What Is the Difference Between the Traditional Method and Hydroponics
We distinguish traditional farming from hydroponics by their reliance on soil versus soil-free systems. Traditional methods use soil for anchoring roots and supplying nutrients, often facing variability in nutrient distribution and higher water consumption.
On the other hand, hydroponics employs inert mediums, delivering precise nutrient solutions directly to roots, which accelerates growth and conserves up to 90% more water. Hydroponics also optimizes space through vertical farming and minimizes soil-borne diseases.
Although the initial setup for hydroponics is costly, the long-term yield efficiency and environmental benefits are considerable. Let's explore the specifics of these methods further.
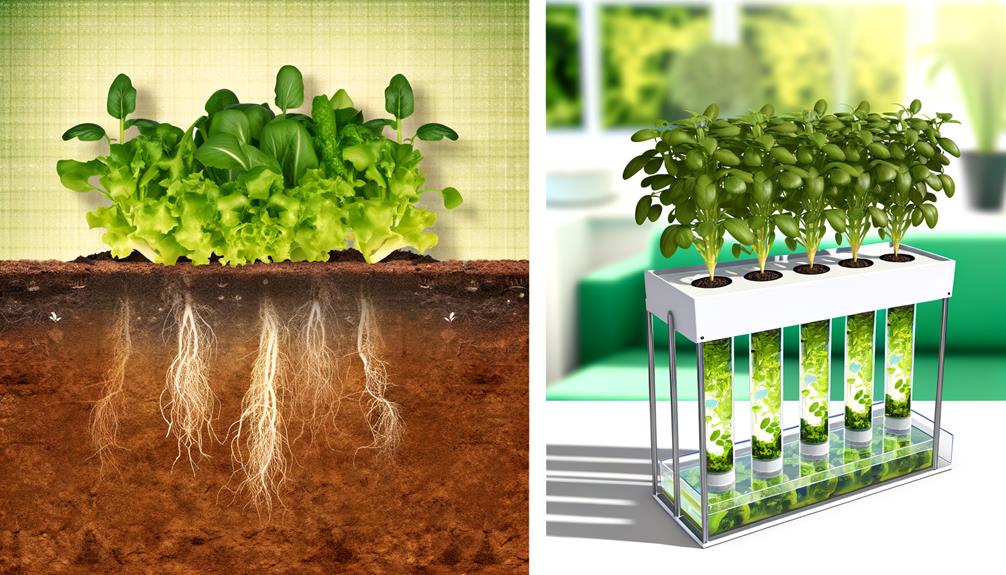

Key Takeaways
- Hydroponics uses nutrient solutions and inert mediums, while traditional farming relies on soil for nutrients, water, and root support.
- Hydroponics conserves up to 90% more water than traditional farming through closed-loop systems and reduced evaporation.
- Hydroponics allows for faster plant growth rates, up to 50% quicker than soil-grown plants, due to optimized nutrient delivery.
- Hydroponics requires less land and can utilize vertical farming, making it more efficient in space usage than traditional methods.
