How You Can Grow Fruit Trees Hydroponically – A Step-by-Step Guide
Growing fruit trees hydroponically is indeed feasible and beneficial. This method allows for precise control over pH levels, nutrient concentrations, and oxygen availability, considerably enhancing growth and fruit yields while utilizing up to 90% less water than traditional soil-based methods.
Dwarf varieties and tropical fruits, such as bananas and papayas, thrive in this setup due to optimized conditions in inert mediums like perlite or vermiculite. Advanced techniques in nutrient management, environmental control, and pollination collectively guarantee healthy development and high productivity.
By mastering these technical aspects, one can achieve exceptional results in hydroponic fruit tree cultivation.

Key Takeaways
- Yes, fruit trees can be grown hydroponically using advanced systems like NFT, DWC, and aeroponics.
- Dwarf varieties and tropical fruits are particularly well-suited for hydroponic cultivation.
- Controlled environments optimize water, nutrient uptake, and environmental conditions for robust growth.
- Hydroponic systems offer higher yields and water efficiency compared to traditional soil methods.
What Is Hydroponics?

Hydroponics is a sophisticated method of cultivating plants in a nutrient-rich, water-based solution, bypassing the need for traditional soil mediums.
This innovative system leverages precise control over environmental variables such as pH balance, nutrient concentration, and oxygenation levels, ensuring ideal plant growth and yield.
Utilizing inert mediums like perlite, vermiculite, or rock wool, hydroponics provides structural support while promoting efficient nutrient uptake.
Advanced hydroponic setups often incorporate automated systems for monitoring and adjusting nutrient delivery, enhancing consistency and reducing human error.
This soil-less cultivation technique is particularly advantageous in controlled environments, enabling year-round production and minimizing the risk of soil-borne diseases.
The integration of hydroponics into agricultural practices exemplifies a significant leap towards sustainable and efficient crop production.
Advantages of Hydroponics
The strategic control over environmental variables inherent to hydroponic systems confers numerous advantages, including optimized nutrient absorption, accelerated plant growth, and higher yields compared to traditional soil-based agriculture.
This precision in nutrient delivery and environmental management results in a more efficient and sustainable cultivation process.
Key benefits include:
- Water Efficiency: Hydroponic systems use up to 90% less water than traditional farming, a critical advantage in areas facing water scarcity.
- Space Utilization: Vertical farming techniques maximize space, allowing for higher density planting and consequently more productive use of limited land.
These factors collectively revolutionize agricultural practices, promising considerable improvements in productivity and sustainability.
Types of Hydroponic Systems
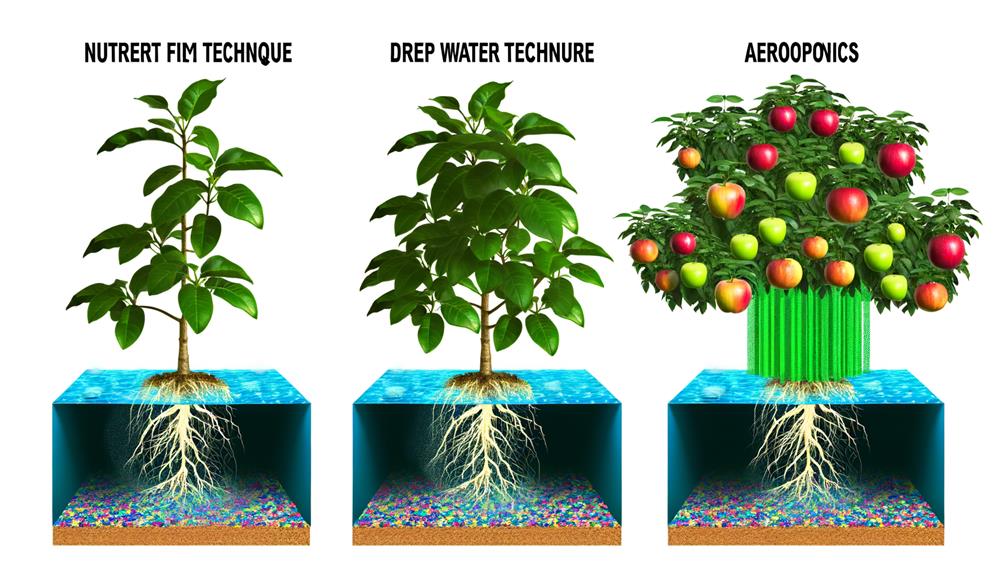
Exploring the diverse array of hydroponic systems reveals various methodologies, each optimized for specific types of crops and cultivation conditions. Key systems include Nutrient Film Technique (NFT), Deep Water Culture (DWC), and Aeroponics, each offering unique advantages for hydroponic fruit tree cultivation. NFT utilizes a continuous flow of nutrient solution over roots, promoting rapid growth. DWC immerses roots in oxygenated water, providing consistent nutrient uptake. Aeroponics, meanwhile, suspends roots in air, delivering nutrients via mist, which enhances oxygen absorption.
| System Type | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| NFT | Continuous nutrient flow over roots |
| DWC | Roots submerged in oxygenated nutrient solution |
| Aeroponics | Roots suspended in air, nutrients via mist |
These systems present innovative solutions for maximizing yield and efficiency, essential for successful hydroponic fruit tree production.
Suitable Fruit Trees
When selecting fruit trees for hydroponic cultivation, dwarf varieties are particularly advantageous due to their manageable size and reduced space requirements.
Additionally, tropical fruits such as bananas, papayas, and avocados demonstrate significant potential for hydroponic systems given their high water and nutrient uptake efficiencies.
These factors collectively optimize growth conditions and enhance yield outcomes within controlled environments.
Dwarf Varieties Preferred
Often favored for hydroponic fruit production, dwarf varieties of fruit trees provide numerous advantages including space efficiency, manageable growth, and high yield potential in controlled environments.
These compact cultivars are particularly suited for innovative horticultural systems due to several key factors:
- Optimized Space Utilization: Dwarf trees require less vertical and horizontal space, allowing for denser planting and maximizing available growing area.
- Simplified Maintenance: The reduced stature of dwarf varieties facilitates easier pruning, training, and harvesting, reducing labor and operational costs.
These attributes underscore the suitability of dwarf fruit trees for modern, resource-efficient hydroponic agriculture.
Tropical Fruits Potential
Tropical fruit trees such as mangoes, papayas, and guavas present a promising potential for hydroponic cultivation due to their adaptability to controlled environments and high market demand.
These species thrive in nutrient-rich, hydroponic systems that provide ideal growth conditions, including consistent temperature, humidity, and light levels.
Mangoes (Mangifera indica) benefit from hydroponic setups that guarantee precise nutrient delivery, reducing soil-borne diseases.
Papayas (Carica papaya), known for their rapid growth cycle, achieve accelerated maturation in controlled hydroponic environments.
Guavas (Psidium guajava) exhibit enhanced fruit quality and yield due to the consistent nutrient availability.
This innovative approach not only maximizes space efficiency but also aligns with sustainability goals, making hydroponic tropical fruit cultivation a viable and lucrative endeavor for modern agriculture.
Nutrient Solutions

