Truffles Grown Hydroponically: A Beginners How-To
Hydroponic cultivation of truffles is a technically intricate yet promising approach aiming to replicate the complex symbiotic relationships truffles form with their host trees in non-soil environments. While hydroponic systems offer precise control over pH, nutrient delivery, and environmental conditions, reproducing the specific mycorrhizal associations truffles require remains challenging.
Current research focuses on optimizing nutrient solutions, monitoring conditions through advanced sensors, and exploring genetic engineering to bolster mycelium growth. Although numerous hurdles exist, ongoing technological innovations hint at potential breakthroughs in sustainable truffle production.
Continue on to encounter deeper insights and cutting-edge research in this promising field.

Key Takeaways
- Truffles can be grown hydroponically, but replicating their complex mycorrhizal relationships is challenging.
- Hydroponic systems provide precise control over nutrient delivery, pH, and environmental conditions essential for truffle cultivation.
- Maintaining ideal nutrient solutions and pH levels requires constant monitoring to ensure optimal truffle growth.
- Advanced hydroponic technology aims to mimic natural symbiotic conditions necessary for truffle development.
Understanding Truffle Biology

Truffle biology, characterized by its complex symbiotic relationship with host trees, involves intricate ecological and physiological interactions that are essential for their growth and development.
Mycorrhizal fungi, such as Tuber spp., form ectomycorrhizal associations with the roots of specific tree species, enhancing nutrient uptake and water absorption. This symbiosis is pivotal for the truffle's fructification, as it facilitates the exchange of carbohydrates and essential minerals.
Research indicates that the truffle's life cycle is heavily influenced by soil properties, microbial communities, and climatic conditions. Understanding these interactions is critical for developing innovative cultivation methods, potentially leading to novel approaches in controlled environments.
Detailed genomic and metabolomic analyses further elucidate the molecular mechanisms underlying truffle-tree symbiosis, providing a foundation for future cultivation advancements.
Basics of Hydroponic Systems
Understanding the basics of hydroponic systems requires examining the various types, such as nutrient film technique (NFT), deep water culture (DWC), and aeroponics, each providing unique advantages for plant growth.
Additionally, the formulation and management of nutrient solutions are critical for optimizing plant health and yield, necessitating precise control of pH levels, electrical conductivity (EC), and nutrient concentrations.
Current research highlights the importance of these variables in achieving successful hydroponic cultivation, particularly for specialized crops like truffles.
Types of Hydroponic Systems
Hydroponic systems, which facilitate plant growth without soil, can be categorized into several types, each with unique mechanisms and advantages tailored to specific cultivation needs.
The primary systems include Nutrient Film Technique (NFT), Deep Water Culture (DWC), Ebb and Flow, Drip Systems, Aeroponics, and Wick Systems.
NFT uses a continuous nutrient solution flow over plant roots, optimizing oxygen and nutrient uptake.
DWC suspends plant roots in oxygenated nutrient solutions, promoting rapid growth.
Ebb and Flow periodically floods and drains the root zone, enhancing nutrient absorption.
Drip Systems deliver a slow, steady nutrient flow to each plant.
Aeroponics mists roots with nutrient solutions, maximizing aeration.
Wick Systems use capillary action to transport nutrients, ideal for smaller setups.
Nutrient Solutions Essentials
A critical component of hydroponic systems is the formulation and management of nutrient solutions, which provide the essential minerals and elements necessary for plant growth.
These solutions typically contain macronutrients such as nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K), alongside micronutrients like iron (Fe), manganese (Mn), and zinc (Zn).
Research indicates that ideal nutrient concentration and pH levels are paramount, often maintained between 5.5 and 6.5.
Precision in nutrient delivery guarantees not only plant health but also maximizes yield and quality.
For innovative hydroponic endeavors, such as truffle cultivation, the challenge lies in replicating the mycorrhizal relationships found in soil ecosystems.
Data-driven adjustments to nutrient solutions can potentially bridge this gap, fostering successful truffle growth hydroponically.
Comparing Soil Vs. Hydroponics
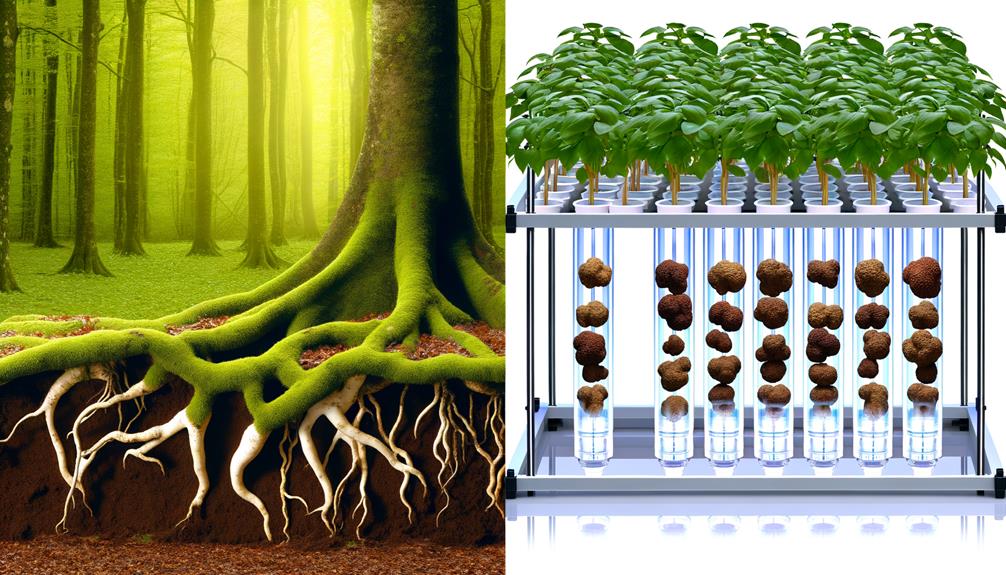

