How You Can Grow Flowers Hydroponically – A Step-by-Step Guide
Yes, you can grow flowers hydroponically by cultivating them in a soilless medium using a nutrient-rich water solution. This method provides essential macro and micronutrients directly to the plant roots, enhancing nutrient absorption rates and growth.
Hydroponic systems, such as Nutrient Film Technique (NFT), Ebb and Flow, and aeroponics, allow precise control over environmental factors like light, temperature, and humidity. Flowers such as roses, orchids, and tulips thrive well under these conditions, producing vibrant blooms with reduced susceptibility to pests and diseases.
By adopting hydroponic techniques, you can achieve accelerated growth rates and superior bloom quality. Discover more about selecting the right system and maintaining ideal growth conditions.

Key Takeaways
- Growing flowers hydroponically accelerates growth rates through direct nutrient delivery without soil.
- Hydroponic systems allow precise control over environmental factors, enhancing bloom quality.
- Popular hydroponic flowers include roses, orchids, tulips, and chrysanthemums.
- Regular maintenance of pH levels and nutrient solutions is crucial for optimal flower growth.
Understanding Hydroponics

Hydroponics, the method of growing plants without soil by using mineral nutrient solutions in an aqueous solvent, offers a scientifically advanced approach to horticulture that maximizes efficiency and control over plant growth conditions.
This technique involves the dissolution of essential macro and micronutrients in water, facilitating direct uptake by plant roots. Research indicates that hydroponic systems enhance nutrient absorption rates and improve growth parameters such as pH levels, electrical conductivity, and dissolved oxygen.
By eliminating soil, hydroponics mitigates soil-borne diseases and pests, leading to healthier plant development. Furthermore, this method allows precise manipulation of environmental factors like light, temperature, and humidity, thereby fostering ideal photosynthetic activity and growth rates.
Consequently, hydroponics represents a transformative innovation in modern agricultural practices.
Benefits of Hydroponic Flowers
Leveraging the advantages of hydroponics, cultivating flowers through this method offers numerous benefits, including accelerated growth rates, enhanced bloom quality, and reduced susceptibility to pests and diseases.
Research demonstrates that hydroponic systems provide ideal nutrient delivery directly to the roots, bypassing soil-related constraints and facilitating quicker nutrient uptake.
Controlled environments in hydroponic setups allow for precise regulation of light, temperature, and humidity, fostering superior floral development.
Additionally, the absence of soil mitigates the risk of soil-borne pathogens and pests, considerably reducing the need for chemical interventions.
This method also promotes resource efficiency by utilizing water more effectively, leading to sustainable and eco-friendly growing practices.
Consequently, hydroponic flower cultivation aligns with innovative agricultural trends and environmental stewardship.
Essential Equipment

