How Chillies Are Grown Hydroponically – A Step-by-Step Guide
Yes, chillies can be grown hydroponically, utilizing soilless cultivation methods that employ nutrient-rich water solutions. Hydroponics offers enhanced growth rates by delivering essential nutrients directly to the root system, which optimizes nutrient uptake and greatly reduces the likelihood of soil-borne diseases and pests.
Key hydroponic systems such as Nutrient Film Technique (NFT), Deep Water Culture (DWC), and Ebb and Flow provide effective frameworks for growing chillies. Maintaining ideal environmental conditions, including temperature, humidity, and pH levels, is vital for achieving prolific yields and superior capsaicin content.
To master these techniques, deeper exploration into system management and nutrient balance is essential.
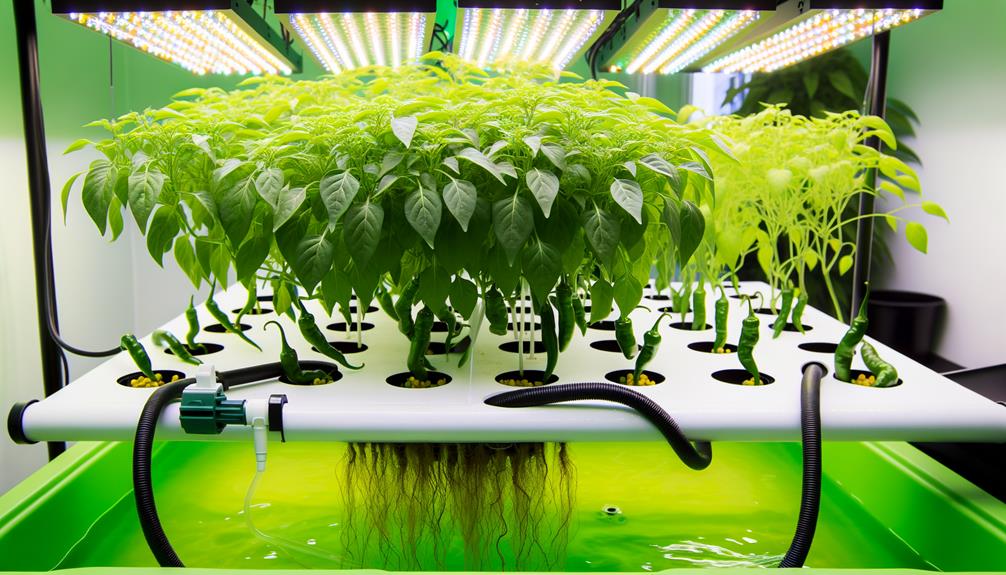

Key Takeaways
- Chillies can be grown hydroponically, benefiting from rapid growth and optimized nutrient uptake.
- Hydroponic systems like NFT, DWC, and Ebb and Flow are suitable for growing chillies.
- Controlled environments reduce soil-borne diseases and pests, promoting healthier chilli plants.
- Hydroponics enables year-round chilli production, independent of seasonal changes.