Comparing the growth of truffles in traditional soil cultivation versus hydroponic systems reveals significant differences in yield, quality, and resource efficiency.
Soil-based truffle cultivation, while well-established, often suffers from inconsistencies in environmental conditions, nutrient availability, and pest control.
Hydroponic systems, however, offer precise control over these variables, potentially resulting in higher yield consistency and quality.
Research indicates that hydroponic cultivation can reduce water usage by up to 90% compared to soil methods, highlighting significant resource efficiency.
Additionally, the controlled environment in hydroponics minimizes pathogen exposure, ensuring healthier truffle development.
Preliminary data suggest that hydroponically-grown truffles may achieve comparable, if not superior, quality metrics regarding aromatic compounds and texture.
This innovative approach warrants further investigation to optimize conditions.
Nutrient Requirements for Truffles
Understanding the specific nutrient requirements for truffle cultivation is crucial for optimizing growth and quality in both traditional soil and hydroponic systems.
Truffles thrive on a symbiotic relationship with host trees, necessitating a balanced nutrient profile that supports both fungal and plant health. Key nutrients include nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, and magnesium, delivered in precise concentrations.
Research indicates that truffles also benefit from micronutrients such as iron, manganese, and zinc. Hydroponic adaptations must guarantee the bioavailability of these elements, often achieved through chelated forms.
Studies show that maintaining a nutrient solution with a pH between 6.0 and 6.5 optimizes uptake. Data-driven approaches and continuous monitoring are crucial to refine nutrient solutions for hydroponic truffle cultivation, enabling potential advancements in yield and quality.
Environmental Conditions Needed
Ideal environmental conditions are essential for the successful cultivation of truffles, particularly in controlled hydroponic systems. Achieving the necessary parameters requires precise control over several factors:
| Parameter | Preferred Range |
|---|---|
| Temperature | 16-22°C |
| Humidity | 70-80% |
| pH Level | 7.5-8.5 |
| Light Exposure | Low, indirect light |
| Air Circulation | Moderate, consistent |
Temperature regulation is paramount, as truffles thrive in moderate climates. Humidity levels must be maintained to mimic natural forest floors, crucial for mycelial growth. The pH of the nutrient solution should be slightly alkaline to match truffle preferences. Additionally, low light exposure reduces stress on the fungi, while consistent air circulation prevents pathogenic infestations, ensuring a healthy hydroponic environment.
Current Research and Experiments
Recent research into the hydroponic cultivation of truffles has introduced innovative growing techniques that challenge traditional methods.
Studies highlight both the potential benefits and significant obstacles, including nutrient delivery systems and root symbiosis optimization.
Preliminary findings suggest promising paths forward, although further experimentation is necessary to validate these approaches.
Innovative Growing Techniques
How are researchers leveraging hydroponic systems to cultivate truffles, an area traditionally reliant on symbiotic tree relationships and specific soil conditions?
Through the integration of advanced hydroponic technology, researchers are exploring controlled environments to mimic the natural symbiotic conditions essential for truffle development.
Utilizing nutrient-rich solutions and precise environmental controls, experiments have demonstrated initial success in mycorrhizal associations with host plants, a critical factor for truffle growth.
Studies emphasize the importance of optimizing variables such as pH levels, temperature, and humidity to replicate the forest floor microhabitat.
This innovative approach aims to enhance truffle yield and reduce dependence on traditional cultivation methods, potentially revolutionizing the truffle farming industry by offering more sustainable and scalable solutions.
Challenges and Discoveries
Researchers investigating hydroponic truffle cultivation face significant challenges, including replicating the complex mycorrhizal networks and maintaining the precise environmental conditions necessary for truffle development.
Current experiments focus on optimizing nutrient solutions and substrate compositions to simulate soil ecosystems.
Key discoveries indicate that truffle mycelium requires specific root exudates from host plants, which are difficult to replicate hydroponically.
Data from trials show inconsistent truffle formation, suggesting that additional variables, such as microbial interactions and soil pH, play critical roles.
Advanced sensor technologies are being employed to monitor and adjust these parameters in real-time.
While promising, the research underscores the intricate balance required for successful hydroponic truffle growth, highlighting both the potential and the complexity of this innovative agricultural frontier.
Potential Benefits of Hydroponics