In hydroponic systems for fruit trees, the formulation of nutrient solutions is critical, encompassing essential macronutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, as well as micronutrients like iron, manganese, and zinc.
Properly balancing pH levels between 5.5 and 6.5 is imperative to enhance nutrient uptake and prevent deficiencies or toxicities.
Advanced monitoring and adjustment techniques guarantee the nutrient solution remains within ideal parameters, promoting vigorous growth and fruit production.
Essential Nutrient Components
A meticulously balanced nutrient solution is fundamental for the ideal growth and health of fruit trees in hydroponic systems. Essential nutrient components must include a precise blend of macro and micronutrients to sustain vigorous growth and fruit production.
Significant macro-elements necessary for the hydroponic cultivation of fruit trees encompass nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K), while critical micronutrients include iron (Fe), manganese (Mn), and zinc (Zn).
- Macronutrients: Guarantee robust vegetative growth and fruit yield.
- Micronutrients: Essential for enzymatic and physiological processes.
Innovative nutrient management strategies are paramount to optimizing hydroponic systems, directly influencing the productivity and health of fruit trees.
Proper formulation and delivery of these nutrients are fundamental for achieving superior results.
Balancing Ph Levels
Properly balancing pH levels in nutrient solutions is critical to ensuring ideal nutrient uptake and preventing deficiencies or toxicities in hydroponically grown fruit trees.
The best pH range for most fruit trees is between 5.5 and 6.5. Deviations from this range can impede the absorption of essential macro and micronutrients, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and trace elements.
Regular monitoring and adjustments using pH meters and appropriate buffering agents are imperative. Acidic solutions can be neutralized with potassium hydroxide or calcium carbonate, while alkaline solutions may require the addition of phosphoric or nitric acid.
Maintaining this delicate balance is fundamental for maximizing growth rates, fruit yield, and overall plant health in hydroponic systems.
Light Requirements
Ensuring ideal light exposure is essential for the successful hydroponic cultivation of fruit trees, as it directly influences photosynthetic efficiency and overall plant health.
Ideal light conditions can be achieved through the use of advanced LED grow lights, which provide a full spectrum of wavelengths tailored to the needs of fruit-bearing plants.
Key considerations include:
- Intensity: Adequate light intensity is vital to facilitate robust growth and fruit production.
- Photoperiod: Managing the duration of light exposure to mimic natural daylight cycles can enhance flowering and fruiting phases.
Properly managed light conditions will maximize growth rates and fruit yield in hydroponic systems.
Temperature and Humidity