Understanding Hydroponics
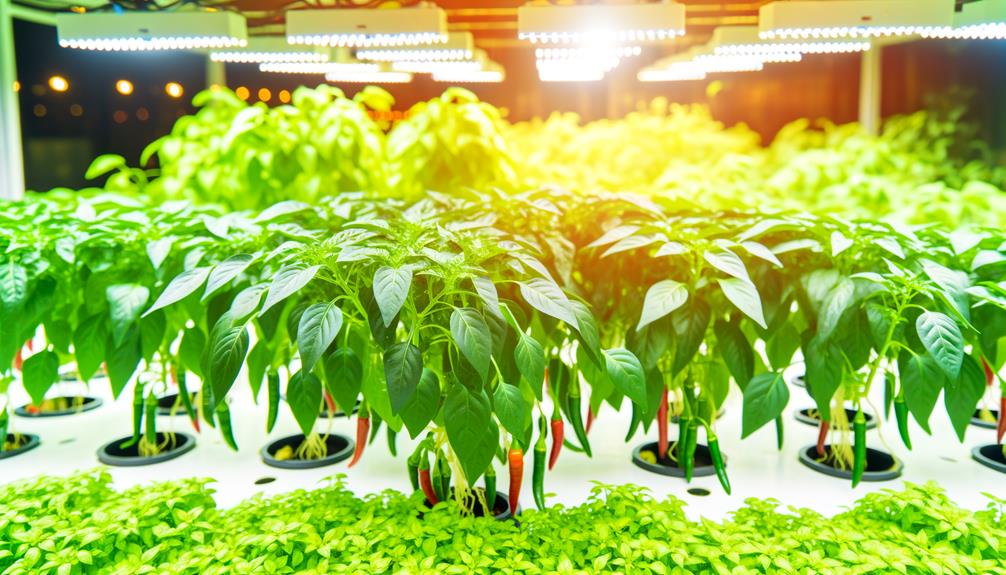

Hydroponics, an advanced method of soilless cultivation, leverages nutrient-rich water solutions to grow plants, offering precise control over environmental variables and resource efficiency.
This technique replaces traditional soil with inert mediums such as perlite, vermiculite, or rock wool, which provides structural support.
Essential nutrients are delivered directly to plant roots via a water-based solution, ensuring ideal absorption and reducing waste.
Parameters such as pH, electrical conductivity, and dissolved oxygen are meticulously monitored and adjusted to cater to specific plant needs.
This method minimizes pest infestations and soil-borne diseases while maximizing growth rates and yield.
Hydroponics is particularly advantageous in controlled environment agriculture (CEA) systems, enabling year-round production irrespective of external climatic conditions, thereby aligning with the goals of modern agronomic innovation.
Benefits of Hydroponic Chillies
Cultivating chillies hydroponically offers significant advantages, including enhanced growth rates, optimized nutrient uptake, and superior yield quality compared to traditional soil-based methods.
Hydroponic systems deliver nutrients directly to the roots, ensuring precise control over nutrient composition and pH levels. This results in faster growth cycles and increased fruit production.
Moreover, hydroponic cultivation minimizes the risk of soil-borne diseases and pests, enhancing plant health and reducing the need for chemical interventions. The controlled environment allows for year-round production, independent of seasonal constraints, thereby ensuring a consistent supply.
Additionally, hydroponic chillies exhibit improved flavor profiles and higher capsaicin content, attributes highly valued in culinary and pharmaceutical applications.
This innovative approach aligns with sustainable agriculture practices, promoting resource efficiency and reduced environmental impact.
Choosing the Right System
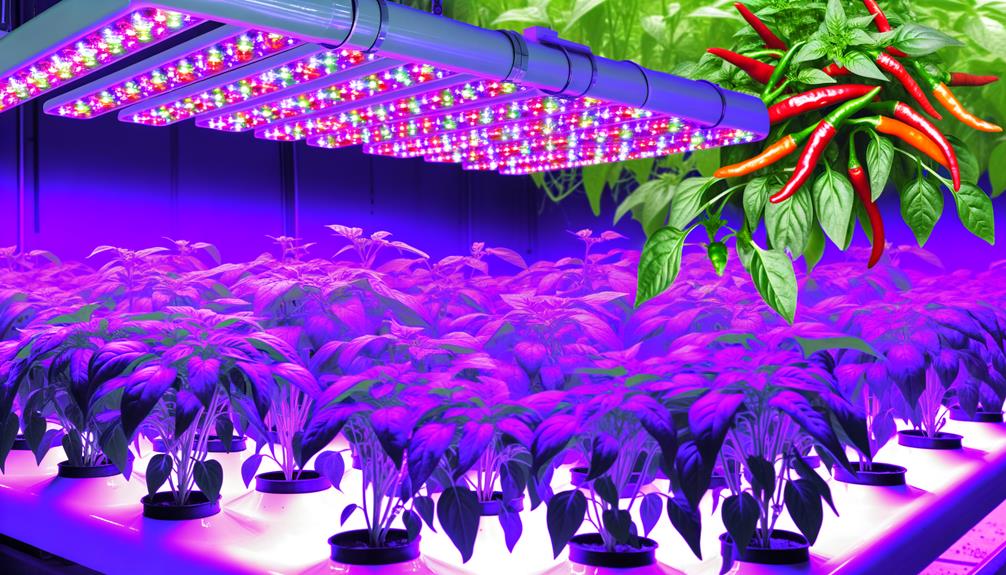

To effectively harness the benefits of hydroponic chilli cultivation, selecting the appropriate hydroponic system is paramount.
