Where Is Hydroponics Used in the World
Hydroponics is utilized globally to improve agricultural productivity and sustainability. In North America's urban centers like New York and Toronto, vertical farming meets the demand for fresh produce.
European countries such as the Netherlands and Spain leverage greenhouse hydroponics to optimize yields and water usage. Middle Eastern nations adopt these systems to combat water scarcity and arid conditions.
Asia's metropolises such as Tokyo and Singapore incorporate indoor farms for food security. Island nations and remote areas use hydroponics to overcome land limitations and support local food production.
Exploring further reveals the transformative impact of these initiatives worldwide.
Key Takeaways
- Urban centers in North America like New York and Toronto utilize hydroponics for sustainable urban farming.
- Greenhouses in the Netherlands and Spain employ hydroponics to maximize productivity and sustainability.
- Desert agriculture in the Middle East, including the UAE and Saudi Arabia, uses hydroponics to address water scarcity.
- Major Asian cities such as Tokyo and Singapore adopt hydroponics for enhanced food security and reduced import dependency.
Urban Centers in North America
Urban centers in North America have increasingly adopted hydroponic systems as a sustainable solution to meet the growing demand for fresh produce in densely populated areas. This shift is supported by evidence showing hydroponics' capacity to yield higher crop outputs compared to traditional soil-based agriculture.
Cities like New York, Chicago, and Toronto are at the forefront, utilizing vertical farming techniques to optimize limited space. Studies indicate that hydroponic systems use up to 90% less water, thereby addressing water scarcity concerns.
Additionally, the reduction in transportation distances minimizes carbon emissions, aligning with urban sustainability goals. These urban hydroponic farms offer a viable alternative to conventional agriculture, ensuring year-round production and contributing to food security in metropolitan regions.
Greenhouses in Europe
Greenhouse-based hydroponic systems have gained significant traction across Europe, driven by the region's commitment to sustainable agricultural practices and food security.
Countries such as the Netherlands and Spain have been at the forefront, leveraging advanced technologies to optimize crop yield and resource efficiency.
In the Netherlands, hydroponic greenhouses cover vast areas, producing over half of the world's greenhouse vegetables despite limited arable land.
Spain's Almería region, known as the 'Sea of Plastic,' utilizes hydroponics extensively to maximize productivity in arid conditions.
These systems reduce water usage by up to 90% compared to traditional farming methods, addressing water scarcity issues.
Europe's regulatory framework also supports innovation in hydroponics, ensuring food safety and quality through stringent standards.
Desert Agriculture in the Middle East
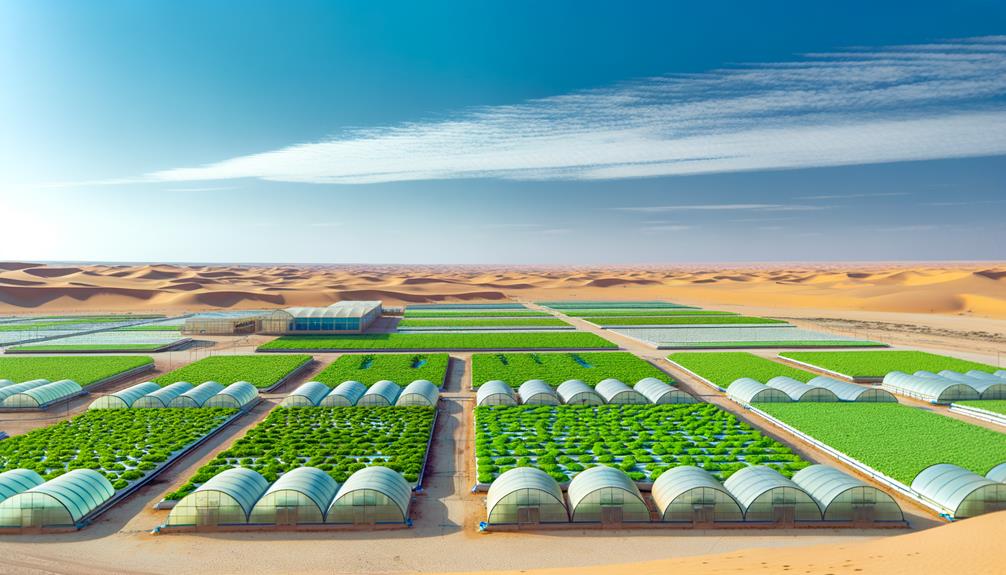

Desert agriculture in the Middle East has increasingly turned to hydroponic systems to overcome the challenges posed by extreme aridity and limited arable land. Countries such as the United Arab Emirates, Saudi Arabia, and Qatar are adopting these advanced agricultural practices to guarantee food security and sustainability. The data below highlights key metrics in the region:
| Country | Water Savings (%) | Crop Yield Increase (%) |
|---|---|---|
| United Arab Emirates | 90 | 30 |
| Saudi Arabia | 85 | 25 |
| Qatar | 88 | 27 |
Hydroponic systems in these arid regions utilize considerably less water compared to traditional farming methods, while also enhancing crop yields. This approach is critical for addressing food production challenges in the Middle East, where water scarcity and desertification are persistent issues.
Indoor Farms in Asia
Indoor farms in Asia are witnessing rapid growth due to urban agriculture expansion, driven by increasing population densities in cities.
The integration of advanced technologies, such as LED lighting and automated controls, enhances productivity and resource efficiency.
This trend contributes greatly to sustainability and food security, addressing the region's challenges of limited arable land and fluctuating climate conditions.
