How to Use Sponges as a Growing Medium in Hydroponics
Yes, you can use sponges for hydroponics as they offer enhanced water retention, ideal aeration, and efficient nutrient delivery. The sponge's capillary action maintains a balanced nutrient solution, benefiting plant development.
However, it is crucial to evaluate potential drawbacks such as limited root support, contamination risks, and less structural integrity compared to rigid media like rockwool. Selecting the right type of sponge, such as polyurethane foam or cellulose sponge, and ensuring proper preparation and maintenance can mitigate these concerns and optimize growth.
For an in-depth understanding of maximizing sponge use in hydroponics, certain steps and evaluations must be explored.

Key Takeaways
- Sponges provide excellent water retention and aeration, ideal for hydroponic systems.
- Porous nature of sponges ensures efficient nutrient delivery and capillary action.
- Various sponge materials like polyurethane foam and cellulose sponge offer different benefits for plant growth.
- Proper preparation, such as sterilization and soaking in nutrient solutions, is crucial for effective use.
Benefits of Using Sponges
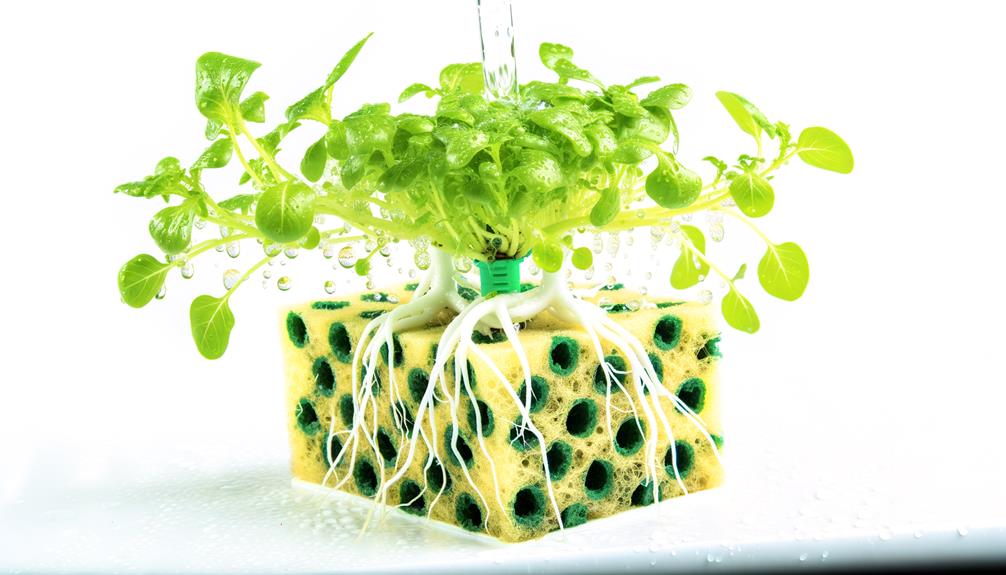

Utilizing sponges in hydroponic systems offers several benefits, including enhanced water retention, ideal aeration, and efficient nutrient delivery to plant roots.
Sponges possess a porous structure that maximizes moisture retention, ensuring a consistent water supply to the root zone. This characteristic minimizes water stress and promotes robust plant growth.
Additionally, the aeration properties of sponges facilitate oxygen exchange, critical for root respiration and overall plant health.
Efficient nutrient delivery is achieved through the sponge's ability to evenly distribute dissolved minerals, ensuring uniform nutrient availability. The capillary action within sponges aids in maintaining a balanced nutrient solution, preventing deficiencies.
Consequently, sponges serve as an effective medium in hydroponic systems, fostering a superior environment for plant development.
Drawbacks to Consider
While sponges offer several advantages for hydroponic systems, there are notable drawbacks that warrant consideration.
Limited root support can impede ideal plant growth, as sponges may not provide sufficient structural stability for root development.
Additionally, the porous nature of sponges can lead to potential contamination issues, fostering environments conducive to pathogen proliferation.
Limited Root Support
One significant drawback of using sponges in hydroponic systems is their limited ability to provide adequate root support for developing plants.
Unlike more rigid media such as rockwool or clay pellets, sponges lack the structural integrity needed to anchor root systems effectively. This can result in plants becoming unstable, particularly as they grow larger and heavier.
In addition, the porous nature of sponges does not facilitate the robust root development necessary for ideal nutrient uptake. The restricted mechanical support can lead to root damage and hinder overall plant health.
Additionally, insufficient root anchorage may cause plants to tilt or collapse, adversely affecting growth and yield. Consequently, sponges may not be the most suitable medium for hydroponic applications requiring substantial root support.
Potential Contamination Issues
In addition to their limited root support, sponges in hydroponic systems pose significant risks of contamination due to their highly porous structure, which can harbor pathogens and promote microbial growth.
This porosity facilitates the retention of moisture, creating an ideal environment for the proliferation of bacteria, fungi, and algae. Pathogenic microorganisms such as Pythium, commonly known as root rot, can thrive in these conditions, jeopardizing plant health and yield.
