Can All Vegetables Be Grown Hydroponically?
Hydroponic systems enable the cultivation of a wide variety of vegetables by providing precisely controlled growing conditions. Leafy greens like lettuce and spinach thrive due to ideal light and nutrient delivery.
Root vegetables such as carrots and beets demand space and specific aeration to prevent rot. Fruiting vegetables, including tomatoes and peppers, benefit from tailored nutrient solutions and light spectrum management.
Herbs exhibit enhanced essential oil content, while cruciferous vegetables achieve greater nutritional value. Even legumes and exotic vegetables demonstrate accelerated growth within hydroponic environments.
Certain challenges exist, but controlled parameters guarantee successful outcomes. Exploring specific needs enhances understanding of hydroponic vegetable cultivation.
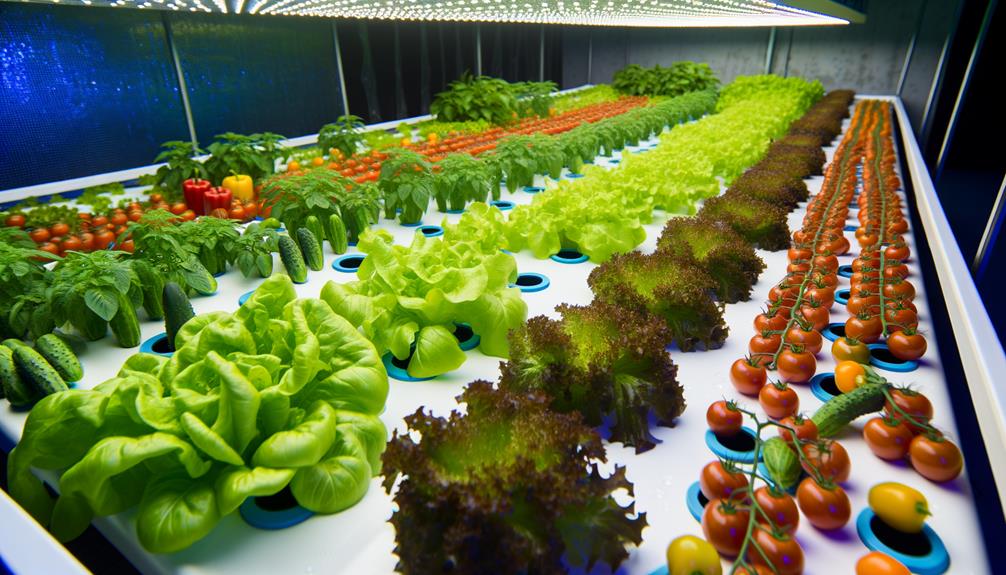

Key Takeaways
- Most vegetables, including leafy greens, root vegetables, and herbs, can be successfully grown hydroponically.
- Hydroponic systems provide a controlled environment suitable for growing a wide variety of vegetables.
- Challenges like space requirements and nutrient needs must be managed for different vegetable types.
- Exotic vegetables also thrive in hydroponic systems, offering opportunities for diverse crop production.
Benefits of Hydroponic Farming

Hydroponic farming offers numerous advantages, including increased crop yields, efficient use of water resources, and the ability to grow vegetables in environments unsuitable for traditional agriculture.
This method leverages nutrient-rich solutions, optimized for plant uptake, resulting in accelerated growth rates and higher productivity per square meter compared to soil-based farming.
Studies indicate that hydroponic systems can reduce water usage by up to 90%, addressing critical challenges in water-scarce regions.
In addition, the controlled environment mitigates pest infestations and diseases, allowing for reduced pesticide application and enhanced crop quality.
By decoupling agriculture from arable land constraints, hydroponics facilitates urban farming, contributing to food security and reducing transportation-related carbon footprints.
This innovative approach exemplifies sustainable agricultural practices in the face of global challenges.
Leafy Greens Success
Achieving success in hydroponically growing leafy greens necessitates understanding the ideal growth conditions, including light intensity, temperature, and humidity levels.
