How Soybeans Are Grown Hydroponically – A Step-by-Step Guide
Yes, soybeans can be grown hydroponically, offering advantages such as reduced soil-borne diseases and efficient water usage—up to 90% less than traditional farming. Ideal growth conditions include 14-16 hours of LED light daily, daytime temperatures of 25-30°C, and balanced nutrient solutions with a pH of 5.8-6.5.
Various hydroponic systems, including Nutrient Film Technique (NFT) and Deep Water Culture (DWC), support effective growth by delivering consistent nutrients and oxygen. While challenges like nutrient imbalances and pH fluctuations exist, advanced techniques and continuous monitoring can address these issues.
Explore further to uncover more specific methodologies and case studies.

Key Takeaways
- Soybeans can be grown hydroponically using nutrient-rich water solutions without soil.
- Hydroponic methods provide precise control over nutrients, pH, and environmental conditions for soybeans.
- LED grow lights supply the required 14-16 hours of light for optimal soybean growth.
- Hydroponic systems like NFT and DWC ensure continuous nutrient and oxygen availability for soybeans.
Understanding Hydroponics
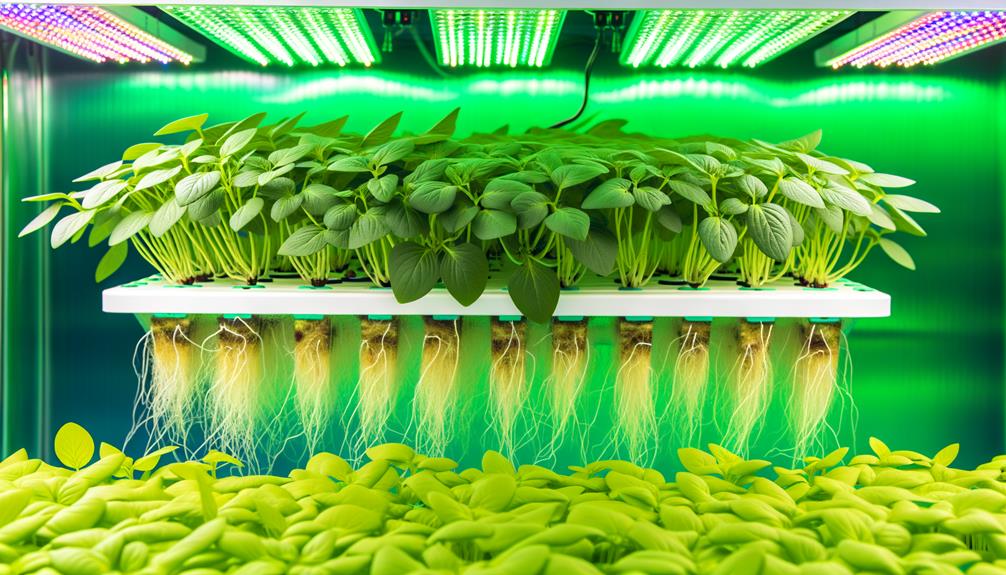

Understanding hydroponics involves examining the soilless cultivation of plants in nutrient-rich water solutions. This method leverages the direct delivery of nutrients to plant roots, bypassing the need for soil, and thereby reducing issues related to soil-borne diseases and pests.
Hydroponic systems can be highly efficient, using up to 90% less water than traditional farming. They offer precise control over nutrient composition, pH levels, and environmental conditions, fostering ideal plant growth and higher yields.
Technological advancements have further enhanced hydroponic systems, integrating automation and monitoring tools for real-time adjustments. This innovative approach is particularly appealing for urban agriculture and regions with poor soil quality, presenting a sustainable alternative to conventional agricultural practices.
Soybean Plant Requirements
Soybean plants require specific environmental conditions, including adequate light, temperature, and nutrient levels, to achieve ideal growth and productivity.
Ideal light intensity ranges between 14-16 hours per day, facilitated by LED grow lights for controlled environments.
