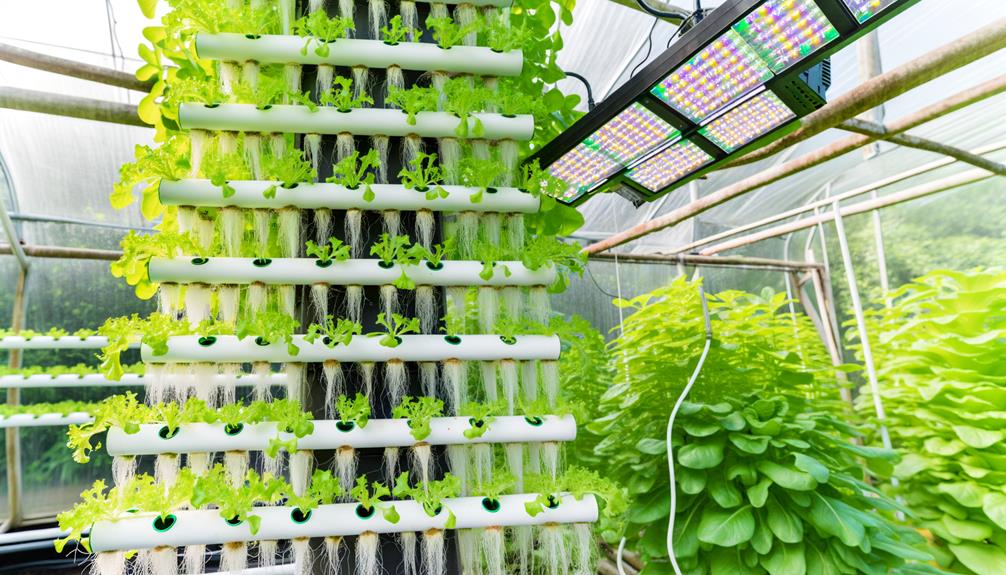

A vertical hydroponic system is an advanced agricultural method where plants are grown in vertically stacked layers without the use of soil, relying instead on a nutrient-rich water solution to deliver essential minerals directly to the plant roots.
This innovative approach maximizes space utilization and enhances the efficiency of nutrient absorption.
By employing controlled environment agriculture (CEA) techniques, these systems optimize factors such as light, temperature, and humidity to foster robust plant growth.
The vertical arrangement allows for a higher density of plants per unit area compared to traditional horizontal farming.
In addition, the absence of soil eliminates soil-borne diseases and pests, reducing the need for chemical interventions, thereby promoting sustainable agricultural practices.
Key Components
Understanding the key components of a vertical hydroponic system is fundamental to comprehending its operational efficiency and the role each part plays in sustaining plant health and growth. Essential components include grow towers, nutrient delivery systems, pumps, and lighting. The grow towers provide vertical planting space, enhancing area utilization. Nutrient delivery systems guarantee precise distribution of water and nutrients. Pumps facilitate the movement of these solutions throughout the system. Lighting, often LED-based, provides the necessary spectrum for photosynthesis.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Grow Towers | Vertical planting space |
| Nutrient Delivery | Precise water and nutrient distribution |
| Pumps | Movement of solutions |
| Lighting | Essential spectrum for photosynthesis |
Together, these components create a highly efficient system, fostering ideal growth conditions and maximizing yield.