Additionally, sponges are difficult to sanitize effectively without damaging their structure, leading to persistent contamination issues. The potential for biofilm development on sponge surfaces exacerbates these challenges, complicating the maintenance of a sterile growing environment.
Consequently, the use of sponges necessitates rigorous monitoring and sanitation protocols to mitigate such risks.
How Sponges Work
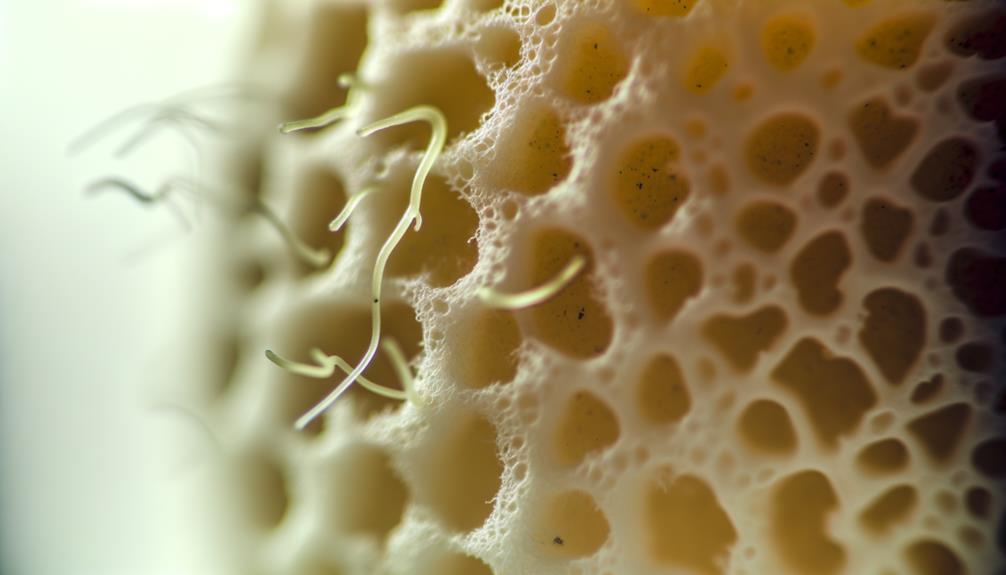
Sponges function through a combination of capillary action and porosity, allowing them to efficiently retain and release water and nutrients in a hydroponic system. Capillary action enables the sponge to draw water upwards against gravity, while porosity determines the volume of water the sponge can hold. The interaction between these properties is essential for maintaining ideal moisture levels and nutrient availability for plant roots. Below is a table summarizing these key characteristics:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Capillary Action | Ability to draw water upwards through narrow spaces |
| Porosity | Measure of the sponge's void spaces |
| Water Retention | Capacity to hold water for extended periods |
| Nutrient Release | Gradual release of absorbed nutrients |
Understanding these properties helps in enhancing hydroponic system performance.
Choosing the Right Sponge
Selecting the appropriate sponge for hydroponics necessitates a thorough evaluation of sponge material types, which directly impact water retention capability and root support strength.
The material composition of the sponge determines its porosity and ability to maintain ideal moisture levels for plant growth.
Additionally, the structural integrity of the sponge is vital for providing adequate support to developing root systems, ensuring stability and nutrient absorption.
Sponge Material Types
Choosing the ideal sponge material for hydroponic systems necessitates a thorough understanding of the various types available, including their hydrophilic properties, durability, and impact on plant health. The selection process is critical, as different sponge materials offer distinct advantages and potential drawbacks.
| Material | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Polyurethane Foam | High durability, good air porosity |
| Melamine Foam | Excellent water absorption, eco-friendly |
| Cellulose Sponge | Biodegradable, high water retention |
| Polyester Sponge | Long-lasting, minimal water retention |
| Natural Sponge | High porosity, organic, potential for contaminants |
Each material should be assessed for its compatibility with plant root systems, potential for mold growth, and ease of cleaning. Professional growers must weigh these factors meticulously to optimize plant growth and system efficiency.
Water Retention Capability
Understanding the water retention capability of sponge materials is paramount for maximizing hydroponic nutrient delivery and root hydration. Effective water retention guarantees consistent moisture levels, facilitating ideal nutrient uptake and promoting vigorous plant growth. Selecting the appropriate sponge involves evaluating its porosity, absorption rate, and retention capacity.
Consider the following critical factors:
- Porosity: A sponge with high porosity offers enhanced water retention and air circulation, preventing root rot and promoting healthy growth.
- Absorption Rate: Rapid absorption rates guarantee that the sponge quickly saturates, providing immediate water availability to roots.
- Retention Capacity: Sponges with superior retention capacities maintain moisture over extended periods, reducing the frequency of watering cycles and minimizing stress on plants.
Choosing the right sponge is essential for achieving sustainable hydroponic systems.