Soil Vs. Soil-Free
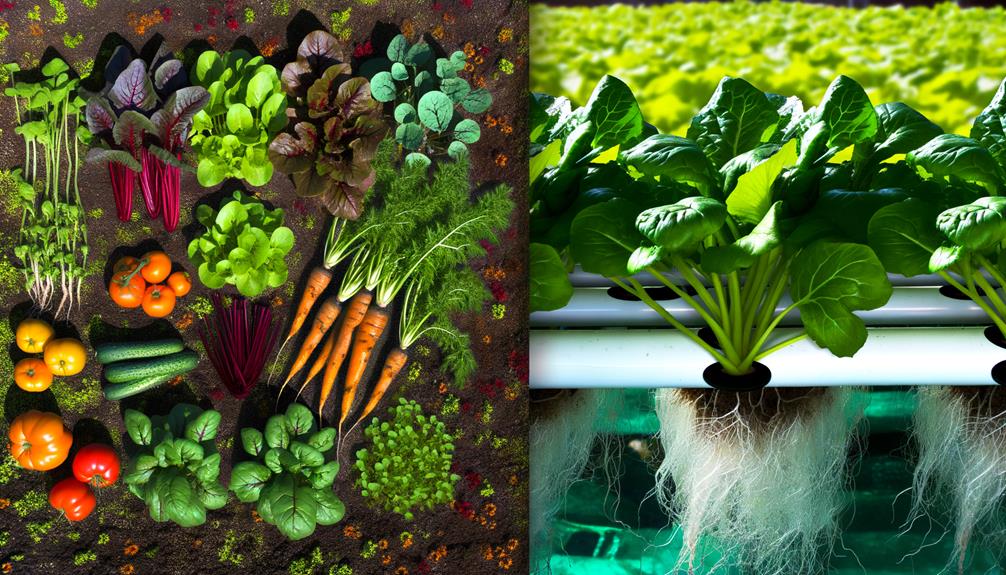

In comparing traditional farming to hydroponics, the most fundamental difference lies in the use of soil versus a soil-free growing medium.
Traditional farming relies on soil to anchor roots, supply nutrients, and retain moisture. Soil's composition affects plant health, productivity, and susceptibility to pests.
However, hydroponics employs inert mediums like perlite, rock wool, or coco coir to support root structures. This method eliminates soil-borne diseases and allows precise control over growing conditions.
By optimizing the root environment, hydroponics often results in faster growth rates and higher yields. Studies show that hydroponic systems can use up to 90% less water than traditional soil-based agriculture, making it a sustainable choice for future food production.
Let's leverage this innovative approach for agricultural advancement.
Nutrient Delivery
Unlike traditional farming, hydroponics delivers nutrients directly to the plant roots through a carefully balanced nutrient solution, allowing for precise control over nutrient uptake and plant health.
By bypassing soil, we eliminate nutrient lockout and variability, ensuring plants receive ideal concentrations of essential minerals like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. This targeted delivery system enhances growth rates and can be fine-tuned to meet the specific needs of different crops.
In traditional soil-based methods, nutrients must first dissolve in water before plants can access them, which can result in uneven distribution and potential deficiencies.
Hydroponics uses recirculating systems to maintain consistent nutrient levels, reducing the risk of under or over-fertilization. This precision fosters healthier plants and maximizes yield, pushing agricultural innovation forward.
Water Usage
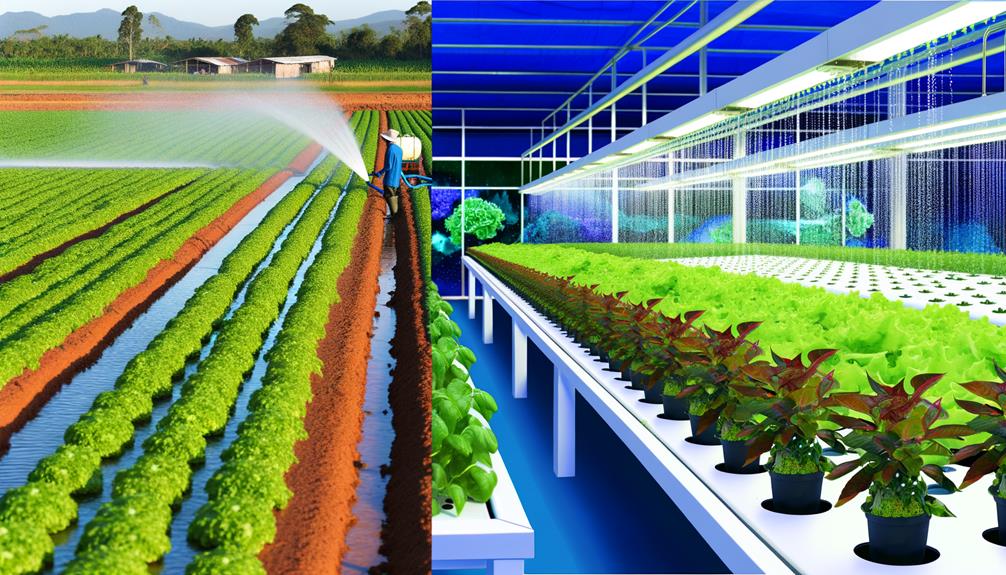

Let's examine water usage in traditional farming versus hydroponics.