Nutrient Solutions
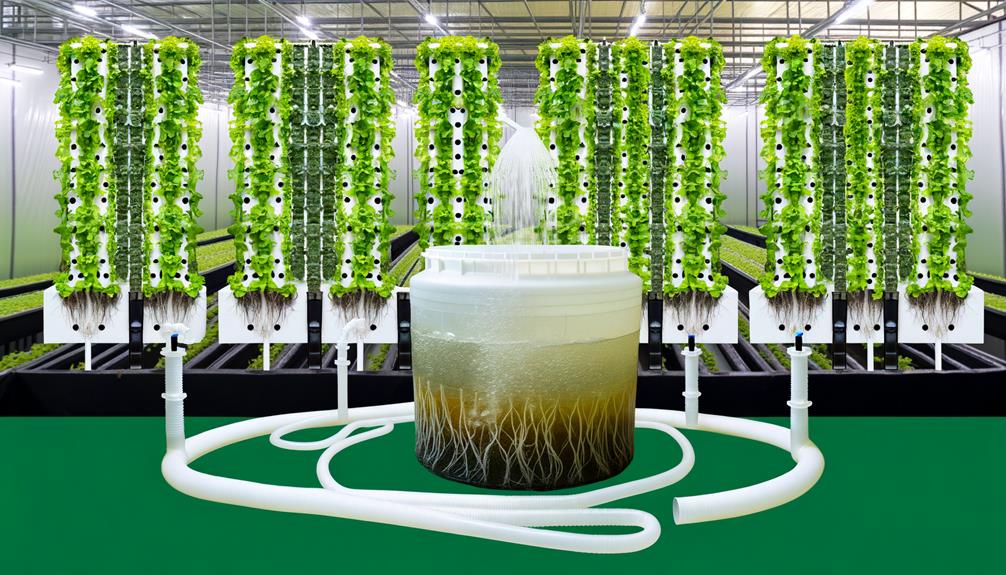

Nutrient solutions, meticulously formulated to meet the specific needs of various plant species, are the lifeblood of a vertical hydroponic system, ensuring ideal growth and development.
These solutions comprise essential macro and micronutrients, including nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium, and trace elements like iron, manganese, and zinc.
Precise pH and electrical conductivity (EC) levels are critical, as they directly influence nutrient availability and uptake efficiency.
Advanced formulations often employ chelates to enhance nutrient solubility and stability.
Water Circulation
Effective water circulation is vital in vertical hydroponic systems to guarantee uniform distribution of nutrient solutions across all plant levels, preventing nutrient deficiencies and promoting ideal growth conditions.
The circulation system typically employs a submersible pump to elevate nutrient-rich water from a reservoir to the topmost tier. Gravity then facilitates a downward flow through a series of channels or tubing, allowing the solution to reach each plant's root zone. This method guarantees continuous oxygenation and optimal nutrient delivery.
Additionally, flow rate calibration and periodic monitoring are essential to prevent stagnation and potential root diseases. Advanced systems may incorporate automated sensors and controllers to adjust flow dynamics in real-time, thereby enhancing the efficiency and reliability of the hydroponic setup.
Lighting Systems
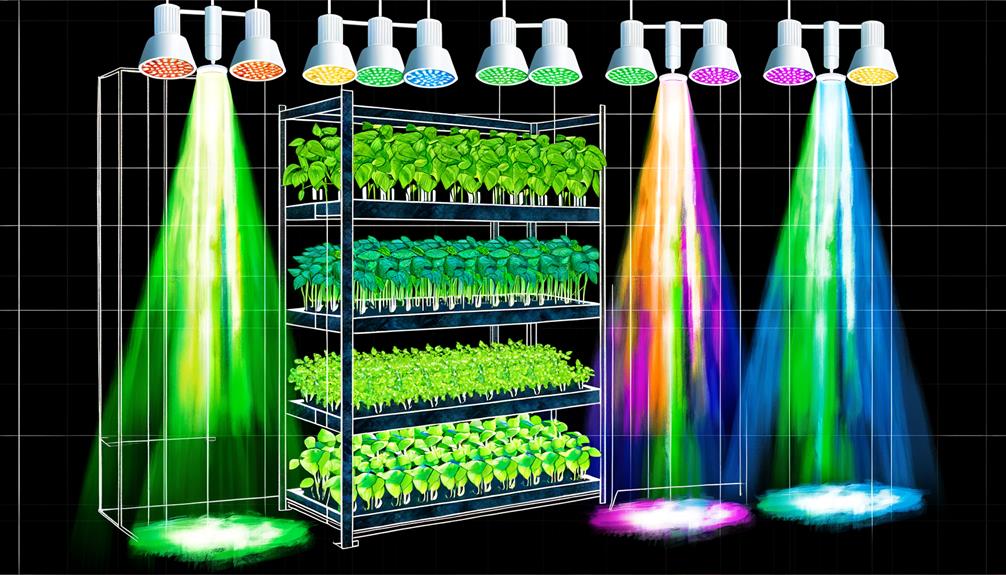
The efficacy of a vertical hydroponic system is greatly influenced by its lighting system, which encompasses various types of grow lights such as LED, fluorescent, and high-pressure sodium lamps.