Temperature control is vital, with ideal daytime temperatures between 25-30°C and nighttime temperatures around 20-25°C.
Nutrient solutions must contain balanced macro and micronutrients, particularly nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, to support various growth stages.
pH levels should be maintained between 5.8-6.5 to guarantee nutrient availability and root health.
Proper air circulation and humidity control, maintaining relative humidity between 60-70%, are essential to prevent fungal diseases and support transpiration.
These parameters collectively create a conducive environment for soybean cultivation.
Benefits of Hydroponic Soybeans

Hydroponic cultivation of soybeans offers numerous advantages, including increased yield potential, reduced water usage, and enhanced control over growing conditions. This innovative method can greatly improve agricultural efficiency.
The benefits include:
- Higher Yields: Hydroponic systems can produce up to 30% more yield compared to traditional soil-based agriculture, owing to optimized nutrient delivery.
- Water Efficiency: Hydroponics uses up to 90% less water than conventional farming, making it an environmentally sustainable option.
- Controlled Environment: Growers can precisely regulate factors such as pH, nutrient concentration, and light exposure, leading to healthier and more robust plants.
- Reduced Pesticide Use: The absence of soil reduces pest-related issues, minimizing the need for chemical pesticides and thereby promoting cleaner produce.
This method embodies a forward-thinking approach to modern agriculture.
Nutrient Solutions for Soybeans
Selecting the ideal nutrient solution is essential for maximizing the growth and productivity of hydroponically grown soybeans.
A balanced nutrient mix should include macronutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, as well as essential micronutrients like iron, manganese, and zinc.
The nutrient concentration must be meticulously calibrated, considering soybeans' specific growth stages, to avoid deficiencies or toxicities.
pH levels should be maintained between 5.8 and 6.5 to enhance nutrient uptake.
Continuous monitoring and periodic adjustments are paramount to sustain optimal conditions.
Employing advanced techniques such as automated nutrient delivery systems can enhance precision and efficiency.
Hydroponic Systems for Soybeans
When considering hydroponic systems for soybeans, two vital aspects warrant attention: nutrient delivery methods and growth medium options.
Efficient nutrient delivery systems, such as drip irrigation or nutrient film technique (NFT), guarantee ideal nutrient uptake and promote healthy plant development.
Concurrently, selecting an appropriate growth medium, whether it be rock wool, perlite, or coco coir, is essential for providing adequate support and aeration to the soybean roots.
Nutrient Delivery Methods
Effective nutrient delivery is essential in hydroponic systems to optimize the growth and yield of soybeans. Various methods guarantee precise nutrient administration, enhancing plant health and productivity.
The following are key nutrient delivery methods in hydroponic systems:
- Nutrient Film Technique (NFT): A thin film of nutrient solution flows over the roots, providing consistent nutrients and oxygen.
- Deep Water Culture (DWC): Roots are submerged in a nutrient-rich solution, promoting rapid growth through constant nutrient availability.
- Aeroponics: Nutrients are delivered as a mist to the roots, maximizing oxygenation and absorption efficiency.
- Ebb and Flow (Flood and Drain): Nutrient solution periodically floods the root zone, then drains away, simulating natural wet-dry cycles.
These methods offer innovative solutions to enhance soybean cultivation in hydroponic systems.
Growth Medium Options
Choosing the appropriate growth medium is vital for maximizing the root support and nutrient uptake in hydroponic systems for soybeans.
Various growth mediums such as rockwool, perlite, and coconut coir offer unique benefits and challenges.
Rockwool provides excellent water retention and aeration, essential for robust root development.
Perlite, known for its lightweight and sterile properties, guarantees optimal drainage and prevents root rot.
Coconut coir, an eco-friendly alternative, enhances moisture retention while maintaining necessary air pockets.
The choice of medium will directly impact root health, nutrient accessibility, and overall plant vigor.