Leveraging hydroponic systems for truffle cultivation offers numerous advantages, including precise control over environmental conditions, which can lead to optimized growth and yield.
Hydroponics facilitates the regulation of nutrient delivery, pH balance, and humidity, creating an environment tailored to the specific requirements of truffles. This method minimizes soil-borne diseases, thereby reducing the need for chemical interventions and enhancing crop quality.
Additionally, data-driven monitoring systems can provide real-time analytics, enabling continuous optimization of growing conditions. Research indicates that hydroponic systems can result in faster growth cycles and potentially increased truffle biomass.
The scalability of hydroponics also offers substantial benefits for meeting commercial demands, providing a sustainable and efficient alternative to traditional cultivation methods.
Challenges and Limitations
While hydroponic systems present numerous advantages for truffle cultivation, they also come with a set of distinct challenges and limitations that must be meticulously managed to guarantee successful outcomes.
Key among these is the replication of the symbiotic relationship between truffles and their host trees, which is notoriously difficult to mimic in controlled environments.
Additionally, maintaining ideal nutrient solutions and pH levels for truffle mycelium growth requires precise calibration and constant monitoring. Data from recent studies indicate that even minor deviations can noticeably impact yield and quality.
Moreover, the initial setup costs and energy requirements for hydroponic systems are substantial, potentially offsetting economic benefits.
These constraints necessitate rigorous research and advanced technological interventions to enhance hydroponic truffle cultivation.
Future Prospects and Innovations

Advancements in genetic engineering and precision agriculture are paving the way for groundbreaking innovations in hydroponic truffle cultivation. Genetic modifications could potentially enhance symbiotic relationships between truffle mycelium and host plants, optimizing nutrient uptake and growth conditions. Precision agriculture technologies, such as sensor-based monitoring systems and automated nutrient delivery, enable the fine-tuning of environmental parameters to mimic natural truffle ecosystems closely.
| Innovation | Description | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Genetic Engineering | Enhancing symbiotic traits in truffle mycelium | Improved growth rates and yields |
| Precision Agriculture | Sensor-based environmental monitoring | Optimized growing conditions |
| Automated Nutrient Delivery | Controlled nutrient supply through automation | Increased efficiency and consistency |
| AI and Machine Learning | Predictive analytics for growth patterns and anomalies | Proactive management and reduced waste |
These innovations could greatly mitigate current limitations, fostering sustainable and scalable hydroponic truffle production.
Conclusion
The cultivation of truffles via hydroponics, though promising, remains largely theoretical.
Just as early aviators faced innumerable challenges before achieving flight, researchers must navigate the complex interplay of nutrient requirements and environmental conditions essential for truffle growth.
Current studies indicate potential benefits, such as controlled environments and optimized nutrient delivery, yet significant obstacles persist.
Continued research and innovation will determine whether hydroponic systems can ultimately support the delicate symbiosis required for truffle cultivation.