Understanding the light spectrum is essential, as different wavelengths affect photosynthesis rates and plant growth stages.
Additionally, ideal light placement guarantees uniform light distribution, reducing shadows and promoting even plant development throughout the vertical structure.
Types of Grow Lights
Grow lights, integral to the efficacy of vertical hydroponic systems, encompass various types such as fluorescent, HID, and LED, each offering distinct advantages and spectral outputs tailored to specific plant growth stages. Fluorescent lights, including T5 and CFL, are energy-efficient and suitable for seedlings and vegetative growth. High-Intensity Discharge (HID) lights, such as Metal Halide (MH) and High-Pressure Sodium (HPS), deliver high-intensity light ideal for flowering and fruiting phases. Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs) provide customizable spectra and superior energy efficiency, enhancing both vegetative and flowering stages.
| Grow Light Type | Key Advantages |
|---|---|
| Fluorescent | Energy-efficient, low heat |
| HID | High-intensity light output |
| LED | Customizable spectra, efficient |
| T5 Fluorescent | Ideal for seedlings |
| HPS | best for flowering |
These lighting systems contribute to enhanced plant growth and productivity in vertical hydroponic setups.
Light Spectrum Importance
Understanding the significance of light spectrum in vertical hydroponic systems is vital for optimizing photosynthesis and promoting robust plant development.
Light spectrum encompasses various wavelengths, each influencing specific physiological processes. Blue light (450-495 nm) drives vegetative growth by inducing chlorophyll production, while red light (620-750 nm) enhances flowering and fruiting by activating phytochrome receptors.
Additionally, ultraviolet (UV) and far-red light can modulate secondary metabolite synthesis and elongation, respectively.
Integrating full-spectrum LED grow lights guarantees plants receive a balanced light profile, mimicking natural sunlight. This spectral customization not only maximizes photosynthetic efficiency but also improves yield quality.
Consequently, understanding and manipulating light spectrum is paramount for achieving superior outcomes in vertical hydroponic systems.
Optimal Light Placement
Strategically positioning lighting systems within vertical hydroponic setups is essential for guaranteeing uniform light distribution and maximizing photosynthetic activity across all plant levels.
Advanced lighting solutions, such as LED grow lights, must be carefully aligned to minimize shadowing and guarantee even light penetration.
Implementing a multi-tier lighting arrangement, where lights are placed both above and between plant layers, can greatly enhance light exposure.
Utilizing adjustable light fixtures allows for the fine-tuning of light intensity and angle, thereby accommodating plant growth stages and specific species requirements.
Integrating sensors and automated controls further refines this process, enabling real-time adjustments to maintain ideal light conditions, thereby maximizing plant health and yield in vertical hydroponic systems.
Plant Growth
Plant growth in a vertical hydroponic system is optimized through the precise control of nutrient delivery, light exposure, and environmental conditions.
Nutrient solutions, tailored to specific plant needs, are delivered directly to the root zone, ensuring efficient uptake and minimizing waste.
High-efficiency LED lighting mimics natural sunlight, providing the spectrum necessary for photosynthesis while minimizing energy consumption.
Environmental parameters such as temperature, humidity, and CO2 levels are meticulously regulated using advanced sensors and automation systems.
This controlled environment promotes accelerated growth rates, higher yields, and improved plant health.
The vertical layout maximizes space utilization, allowing for increased plant density without compromising access to essential growth factors.
This method fosters an innovative, sustainable approach to modern agriculture.