In hydroponics, we utilize water conservation techniques that greatly reduce water consumption compared to soil-based methods.
Studies show that hydroponic systems can be up to 90% more water-efficient due to closed-loop irrigation and reduced evaporation.
Water Conservation Techniques
Utilizing hydroponics drastically reduces water consumption compared to traditional farming methods, as it recirculates and reuses water within a closed system.
In hydroponics, we employ nutrient-rich water solutions that minimize wastage by continuously cycling through the system. Evaporation losses are greatly reduced, and water is directed precisely to plant roots, enhancing absorption efficiency.
According to research, hydroponic systems can use up to 90% less water than soil-based agriculture. Additionally, sensors and automation guarantee ideal water delivery, further conserving resources.
Irrigation Efficiency Comparison
Hydroponic systems demonstrate superior irrigation efficiency by using markedly less water per unit of crop yield compared to traditional soil-based methods. We find that hydroponics recirculate water, minimizing waste.
In traditional farming, much of the water is lost to evaporation, runoff, and soil absorption. Studies show hydroponic systems can reduce water usage by up to 90%.
Additionally, precise nutrient delivery in hydroponics guarantees plants receive ideal hydration without excess. This controlled environment allows us to closely monitor and adjust water levels, further enhancing efficiency.
In contrast, traditional methods rely on less predictable natural factors. For those of us seeking innovative, sustainable agriculture, hydroponics offers a clear advantage in water conservation and resource management.
Space Requirements
When comparing space requirements, we find hydroponics excels in land utilization efficiency, often requiring considerably less area than traditional farming.
Its vertical farming potential allows us to maximize crop yield per square foot, making it an ideal solution for urban farming.
These attributes make hydroponics a highly viable option in densely populated areas.
Land Utilization Efficiency
In terms of land utilization efficiency, traditional farming often demands extensive acreage, whereas hydroponic systems can yield equivalent or greater outputs within a strikingly smaller footprint. By leveraging soilless growth media and nutrient-rich water solutions, hydroponics maximizes spatial efficiency.
Consider these compelling advantages:
- Reduced Land Requirements: Hydroponics uses up to 90% less land compared to conventional methods.
- Optimized Yield: Enhanced control over growing conditions translates to higher crop densities.
- Urban Integration: Hydroponic systems can be implemented in urban settings, revitalizing unused spaces.
When we embrace hydroponics, we're not just optimizing land usage; we're pioneering a transformative approach to sustainable agriculture that aligns with our drive for innovation.
Vertical Farming Potential
Building upon the spatial efficiency of hydroponics, vertical farming revolutionizes the agricultural landscape by stacking multiple layers of crops within the same footprint, markedly reducing space requirements.
Utilizing vertical racks and LED grow lights, we can achieve higher crop yields per square meter compared to traditional farming. This method optimizes light exposure and nutrient delivery, enhancing photosynthesis and plant growth. As a result, we maximize land use, making vertical farming an ideal solution for densely populated areas.
Furthermore, vertical farming reduces the need for large tracts of arable land, preserving natural ecosystems and biodiversity. By employing advanced automation and monitoring systems, we can precisely control environmental conditions, ensuring consistent crop quality and minimizing resource waste.
Urban Farming Viability
Urban farming presents a viable solution to space constraints in cities by utilizing rooftops, vacant lots, and other underused urban spaces for agricultural activities. By leveraging these often-overlooked areas, we can maximize land use efficiency and bring fresh produce closer to urban consumers. Hydroponic systems, in particular, enable us to grow more food in less space compared to traditional soil-based methods.