As a result, selecting a medium that aligns with specific hydroponic system requirements and environmental conditions is vital for successful soybean cultivation.
Lighting and Temperature Control
Effective lighting and temperature regulation are critical for optimizing soybean growth in hydroponic systems.
Ensuring the correct light spectrum and temperature range can greatly influence photosynthesis and plant development.
Additionally, adjusting light exposure according to seasonal variations can further enhance growth efficiency.
Optimal Light Spectrum
Consistently maintaining an ideal light spectrum is vital for maximizing the growth and yield of hydroponically grown soybeans.
Tailoring the light spectrum to the specific needs of soybean plants can greatly enhance photosynthesis and nutrient absorption.
Key considerations include:
- Blue Light (400-500 nm): Promotes vegetative growth and robust root development.
- Red Light (600-700 nm): Facilitates flowering and fruiting, essential for pod production.
- Far-Red Light (700-800 nm): Influences seed germination and elongation, optimizing plant height.
- Green Light (500-600 nm): Enhances canopy penetration, ensuring lower leaves receive sufficient light.
Temperature Range Requirements
Maintaining an ideal temperature range is equally important as light spectrum management for the successful cultivation of hydroponic soybeans.
Ideal temperature conditions for hydroponic soybean growth typically range between 70-80°F (21-27°C) during the day and 60-70°F (16-21°C) at night.
Temperature control is vital, as deviations can lead to impaired growth, reduced yields, or increased susceptibility to diseases.
Advanced systems often integrate automated climate control technologies to maintain these parameters consistently.
Utilizing sensors and climate control software guarantees precision in temperature regulation, fostering an environment conducive to robust soybean development.
Seasonal Light Adjustments
Adjusting light and temperature settings in hydroponic systems is essential to accommodate seasonal variations and secure consistent soybean growth. Effective management of these parameters guarantees that soybeans receive ideal conditions throughout their growth cycle.
Key considerations include:
- Photoperiod Adjustments: Varying light durations to mimic natural daylight changes, essential for regulating soybean flowering and vegetative growth phases.
- Light Intensity Control: Utilizing adjustable LED systems to provide adequate light intensity, maximizing photosynthesis without causing plant stress.
- Temperature Regulation: Employing climate control systems to maintain perfect temperature ranges of 70-85°F during daytime and 60-70°F at night.
- Humidity Management: Securing relative humidity levels between 60-70% to prevent fungal diseases and enhance nutrient uptake.
These adjustments foster a controlled environment conducive to robust soybean production.
Common Challenges and Solutions

One of the primary challenges in hydroponic soybean cultivation is managing nutrient imbalances which can profoundly impact plant health and yield. Nutrient solutions must be meticulously monitored and adjusted to guarantee ideal growth conditions. Additionally, root diseases can proliferate in hydroponic systems if not properly controlled, and maintaining adequate oxygen levels in the root zone is vital.
| Challenge | Solution |
|---|---|
| Nutrient Imbalances | Regular monitoring and tailored adjustments |
| Root Diseases | Implementing sterilization protocols |
| Oxygen Deficiency | Aeration systems to maintain root health |
| pH Fluctuations | Consistent pH monitoring and adjustments |
| Water Temperature | Using chillers/heaters to stabilize temperature |
Implementing these solutions can greatly enhance the productivity and sustainability of hydroponic soybean systems, fostering innovation in agricultural practices.
Case Studies of Success
Case studies of successful hydroponic soybean cultivation highlight innovative growing techniques that have led to significant improvements in yield and quality.
These examples also provide valuable insights into the commercial viability of hydroponic systems for soybean production.
Innovative Growing Techniques
Several pioneering agricultural enterprises have demonstrated the efficacy of hydroponic systems for soybean cultivation through meticulously documented case studies. These success stories highlight innovative techniques that optimize growth conditions and resource efficiency.
Key methods include:
- Nutrient Film Technique (NFT): This involves a thin film of nutrient solution flowing over the plant roots, ensuring constant nutrient availability and oxygenation.