Key systems include Nutrient Film Technique (NFT), Deep Water Culture (DWC), and Ebb and Flow.
NFT is efficient for its continuous nutrient flow, reducing the risk of root diseases.
DWC immerses roots in oxygen-rich nutrient solutions, fostering rapid growth.
Ebb and Flow systems periodically flood the root zone, guaranteeing ideal nutrient uptake and aeration.
Each system's efficacy hinges on precise control of environmental parameters such as pH, electrical conductivity (EC), and dissolved oxygen levels.
Understanding the specific requirements of chilli plants and aligning them with the system's capabilities guarantees maximized yield and resource efficiency, driving innovative agricultural practices.
Nutrient Solutions
Ideal nutrient solutions are essential for hydroponic chilli cultivation, ensuring that plants receive a balanced mix of important macro and micronutrients for robust growth and high yield.
The primary macronutrients required include nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K), each playing a significant role in plant development. Secondary nutrients, such as calcium (Ca), magnesium (Mg), and sulfur (S), are also indispensable.
Micronutrients like iron (Fe), manganese (Mn), boron (B), zinc (Zn), copper (Cu), and molybdenum (Mo) further enhance metabolic functions.
Precision in the concentration and pH levels of the nutrient solution is paramount, typically maintained between 5.5 and 6.5.
Innovations in nutrient delivery and monitoring systems can optimize absorption rates, ensuring maximum efficiency and sustainable cultivation practices.
Optimal Growing Conditions

Achieving ideal growing conditions for hydroponic chillies necessitates meticulous control of environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, light intensity, and air circulation.
Ideal temperature ranges from 20°C to 30°C, with relative humidity maintained between 50% and 70% to prevent fungal diseases.
Light intensity should be calibrated to provide 14-16 hours of light daily, using full-spectrum LED grow lights to replicate the solar spectrum.
Effective air circulation is critical to preventing stagnation and promoting robust plant respiration; therefore, integrating oscillating fans and proper ventilation systems is recommended.
Continuous monitoring and adjustments guarantee that parameters remain within ideal ranges, fostering prolific growth and maximizing yield potential.
Such precision in environmental control underscores the innovation inherent in hydroponic chilli cultivation.
Common Challenges
Despite the numerous advantages of hydroponic chilli cultivation, growers often encounter challenges such as nutrient imbalances, pest infestations, and system failures.
Nutrient imbalances can arise due to the precise requirements of chilli plants for specific macro and micronutrients. An incorrect nutrient formulation can lead to deficiencies or toxicities, adversely affecting plant health and yield.
Additionally, hydroponic systems can be susceptible to pest infestations, which can be exacerbated in controlled environments where natural predators are absent.
System failures, such as pump malfunctions or power outages, can disrupt the delicate balance of water, nutrients, and oxygen that hydroponic systems depend on.
Addressing these challenges requires rigorous monitoring, prompt intervention, and a thorough understanding of hydroponic principles and chilli plant physiology.