Consider the benefits:
- Reduced transportation costs and emissions
- Increased local food security
- Enhanced urban biodiversity
These advantages highlight the critical role of urban farming in sustainable city planning. By integrating hydroponics into urban environments, we're not only addressing space limitations but also fostering a resilient, innovative food system.
Growth Rate
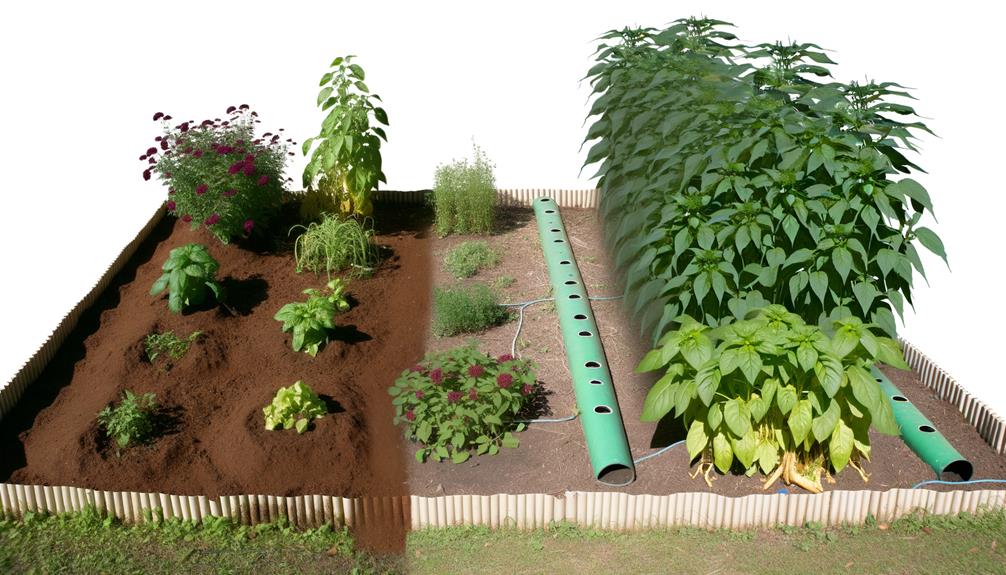

Hydroponic systems typically achieve faster plant growth rates compared to traditional soil-based methods due to optimized nutrient delivery and controlled environmental conditions.
By directly supplying plants with a balanced nutrient solution, we eliminate the inefficiencies of nutrient uptake from soil. The precise control over pH levels and electrical conductivity guarantees that plants receive the exact nutrients they need, promoting robust growth.
Additionally, hydroponics allows us to maintain ideal humidity, temperature, and light conditions, which greatly accelerates photosynthesis. Studies have shown that hydroponically grown plants can mature up to 50% faster than their soil-grown counterparts.
This efficiency not only reduces the time from seed to harvest but also enhances overall yield, making hydroponics a compelling option for innovative agriculture.
Pest and Disease Control
In hydroponic systems, we greatly reduce the risk of pests and diseases by eliminating soil, which is a common breeding ground for many pathogens. By using sterile growing mediums and controlled environments, we can manage and monitor the health of our plants more effectively. This translates to fewer chemical interventions and higher crop yields.
Consider the advantages:
- Lower Pest Incidence: Without soil, pests like nematodes and soil-borne insects are virtually nonexistent.
- Disease Prevention: Pathogens such as fungi and bacteria have reduced opportunities to thrive.
- Controlled Environment: Precise regulation of humidity, temperature, and nutrients inhibits pest and disease proliferation.