- Aeroponics: Plants are suspended in air while roots are misted with nutrient solutions, promoting rapid growth and efficient nutrient uptake.
- Deep Water Culture (DWC): Roots are submerged in a nutrient-rich solution, enhancing water and nutrient absorption.
- Vertical Farming: Space-efficient vertical stacks allow for higher crop density, maximizing yield per square foot.
These techniques collectively underscore hydroponics' potential for sustainable soybean production.
Yield and Quality Improvements
Building on the innovative growing techniques, documented case studies reveal significant yield and quality improvements in hydroponically grown soybeans.
For instance, a study conducted at the University of Arizona demonstrated a 30% increase in soybean yield compared to traditional soil cultivation. Additionally, the controlled environment of hydroponics led to a notable enhancement in protein content and uniformity of seed size.
Another case in Japan showcased a 25% reduction in crop cycle time, attributed to optimized nutrient delivery and environmental control.
These advancements not only highlight the potential for higher productivity but also underscore the capacity for producing superior quality soybeans.
Such empirical evidence underscores the transformative potential of hydroponics in enhancing soybean cultivation outcomes.
Commercial Viability Insights
Real-world examples of commercial hydroponic soybean operations provide compelling evidence of the method's economic and practical feasibility. Key case studies highlight the following:
- Urban Farms: Several urban farms have successfully integrated hydroponic systems to grow soybeans, achieving consistent yields and addressing local food demands.
- Technology Firms: Companies specializing in agricultural technology have developed sophisticated hydroponic systems, showcasing efficiency and scalability.
- Sustainability Projects: Environmental initiatives have adopted hydroponic soybean farming to reduce water usage and minimize land degradation.
- Academic Research: Universities have conducted extensive research, demonstrating the profitability and sustainability of hydroponic soybeans under controlled conditions.
These instances underscore the innovative potential and commercial viability of hydroponic soybeans, providing a roadmap for future agricultural advancements.
Economic Considerations

How do the economic implications of hydroponic soybean cultivation compare to traditional farming methods? Analyzing costs, yields, and market prices reveals key differences. Initial setup costs for hydroponics are higher due to specialized equipment and infrastructure. However, hydroponics offers higher yield per square meter, reduced water usage, and minimized pesticide requirements, potentially offsetting initial investments over time.
| Factor | Traditional Farming | Hydroponic Farming |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Setup Costs | Low | High |
| Yield per m² | Moderate | High |
| Water Consumption | High | Low |
| Pesticide Usage | High | Low |
| Long-term Viability | Moderate | High |
This comparative analysis underscores the need for careful consideration of long-term benefits versus upfront costs in adopting hydroponic systems for soybean cultivation.
Future Prospects and Innovations
Frequently, advancements in biotechnology and automation are poised to revolutionize hydroponic soybean cultivation, driving increased efficiency and sustainability. These innovations promise to address current limitations and reveal new potential for the industry.
Key areas of focus include:
- Genetic Engineering: Enhancing soybean varieties for better hydroponic compatibility and increased yield.
- Automated Systems: Implementing robotics and AI for precise nutrient delivery and environmental control.
- Resource Optimization: Developing closed-loop systems to minimize water and nutrient waste.
- Data Analytics: Utilizing big data to optimize growth conditions and predict potential issues.
These advancements not only aim to boost productivity but also to guarantee that hydroponic soybean farming becomes a viable, eco-friendly alternative to traditional agricultural practices.
Conclusion
The cultivation of soybeans through hydroponic methods symbolizes the convergence of tradition and innovation in agriculture.
This technique not only meets the specific requirements of soybean plants but also offers numerous benefits, including optimized nutrient delivery and space efficiency.
While challenges exist, successful case studies illuminate the path forward.
Economic viability and future advancements hold promise for expanding hydroponic soybean farming, representing seeds of potential growth in sustainable agriculture.