Proper formulation and monitoring of nutrient solutions tailored to the specific requirements of leafy greens are essential to maximizing yield and quality.
Additionally, addressing common challenges such as pest management and nutrient imbalances can greatly enhance the productivity and sustainability of hydroponic systems.
Optimal Growth Conditions
To guarantee the successful cultivation of leafy greens in a hydroponic system, it is essential to meticulously control and fine-tune key environmental parameters such as light intensity, nutrient concentration, pH levels, and temperature.
Empirical studies have demonstrated that maintaining these factors within specific ranges greatly enhances growth rates and biomass yield.
Key conditions for ideal leafy greens growth include:
- Light Intensity: 12-16 hours of light per day, with a photosynthetic photon flux density (PPFD) of 150-250 µmol/m²/s.
- Nutrient Concentration: Electrical conductivity (EC) levels between 1.2-2.0 mS/cm.
- pH Levels: Ideal range of 5.5-6.5 for nutrient uptake.
Adhering to these parameters fosters robust and healthy plant development.
Nutrient Solutions Required
A critical component for the successful cultivation of leafy greens in hydroponic systems is the precise formulation of nutrient solutions tailored to meet the specific physiological needs of the plants.
Essential macronutrients, including nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, must be meticulously balanced to enhance growth rates and leaf development. In addition, micronutrients such as magnesium, calcium, and iron are imperative to prevent deficiencies that could impede chlorophyll production and photosynthesis.
Empirical studies have demonstrated that electrical conductivity (EC) levels between 1.2-2.0 mS/cm, combined with a pH range of 5.5-6.5, are ideal for nutrient uptake in leafy greens.
Innovations in automated dosing systems and real-time nutrient monitoring are advancing precision agriculture, ensuring that hydroponic leafy greens receive consistent and ideal nutrient delivery for superior yield and quality.
Common Challenges Faced
Despite the advancements in nutrient management, hydroponic cultivation of leafy greens is not without its challenges, particularly issues related to pest control, disease management, and maintaining ideal environmental conditions. These challenges necessitate a thorough approach to guarantee peak growth and yield.
Key considerations include:
- Pest Control: Effective strategies to manage aphids, whiteflies, and fungal gnats.
- Disease Management: Monitoring and prevention of root rot and powdery mildew are vital.
- Environmental Conditions: Maintaining stable temperature, humidity, and light levels is fundamental for plant health.
Thus, while hydroponic systems offer significant advantages, meticulous attention to these factors is fundamental for the successful cultivation of leafy greens.
Root Vegetables Challenges
Cultivating root vegetables hydroponically presents unique challenges primarily related to space and support requirements, necessitating tailored system designs to accommodate their vertical and horizontal growth patterns.
Additionally, the selection of an appropriate growth medium is critical for providing adequate aeration and nutrient delivery, with materials such as coconut coir or perlite being evaluated for their efficacy.
Evidence indicates that these parameters notably influence root morphology and overall yield, underscoring the need for meticulous planning and resource allocation in hydroponic setups.
Space and Support Needs
Root vegetables present unique challenges in hydroponic systems due to their extensive space and support requirements for ideal growth. These challenges necessitate innovative adaptations to traditional hydroponic setups to optimize growth conditions.
Scientific studies have identified the following key factors that must be addressed:
- Space Allocation: Root vegetables such as carrots and beets need ample vertical and horizontal space to develop properly.
- Support Structures: Adequate support systems are essential to prevent structural deformities and guarantee uniform growth.
- Nutrient Distribution: Efficient nutrient delivery systems are critical to meet the high demand for essential minerals.
Addressing these factors can considerably enhance the feasibility of hydroponically cultivating root vegetables.
Growth Medium Choices
Selecting an appropriate growth medium is critical for hydroponically cultivating root vegetables, as it directly influences root development, nutrient uptake, and overall plant health.