Root Support Strength
How does the structural integrity of a hydroponic sponge influence root support strength and overall plant stability?
The mechanical properties of the sponge, including tensile strength and compressive resilience, are vital for maintaining root anchorage. A sponge with ideal porosity and density guarantees that roots can penetrate and establish a network without collapsing the medium.
This structural consistency offers a stable foundation, preventing root displacement during nutrient solution circulation. Additionally, the sponge's durability against degradation assures longevity, reducing the need for frequent replacements.
Selecting a sponge that balances flexibility with robustness is important for promoting healthy root development and sustaining plant stability, especially in dynamic hydroponic systems where mechanical stress and nutrient flow are constant factors.
Setting up With Sponges
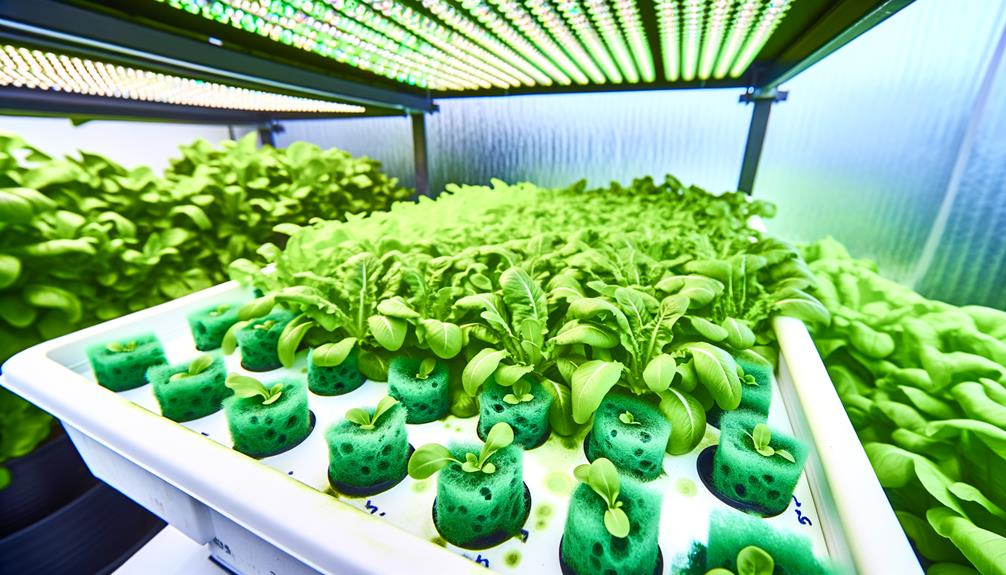

To set up a hydroponic system using sponges, begin by selecting high-density, non-toxic sponges specifically designed for horticultural use. These sponges offer ideal water retention and aeration properties, essential for root development.
- Sterilization: Verify sponges are sterilized to eliminate any pathogens that could harm plant health.
- Cutting and Placement: Precisely cut the sponges into suitable sizes, verifying they fit snugly into your hydroponic containers.
- Nutrient Solution: Soak the sponges in a balanced nutrient solution, allowing them to absorb essential minerals before planting seeds or transplanting seedlings.
This method facilitates a controlled environment, enhancing root oxygenation and nutrient uptake, essential for vigorous plant growth and high yield in hydroponic systems. Additionally, maintaining optimal water circulation and pH levels ensures that plants receive consistent nourishment, preventing nutrient deficiencies. By carefully managing these factors, growers can focus on maximizing growth with NPK, which provides the essential macronutrients needed for robust development. This approach not only improves plant health but also increases overall efficiency in hydroponic cultivation.
Tips for Success
Guaranteeing ideal results in hydroponic systems utilizing sponges necessitates meticulous attention to several vital factors, including nutrient concentration, pH balance, and environmental conditions. Proper nutrient management is essential; hydroponic nutrient solutions should be precisely formulated to secure optimal plant growth. Regular monitoring and adjustment of pH levels, maintaining between 5.5 and 6.5, is critical to prevent nutrient lockout.
| Vital Factor | Ideal Range/Condition |
|---|---|
| Nutrient Concentration | EC: 1.0-2.5 mS/cm |
| pH Balance | pH: 5.5-6.5 |
| Environmental Conditions | Temp: 18-24°C, Humidity: 50-70% |
Additionally, maintaining appropriate environmental conditions, including temperature and humidity, supports vigorous plant development. Consistent observation and adjustment of these parameters guarantee a thriving hydroponic system using sponges.
Conclusion
Coincidentally, the utilization of sponges in hydroponics aligns with advancements in sustainable agricultural practices.
Despite certain drawbacks such as potential contamination and varying moisture retention, the benefits, including cost-effectiveness and ease of setup, are significant.
Understanding the properties and selecting the appropriate sponge type are essential for ideal plant growth.
By implementing precise methodologies and adhering to best practices, hydroponic systems using sponges can achieve remarkable efficiency and productivity, contributing to the future of innovative farming.