Pest and Disease Management
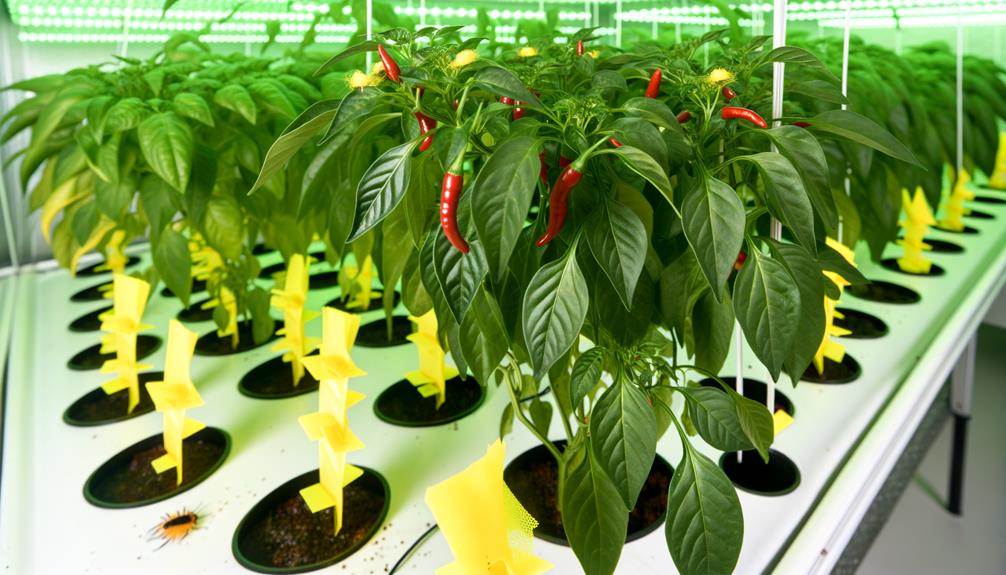

Effective pest and disease management in hydroponic chilli cultivation necessitates a thorough integrated pest management (IPM) strategy tailored to the unique environment of soilless systems. Utilizing biological controls, such as beneficial insects, and chemical controls, like targeted biopesticides, guarantees robust plant health. Monitoring environmental variables, including humidity and temperature, is essential to prevent outbreaks of pathogens such as Pythium and Fusarium. Implementing regular inspections and employing physical barriers like insect netting further fortifies defense mechanisms.
| Pest/Disease | Symptoms | Management Practices |
|---|---|---|
| Aphids | Distorted leaves | Introduce ladybugs |
| Spider Mites | Webbing on foliage | Use miticides |
| Pythium | Root rot | Maintain proper oxygen levels |
| Fusarium | Wilted plants | Apply fungicides |
| Thrips | Silvery streaks | Use sticky traps |
Precision in these practices guarantees minimal disruptions to chilli growth in hydroponic systems.
Harvesting and Yield
Optimizing the timing and methods of harvesting is critical to maximizing yield and ensuring the quality of hydroponically grown chillies. To achieve ideal results, consider the following steps:
- Maturity Assessment: Monitor fruit ripeness by evaluating color change and firmness. Harvest when chillies reach their full color and size for peak flavor and nutrient content.
- Harvesting Techniques: Use sterilized, sharp tools to cut the chillies, minimizing plant stress and potential pathogen entry. Avoid pulling to prevent plant damage.
- Post-Harvest Handling: Immediately store in cool, dry conditions to prolong shelf-life and preserve quality. Rapid cooling inhibits decay and maintains texture.
Implementing these strategies will enhance both yield and quality, propelling hydroponic chilli cultivation towards innovative agricultural practices.
Conclusion
Hydroponically grown chillies, flourishing in nutrient-rich aqueous environments, exhibit robust growth and enhanced yields.
The precise control over nutrient delivery and environmental conditions mimics a horticultural symphony, orchestrating ideal plant health.
Despite challenges such as pest management and system maintenance, the sustainable and efficient nature of hydroponics presents a promising avenue for chilli cultivation.
This innovative approach, anchored in scientific principles, underscores the potential for high-quality, bountiful harvests in controlled agricultural settings.