Traditional media such as Rockwool and perlite, while effective for leafy greens, may not provide sufficient support or space for tuber expansion.
Innovations like coconut coir and expanded clay pellets offer improved aeration and moisture retention, but their efficacy varies based on particle size and consistency.
Research indicates that hybrid systems integrating these media with nutrient film techniques can enhance growth conditions.
However, challenges such as root deformation and nutrient imbalances persist.
Advanced solutions, including automated nutrient delivery and root zone monitoring, are essential for overcoming these barriers and achieving ideal yields in hydroponic root vegetable cultivation.
Fruiting Vegetables Viability
Examining the viability of fruiting vegetables in hydroponic systems necessitates a detailed analysis of factors such as nutrient delivery efficiency, light spectrum enhancement, and environmental control parameters.
Research indicates that hydroponically grown fruiting vegetables, including tomatoes, peppers, and cucumbers, exhibit comparable or superior yields to traditional soil cultivation when these factors are meticulously managed.
Critical components to guarantee success in hydroponic fruiting vegetables include:
- Nutrient Solution Composition: Accurate formulation tailored to the specific needs of fruiting vegetables.
- Light Spectrum Management: Utilization of LED lighting to mimic natural sunlight and enhance photosynthetic efficiency.
- Temperature Regulation: Maintaining ideal thermal conditions to promote robust growth and fruiting.
Such precision-driven methodologies underscore the potential for high-yield, sustainable hydroponic agriculture.
Herbs in Hydroponics
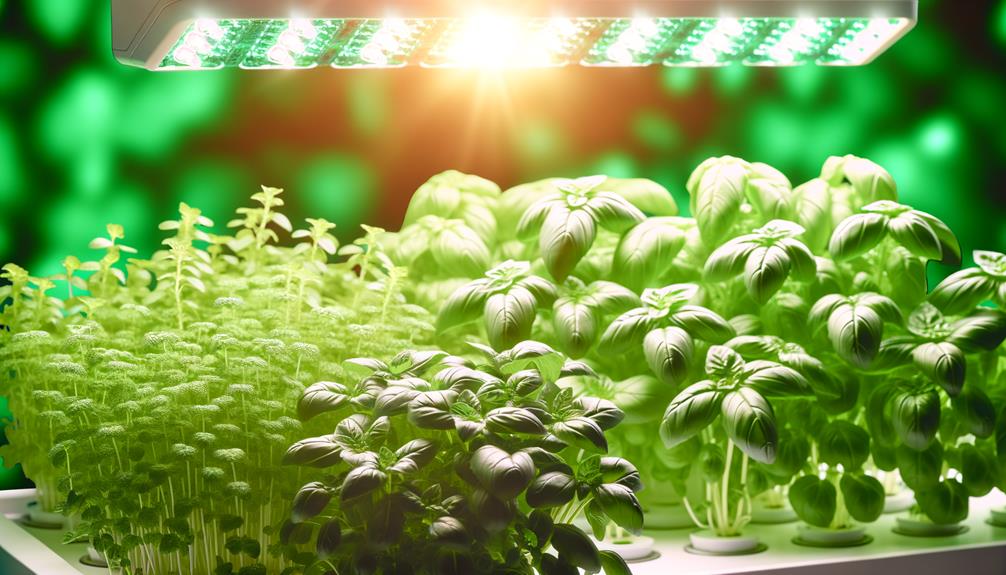

In addition to fruiting vegetables, hydroponic systems are highly conducive to cultivating a variety of herbs, where precise control over nutrient delivery and environmental conditions can result in ideal growth and potent flavor profiles. The hydroponic cultivation of herbs such as basil, mint, and cilantro has demonstrated significant advantages in growth rate and bioactive compound concentration. Research indicates that hydroponically grown herbs often exhibit higher essential oil content, enhancing their aromatic and medicinal properties. Below is a comparative table illustrating key parameters for optimal growth of selected herbs in hydroponic systems:
| Herb | Ideal pH Range | Light Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| Basil | 5.5 – 6.5 | 14-16 hours/day |
| Mint | 6.0 – 7.0 | 12-14 hours/day |
| Cilantro | 6.2 – 6.8 | 12-14 hours/day |
This precise control underscores hydroponics' potential in producing high-quality herbs.