Cost Implications
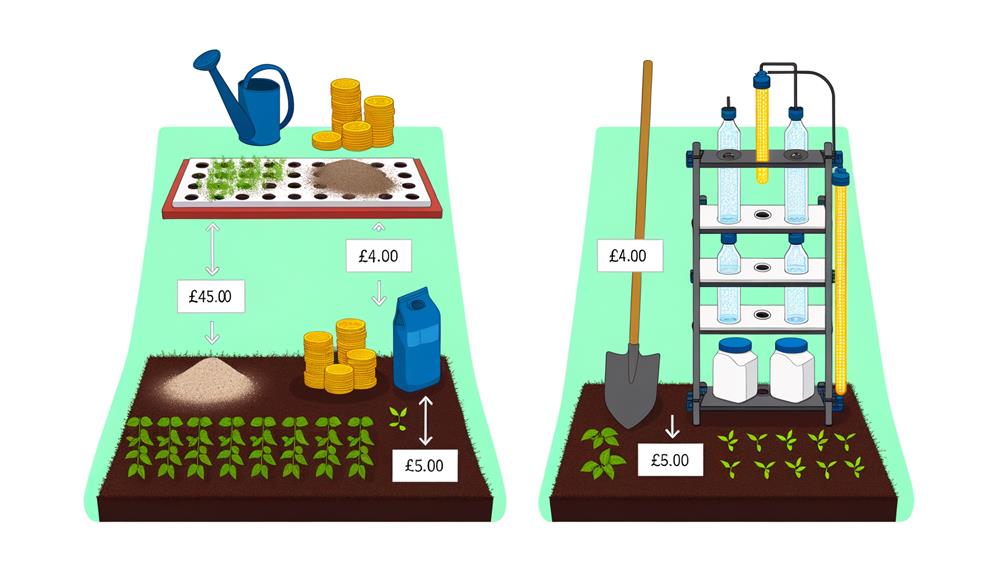
When comparing traditional farming methods to hydroponics, we must consider the initial setup costs and long-term financial implications.
Traditional farming typically requires lower upfront costs, relying on soil, basic tools, and manual labor. In contrast, hydroponics demands significant initial investment in specialized equipment, nutrient solutions, and controlled environment systems.
However, hydroponics can offer higher yields per square meter, reducing the need for extensive land. Additionally, the precise nutrient delivery minimizes waste, potentially lowering ongoing costs.
Labor expenses can also decrease due to automation and reduced pest management needs. Over time, these efficiencies may offset the initial expenditure, making hydroponics financially viable for innovative growers seeking sustainable, high-density agricultural solutions.
Environmental Impact
Evaluating the environmental impact of traditional farming versus hydroponics reveals significant differences in water usage, land efficiency, and chemical runoff.
Traditional farming often leads to excessive water consumption and significant soil degradation. In contrast, hydroponics employs recirculating water systems that reduce usage by up to 90%.
Additionally, hydroponics eliminates the need for arable land, allowing crop growth in urban settings and reducing habitat destruction. Chemical runoff, a major issue in traditional agriculture, is minimized in hydroponic systems due to controlled nutrient delivery.
- Water conservation: Hydroponics uses 90% less water.
- Land efficiency: No need for fertile soil.
- Reduced runoff: Controlled nutrient application.
These factors make hydroponics a more sustainable choice for future agriculture.
Crop Varieties

Hydroponic systems can support a diverse array of crop varieties, including leafy greens, herbs, and certain fruits, due to their controlled growing environments.
We can cultivate nutrient-sensitive crops like lettuce, spinach, and basil with high yield and quality. The absence of soil-borne diseases and pests in hydroponics minimizes plant stress, optimizing growth rates.
Additionally, crops such as strawberries and tomatoes thrive in these systems, benefiting from precise nutrient delivery and pH regulation.
Compared to traditional methods, hydroponics allows for year-round production and faster crop cycles, essential for meeting market demands.
Furthermore, we can experiment with less conventional crops, pushing the boundaries of agricultural innovation.
This adaptability underscores hydroponics' potential in addressing food security challenges.
Conclusion
After comparing traditional methods and hydroponics, we see clear differences: soil versus soil-free, varying nutrient delivery systems, and distinct water usage patterns.
Hydroponics often demands less space and offers faster growth rates, but it comes with higher initial costs.
Pest control is simplified, yet hydroponics' environmental impact remains debatable.
While both methods effectively cultivate crops, the choice ultimately hinges on specific needs and resources.
Let's embrace the scientific advancements in agriculture to optimize our food production.






