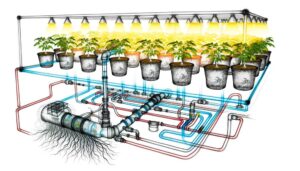
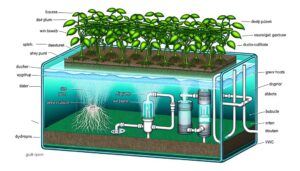
7 Reasons Hydroponic Systems Have Advantages Over Soil Systems
Hydroponic systems outperform traditional soil agriculture by ensuring faster plant growth, increased yields, and superior water efficiency. Plants grow 20-50% faster due to ideal nutrient delivery and controlled environmental factors.
Yields can increase by 30-50%, driven by precise management of nutrients and light. Hydroponics uses up to 90% less water through efficient recirculation, and the controlled conditions drastically reduce pest and disease incidence.
Vertical farming techniques further enhance space utilization, producing up to ten times more per square foot. These benefits underscore hydroponics' potential to revolutionize agricultural practices and sustainability, further details of which could prove enlightening.

Key Takeaways
- Hydroponics ensures 20-50% faster plant growth through optimal nutrient delivery and environmental control.
- Hydroponic systems yield 30-50% more produce compared to traditional soil farming.
- Hydroponics uses up to 90% less water than conventional agriculture.
- Controlled environments in hydroponics significantly reduce pests and diseases.
Faster Plant Growth

Hydroponic systems frequently enable faster plant growth by providing ideal nutrient delivery and environmental control. This accelerated growth is attributed to the precise management of essential nutrients, pH levels, and water availability, which are critical for peak plant health.
Unlike traditional soil-based cultivation, hydroponics eliminates the variability and inefficiencies associated with soil nutrient uptake. Empirical studies have demonstrated that plants grown hydroponically can achieve growth rates 20-50% faster than their soil-grown counterparts.
Additionally, the use of closed systems minimizes water loss through evaporation, ensuring that plants receive a consistent supply of nutrients. This enhanced nutrient solution fosters robust root development and enhances photosynthesis efficiency, paving the way for more resilient and rapidly growing plants.
Such advancements underscore hydroponics' potential to revolutionize modern agriculture.
Higher Yields
Building on the accelerated growth rates, hydroponic systems also demonstrate the capability to considerably enhance crop yields by optimizing resource utilization and minimizing environmental stressors. Empirical data indicates that hydroponic setups can yield up to 30-50% more produce compared to traditional soil farming. This substantial increase is attributable to precise control over nutrient delivery, pH levels, and light conditions. Furthermore, the absence of soil-borne diseases and pests further augments productivity. The following table illustrates comparative yield data:
| Crop Type | Soil System Yield (kg/m²) | Hydroponic Yield (kg/m²) |
|---|---|---|
| Lettuce | 2.9 | 4.5 |
| Tomatoes | 5.1 | 7.8 |
| Cucumbers | 3.4 | 5.2 |
| Strawberries | 2.0 | 3.1 |
| Spinach | 1.8 | 3.0 |
These findings underscore hydroponics' potential in revolutionizing agricultural productivity through innovative practices.
Water Efficiency
Water efficiency in hydroponic systems greatly surpasses that of traditional soil-based agriculture, utilizing up to 90% less water through closed-loop irrigation and recirculation methods.
This significant reduction is achieved by minimizing water loss due to evaporation, runoff, and soil absorption. In hydroponics, water is recaptured and reused, allowing for precise control over nutrient delivery and reducing waste.
Research indicates that hydroponic systems can produce the same amount of crops using only a fraction of the water required by conventional farming. This efficiency is essential in areas facing water scarcity, making hydroponics a sustainable alternative.
Additionally, the ability to monitor and adjust water usage in real-time further enhances resource management, promoting environmental conservation and agricultural innovation.
Fewer Pests and Diseases
A notable reduction in pests and diseases is observed in hydroponic systems due to the controlled environment and absence of soil-borne pathogens.
In traditional soil-based agriculture, soil acts as a reservoir for numerous pathogens and pests, which can exacerbate crop morbidity. Hydroponic systems mitigate these risks by eliminating soil, thereby reducing exposure to common soil-borne diseases such as Fusarium wilt and root-knot nematodes. Additionally, the controlled environment of hydroponic systems allows for better regulation of nutrients and oxygen levels, further promoting plant health. Proper water management and sterilization techniques play a crucial role in hydroponic root rot prevention, ensuring that harmful pathogens do not proliferate in the nutrient solution. As a result, crops grown hydroponically often exhibit improved growth rates and higher yields compared to their soil-grown counterparts.
Additionally, the controlled environment of hydroponics allows for precise regulation of humidity, temperature, and nutrient levels, further reducing the likelihood of pest infestations.
Studies indicate that this controlled approach not only enhances plant health but also diminishes the need for chemical pesticides, aligning with sustainable agricultural practices.
This innovative method consequently offers a robust solution for healthier crop production.
Space Utilization

Hydroponic systems often maximize space utilization by enabling vertical farming and high-density planting, thereby considerably increasing crop yield per unit area.
This is achieved through the use of vertically stacked layers, which allow multiple tiers of crops to grow within the same footprint.
Comparative studies have shown that hydroponic systems can yield up to 10 times more produce per square foot than traditional soil-based systems.
Additionally, the controlled environment of hydroponics minimizes the need for extensive spacing between plants, leading to efficient use of horizontal and vertical space.
Innovations such as aeroponic towers and modular designs further enhance spatial efficiency, making hydroponics a viable solution for urban agriculture and areas with limited arable land.
Conclusion
To summarize, the hydroponic system outpaces traditional soil methods by accelerating plant growth, enhancing yield, optimizing water usage, and reducing pest and disease occurrences.
This method also maximizes spatial efficiency, turning every inch into a productive oasis.
The advantages presented form a compelling case for hydroponics as a superior agricultural practice.
Consequently, the hydroponic system stands as a beacon of innovation, promising a sustainable and efficient future for horticulture.