Understanding the essential equipment for hydroponic flower cultivation is critical for optimizing growth and ensuring plant health.
Key components include hydroponic growth mediums, which provide structural support and water retention, and nutrient delivery systems, designed to supply a balanced mix of essential minerals directly to the root zone.
These elements are fundamental in creating a controlled environment that maximizes efficiency and yield.
Hydroponic Growth Mediums
A critical component of a successful hydroponic system is the selection of an appropriate growth medium, which serves as the structural basis for root support and nutrient delivery. Various growth mediums offer distinct advantages based on their physical properties, water retention capacity, and aeration potential.
Research highlights the following popular choices:
- Rockwool: Known for excellent water retention and aeration, ideal for seedlings and mature plants.
- Clay Pellets: Provide optimal drainage and are reusable, making them cost-effective.
- Coco Coir: Derived from coconut husks, this medium offers sustainable, high water-holding capacity.
- Perlite: Lightweight and highly porous, it enhances drainage and aeration, preventing root rot.
Selecting the right medium is pivotal for maximizing plant health and maximizing hydroponic system efficiency.
Nutrient Delivery Systems
While the selection of an appropriate growth medium is foundational, the efficacy of a hydroponic system also heavily relies on the precision and efficiency of its nutrient delivery systems.
These systems must guarantee the ideal concentration of macronutrients, micronutrients, and pH levels to sustain robust floral growth. Essential equipment includes nutrient reservoirs, air pumps, and precise dosing systems.
Research indicates that automated delivery systems, such as drip irrigation and nutrient film techniques (NFT), provide superior control over nutrient distribution. Advanced technologies like electrical conductivity (EC) and pH sensors further enhance nutrient management by providing real-time data, enabling dynamic adjustments.
Such innovations are critical in minimizing nutrient waste and maximizing the growth potential of hydroponically cultivated flowers.
Best Flowers for Hydroponics
Selecting the ideal flowers for hydroponic cultivation requires consideration of specific botanical characteristics and environmental adaptability.
Common hydroponic flowers such as orchids, roses, and gerberas thrive under controlled conditions that replicate their native growth habitats.
Understanding the nuances of flower growth conditions and tailoring hydroponic system types to meet these needs is essential for maximizing floral yield and quality.
Popular Hydroponic Flowers
Hydroponic cultivation frequently excels with certain flower species due to their adaptability to soilless environments and efficient nutrient uptake. Research indicates several flowers exhibit peak growth under hydroponic conditions. These species demonstrate resilience and enhanced blossoming, making them ideal for hydroponic systems.
- Roses: Known for their high market value, roses thrive hydroponically with precise nutrient management.
- Orchids: Their epiphytic nature makes them particularly suitable for hydroponic environments, where root aeration is critical.
- Tulips: Efficient nutrient absorption and rapid growth cycles render tulips a popular hydroponic choice.
- Chrysanthemums: These flowers benefit from controlled environments, resulting in vibrant blooms and extended flowering periods.
These flowers exemplify the intersection of botanical science and innovative agricultural techniques.
Flower Growth Conditions
Understanding the ideal growth conditions for hydroponic flowers involves a detailed analysis of factors such as nutrient formulation, light intensity, pH levels, and temperature regulation.
Optimal nutrient solutions should contain a balanced mix of macro and micronutrients tailored to each flower species.
Light intensity and photoperiod play essential roles; for instance, orchids thrive under moderate light, while roses require higher intensity.
Maintaining a pH range between 5.5 and 6.5 is critical to guarantee nutrient availability.
Temperature regulation is equally important; most hydroponic flowers flourish within a range of 18-24°C.
Research indicates that marigolds, petunias, and geraniums exhibit robust growth under these controlled conditions, making them excellent candidates for hydroponic cultivation.
Hydroponic System Types
Exploring various hydroponic system types reveals distinct advantages for cultivating specific flower species, each benefiting from tailored environmental conditions and nutrient delivery methods.
Research indicates the following systems are ideal for various flowers:
- NFT (Nutrient Film Technique): Ideal for lightweight flowers like petunias, as it provides a constant, thin film of nutrients.
- Ebb and Flow (Flood and Drain): Suitable for heavier flowers such as chrysanthemums, offering periodic nutrient-rich flooding.
- Drip System: Excellent for roses, allowing precise nutrient and water control through emitters.
- Aeroponics: Beneficial for orchids, utilizing misting to deliver nutrients directly to roots, promoting rapid growth.
These systems, each with unique mechanisms, enhance flower cultivation by improving growth conditions and ensuring efficient nutrient uptake.
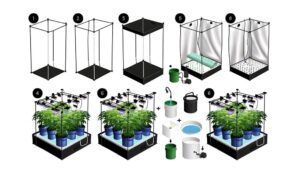
Setting Up Your System