Maintenance Tips
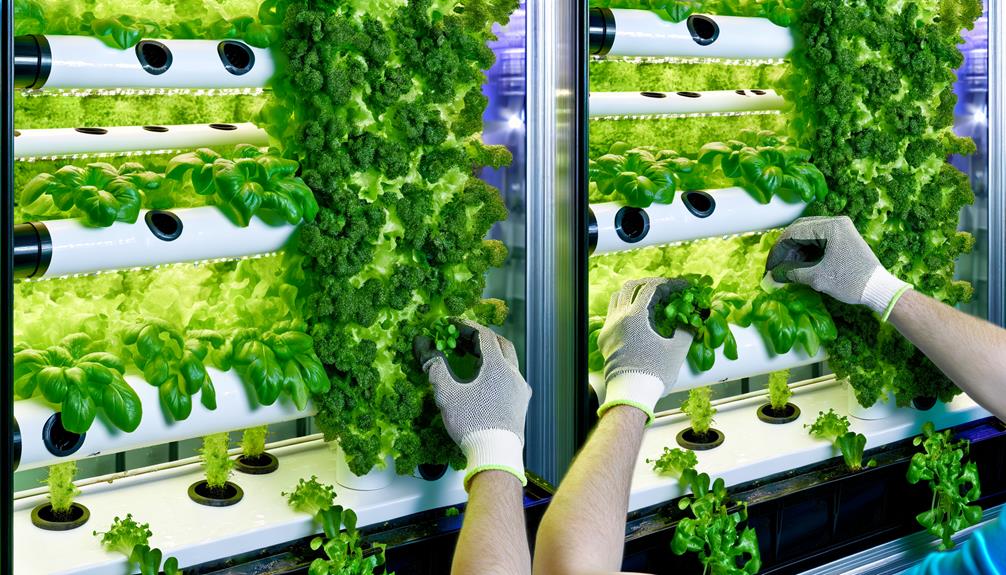

Effective maintenance of a vertical hydroponic system necessitates regular system checks and meticulous nutrient solution management. This involves monitoring pH levels, electrical conductivity, and water temperature to ensure optimal plant growth. Proper cleaning and sanitation practices help prevent algae buildup and blockages in the system. For a detailed understanding of these practices, a hydroponic fodder system overview can provide valuable insights into efficient nutrient delivery and overall system upkeep.
Ensuring the integrity of pumps, tubing, and grow lights is essential to prevent malfunctions that could disrupt plant growth.
Additionally, precise monitoring and adjustment of nutrient concentrations and pH levels in the solution are imperative to sustain ideal plant health and productivity.
Regular System Checks
To guarantee the ideal performance and longevity of a vertical hydroponic system, regular system checks and maintenance are imperative for identifying and addressing potential issues before they escalate.
System audits should include a thorough inspection of all components, verifying maximum functionality and preventing malfunctions.
- Pump Efficiency: Verify the operational status of water and nutrient pumps to prevent flow inconsistencies.
- pH and EC Monitoring: Routinely measure pH and electrical conductivity to maintain balanced nutrient uptake.
- Structural Integrity: Inspect the framework for signs of wear or damage that could compromise stability.
Adhering to these guidelines guarantees a robust, high-yield vertical hydroponic system, fostering innovative agricultural practices.
Nutrient Solution Management
Maintaining an ideal nutrient solution involves precise monitoring and adjustment of nutrient concentrations, pH levels, and temperature to guarantee maximum nutrient absorption by the plants.
Employing an electrical conductivity (EC) meter allows accurate measurement of nutrient concentration, ensuring best ionic balance.
Regular pH testing, ideally maintaining a range between 5.5 and 6.5, prevents nutrient lockout and promotes efficient nutrient uptake.
Temperature control, ideally between 18-22°C, is critical to prevent root zone stress and maintain dissolved oxygen levels.
Replenishing and revitalizing the nutrient solution regularly, alongside using automated dosing systems, enhances consistency and reduces the risk of nutrient imbalances.
Implementing digital monitoring systems can provide real-time data, facilitating timely interventions and ensuring the vertical hydroponic system operates at peak efficiency.
Conclusion
The intricate dance of water, nutrients, and light within a vertical hydroponic system creates a lush tapestry of growth, where each plant thrives in an orchestrated balance.
This harmonious integration of cutting-edge technology and natural processes fosters an environment of sustained, vigorous plant development.
As the roots bathe in nutrient-rich solutions, and the leaves bask under meticulously calibrated lighting, the verdant spectacle stands as a demonstration to the marvels of modern agricultural science.