Cruciferous Vegetables Insights
Hydroponic systems provide a superior environment for cultivating cruciferous vegetables, allowing for precise manipulation of nutrient solutions and growth conditions to maximize yield and quality. This method offers significant advantages for crops such as broccoli, cauliflower, cabbage, and kale.
Scientific evidence supports the efficacy of hydroponics in promoting robust plant health and accelerated growth rates. Detailed analysis reveals that nutrient uptake efficiency is markedly improved, leading to higher nutritional content in the harvested produce.
- Increased Growth Rate: Controlled environments enhance photosynthesis and metabolic activities.
- Resource Efficiency: Hydroponics uses less water compared to traditional soil-based farming.
- Pest and Disease Management: Reduced exposure to soil-borne pests and pathogens.
Legumes in Hydroponics

Cultivating legumes through hydroponic systems offers a highly efficient and sustainable approach to producing nutrient-rich crops such as beans, lentils, and peas.
Hydroponic legume cultivation leverages controlled environments to optimize growth variables, including nutrient composition, pH levels, and light exposure. Studies have shown that hydroponically grown legumes exhibit accelerated growth rates and enhanced yield compared to traditional soil farming.
In addition, the closed-loop system reduces water usage by up to 90%, addressing critical sustainability concerns. Nutrient film technique (NFT) and deep water culture (DWC) are particularly effective methods for legume propagation.
Moreover, hydroponic systems mitigate soil-borne diseases and pests, ensuring healthier and more resilient plants. This innovative approach aligns with contemporary agricultural demands for resource efficiency and high productivity.
Exotic Vegetables Potential
The incorporation of exotic vegetables into hydroponic systems offers significant potential for diversifying crop portfolios and meeting niche market demands. Hydroponic cultivation of exotic vegetables, such as wasabi, bok choy, and heirloom tomatoes, has shown promising results in controlled environments. Scientific studies indicate that these vegetables can achieve ideal growth rates and high nutritional value when provided with precise nutrient formulations and environmental controls.
Key benefits include:
- Enhanced growth rate: Exotic vegetables often exhibit accelerated growth in hydroponic systems compared to traditional soil cultivation.
- Resource efficiency: Hydroponics requires less water and land, making it a sustainable option for high-value crops.
- Market premium: Exotic vegetables often fetch higher prices due to their rarity and unique flavors.
Troubleshooting Common Issues

Effective troubleshooting in hydroponic vegetable cultivation necessitates a thorough understanding of common issues such as nutrient imbalances, pH fluctuations, and pest infestations.
Nutrient imbalances can be identified through leaf discoloration and stunted growth; they often require precise adjustments in nutrient solution concentrations.
pH fluctuations, detrimental to nutrient uptake, should be monitored using pH meters and stabilized via buffering agents.
Pest infestations, although less prevalent in hydroponics, can be mitigated through integrated pest management (IPM) strategies, including biological controls and organic pesticides.
Regular system checks for root health, water temperature, and dissolved oxygen levels are essential.
Implementing these evidence-based practices guarantees optimized plant health and maximizes yield potential, fostering innovation in hydroponic systems.
Conclusion
Hydroponic farming offers a revolutionary approach to agriculture, juxtaposing the success of leafy greens with the challenges faced by root vegetables.
While fruiting vegetables and herbs exhibit high viability, cruciferous vegetables and legumes present unique opportunities and hurdles.
Exotic vegetables underscore the potential diversity achievable through hydroponics.
Addressing common issues with evidence-based strategies solidifies hydroponics as a versatile yet complex method of cultivation, demanding a nuanced understanding of each vegetable's specific requirements.