To initiate the process of setting up your hydroponic system, it is vital to select the appropriate type of system based on the specific requirements of the flower species you wish to cultivate.
Diverse hydroponic systems, such as nutrient film technique (NFT), deep water culture (DWC), and aeroponics, offer unique benefits suited to different floral species.
Precise control over environmental variables—such as light, temperature, and humidity—is paramount.
Utilize high-efficiency LED grow lights to simulate natural light cycles.
Employ water pumps and air stones to guarantee adequate oxygenation and nutrient distribution.
Implement pH and electrical conductivity (EC) meters for monitoring water quality.
These elements collectively create an optimized environment, facilitating robust floral growth and maximizing phenotypic expression.
Nutrient Solutions Explained
Properly managing nutrient solutions is fundamental to guaranteeing the ideal growth and health of flowers in hydroponic systems.
Nutrient solutions provide essential macro and micronutrients to plants, facilitating peak physiological functions. These solutions typically consist of water-soluble fertilizers that deliver balanced proportions of nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K), alongside trace elements such as calcium, magnesium, and iron.
To formulate an effective nutrient solution, consider:
- Concentration: Maintain precise nutrient concentrations to prevent deficiencies or toxicities.
- pH Level: Adjust pH to the optimal range (usually 5.5-6.5) for nutrient uptake.
- Electrical Conductivity (EC): Monitor EC to guarantee the solution's salinity is within acceptable limits.
- Oxygenation: Aerate the solution to enhance root respiration and nutrient absorption.
These factors collectively support robust floral development in hydroponic environments.
Maintenance Tips

Regularly maintaining hydroponic systems guarantees ideal conditions for flower growth and prevents potential issues related to nutrient imbalances, pH fluctuations, and pathogen proliferation. To achieve this, it is vital to monitor and adjust pH levels, confirm nutrient solutions are replenished and balanced, and sanitize the system to prevent pathogen buildup.
| Maintenance Task | Frequency |
|---|---|
| pH Level Check | Daily |
| Nutrient Solution Refresh | Weekly |
| System Sanitization | Bi-weekly |
Consistent monitoring and adjustment of pH levels are essential, as deviations can affect nutrient uptake. Weekly replenishment of nutrient solutions confirms a continuous supply of essential minerals. Bi-weekly system sanitization mitigates the risk of microbial contamination, fostering a healthy root environment. Adhering to these practices promotes optimal growth and flowering.
Common Challenges
Hydroponic flower cultivation often encounters challenges such as nutrient deficiencies, pH imbalances, and pathogen invasions, each of which can considerably hinder plant health and development. Addressing these issues requires a nuanced understanding of plant physiology and hydroponic systems.
- Nutrient Deficiencies: Miscalculations in nutrient solutions can lead to inadequate essential minerals, causing stunted growth and poor flowering.
- pH Imbalances: The ideal pH range for most flowers is between 5.5 and 6.5. Deviations can impair nutrient uptake, leading to deficiencies even if nutrients are present.
- Pathogen Invasions: Hydroponic systems are susceptible to fungal and bacterial infections, exacerbated by high humidity and stagnant water.
- Environmental Control: Inconsistent temperature and light can disrupt photosynthesis and metabolic processes, affecting overall plant vigor.
Understanding and mitigating these challenges is essential for successful hydroponic flower cultivation. This involves carefully monitoring nutrient levels, maintaining optimal water quality, and ensuring proper lighting conditions for healthy plant growth. Growers who want to learn how to grow roses hydroponically must focus on providing a balanced nutrient solution and a well-aerated root environment to maximize bloom production. By implementing these strategies, cultivators can overcome common obstacles and achieve vibrant, high-yield flower harvests.
Conclusion
Hydroponic flower cultivation offers numerous advantages, including efficient resource use and faster growth rates, akin to a well-tuned machine operating at peak performance.
Essential equipment and nutrient solutions are critical for success, while selecting suitable flower species enhances outcomes.
Regular maintenance and addressing common challenges are imperative for sustained productivity.
Overall, hydroponics represents a scientifically validated method for optimizing floral growth, thereby promising significant advancements in horticultural practices.