Urban Agriculture Expansion
As urbanization intensifies in Asia, the proliferation of indoor farms represents a strategic adaptation to meet the rising demand for sustainable food production.
Major cities like Tokyo, Singapore, and Shanghai are leading this transformation. These urban centers employ hydroponic systems to optimize space utilization and guarantee year-round crop production.
Evidence from a 2022 study by the Asia Society highlights significant yield improvements and resource efficiency in these hydroponic setups.
This shift is not merely an environmental necessity but also an economic strategy, reducing dependency on imported produce and mitigating supply chain vulnerabilities.
Technological Advancements Integration
Technological advancements in hydroponic systems are revolutionizing indoor farming practices in major Asian cities, enhancing both productivity and sustainability. Key innovations have enabled these urban farms to maximize space and resource efficiency, addressing the challenges posed by limited land and high population densities.
- LED Lighting: Provides ideal light spectra for plant growth, reducing energy consumption.
- Automated Nutrient Delivery Systems: Guarantee precise nutrient delivery, minimizing waste.
- Climate Control Technologies: Maintain perfect growing conditions, improving yield consistency.
- Vertical Farming Structures: Utilize vertical space, greatly increasing crop output per square meter.
These technologies collectively position indoor hydroponic farms as a viable solution for urban food production in Asia.
Sustainability and Food Security
Sustainable hydroponic farming practices in Asian cities are emerging as an essential strategy to bolster food security amidst rapid urbanization and environmental challenges.
Evidence from Singapore and Tokyo highlights how indoor farms maximize limited urban space, enabling year-round production of fresh vegetables.
According to a 2021 study by the Singapore Food Agency, hydroponic systems can yield up to 30% more produce per square meter compared to traditional agriculture. Additionally, these systems use 90% less water, addressing critical water scarcity issues.
In Tokyo, indoor farms utilize advanced LED lighting and climate control, reducing dependency on external weather conditions.
These innovations not only enhance productivity but also contribute greatly to the sustainability and resilience of urban food systems in Asia.
Island Nations and Hydroponics
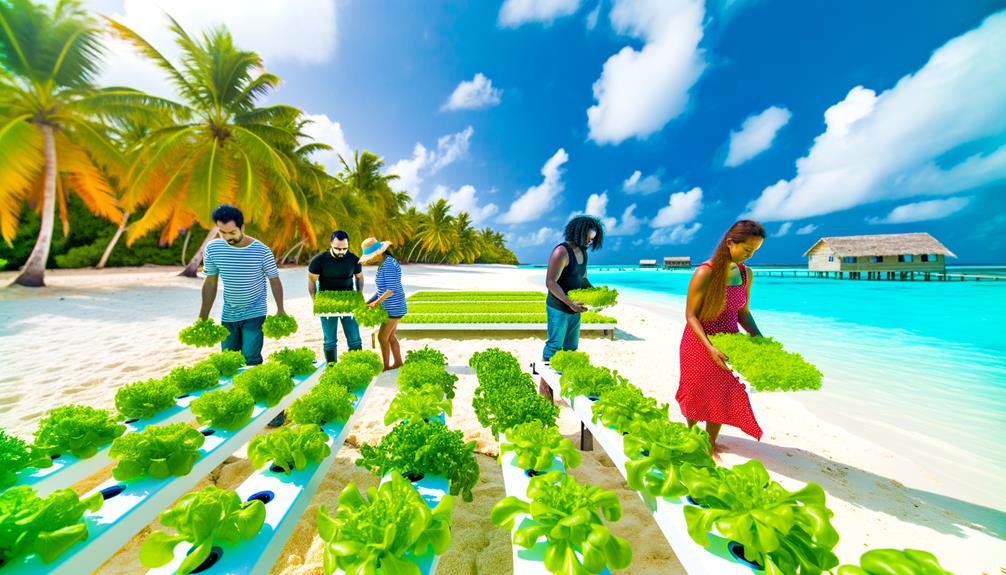

Island nations frequently turn to hydroponics as an innovative solution to address their limited arable land and challenging agricultural conditions. This method offers a sustainable way to guarantee food security and reduce dependency on imports.
The benefits of hydroponics in island nations include:
- Efficient Water Use: Hydroponics systems can use up to 90% less water than traditional farming.
- Space Optimization: Vertical farming techniques maximize limited space.
- Year-Round Production: Controlled environments mitigate seasonal constraints.
- Reduced Transportation Costs: Local production minimizes the need for imported goods.
These factors collectively make hydroponics a viable and strategic choice for island nations aiming to achieve agricultural resilience.
Remote and Rural Areas
In addition to island nations, remote and rural areas also benefit greatly from hydroponics due to its ability to enhance food production in regions with limited access to fertile land and conventional farming resources.
According to recent studies, hydroponic systems can yield crops up to 50% faster than traditional soil-based methods, making them ideal for isolated communities.
For instance, Alaska's remote villages have successfully adopted hydroponics to grow fresh produce year-round, despite harsh climatic conditions.
Moreover, hydroponics requires up to 90% less water, a critical advantage in arid rural areas.
This technology not only mitigates food insecurity but also offers sustainable agricultural practices, thereby supporting the socio-economic development of these communities.
Conclusion
Hydroponics has gained global prominence, becoming a versatile solution for diverse agricultural challenges.
Urban centers in North America and greenhouses in Europe leverage hydroponics to maximize space and yield.
In the Middle East, it is akin to an oasis, enabling cultivation in arid deserts.
Asia's indoor farms and island nations utilize it to overcome limited arable land.
Even remote and rural areas benefit from its efficiency and sustainability, demonstrating hydroponics' transformative potential worldwide.