Regulating temperature and humidity precisely is paramount for maximizing the growth and productivity of hydroponically grown fruit trees.
Ideal temperature ranges for most fruit trees are between 65°F and 75°F, with night temperatures slightly lower to simulate natural conditions. Deviations can lead to subpar photosynthesis rates and stress responses.
Concurrently, maintaining relative humidity levels between 40% and 60% is critical to prevent transpiration issues and pathogen proliferation.
Advanced climate control systems, integrating sensors and automated adjustments, guarantee consistent environmental parameters. These systems not only foster peak physiological processes but also mitigate risks associated with fluctuating conditions.
The synergy of precise temperature and humidity control creates a stable microenvironment conducive to robust growth and fruit yield in hydroponic systems.
Pollination Techniques
Pollination is a critical aspect of fruit tree cultivation in hydroponic systems, necessitating precise techniques to guarantee successful fruit set.
Hand pollination methods, such as using soft brushes or vibrating tools, can effectively transfer pollen in controlled environments.
Additionally, incorporating natural pollinators like bees can enhance pollination efficiency and improve overall yield quality.
Hand Pollination Methods
Hand pollination plays a vital role in hydroponic fruit tree cultivation, effectively facilitating the transfer of pollen in the absence of natural pollinators. This manual intervention guarantees successful fertilization, fundamental for fruit set and yield. Employing meticulous techniques can enhance pollination efficacy.
- Brush Technique: Utilizing a fine, soft brush to transfer pollen directly from anthers to stigmas.
- Electric Pollinators: Deploying battery-operated devices that mimic the vibration of bees, dislodging pollen efficiently.
These methods demand precision and consistency to replicate the intricate process performed by natural agents.
Understanding the specific pollination requirements of each fruit tree species is essential for achieving the best outcomes in hydroponic systems.
Benefits of Pollinators
In hydroponic fruit tree cultivation, integrating pollinators not only enhances fruit set and quality but also optimizes genetic diversity and plant health.
Employing natural pollinators such as bees or introducing artificial techniques like mechanical pollinators can greatly improve the efficiency of cross-pollination. This process guarantees robust fruit development and reduces the likelihood of genetic bottlenecks, thereby promoting healthier, more resilient plants.
Additionally, the presence of pollinators can stimulate plant hormonal responses, leading to better growth rates and fruit yields.
For controlled environments, precision pollination techniques, including the use of air-blown pollen or robotic pollinators, offer consistent results.
Common Challenges
One of the paramount challenges in cultivating fruit trees hydroponically is managing the precise nutrient balance required to support ideal growth and fruit production. This entails a meticulous approach to guarantee that macronutrients and micronutrients are delivered in optimal proportions.
Additionally, maintaining stable environmental conditions is vital, given that fluctuations can adversely affect physiological processes.
- Nutrient Solution Management: Achieving the correct pH and electrical conductivity levels to facilitate nutrient uptake.
- Root Zone Aeration: Confirming proper oxygenation to prevent root rot and promote healthy root development.
Each of these factors demands continuous monitoring and adjustment, underscoring the complexity of hydroponic fruit tree cultivation.
Real-World Examples
Examining real-world examples of hydroponic fruit tree cultivation reveals valuable insights into the practical applications and outcomes of this innovative growing method. For instance, commercial growers have successfully implemented hydroponic systems to cultivate fruit trees in controlled environments, leading to increased yields and optimized resource use. These examples demonstrate the potential for sustainable agriculture, especially in urban settings where space and soil quality may be limited. Understanding how to grow trees hydroponically involves exploring various techniques, such as nutrient film systems and deep-water culture, to ensure healthy root development and efficient nutrient absorption.
One notable example is the Eden Project in the UK, which has successfully grown dwarf varieties of citrus trees using nutrient film technique (NFT) systems. Their results demonstrate enhanced growth rates and fruit yields compared to traditional soil-based methods.
Similarly, AeroFarms in the United States has explored vertical hydroponic systems for dwarf apple trees, achieving ideal root aeration and nutrient uptake.
These case studies highlight not only the feasibility but also the potential for scalability of hydroponic fruit tree cultivation, underscoring its promise for urban agriculture and sustainable food production systems.
Getting Started

Starting on the journey of growing fruit trees hydroponically requires a thorough understanding of system design, nutrient management, and environmental control to guarantee ideal plant health and yield.
The initial phase involves selecting the appropriate hydroponic system, such as nutrient film technique (NFT), deep water culture (DWC), or aeroponics, each offering unique advantages and challenges. Additionally, precise nutrient formulations tailored for fruit trees are essential to support growth stages, from vegetative to fruiting phases.
Key considerations include:
- System Selection: Choose an appropriate hydroponic system based on space, budget, and tree species.
- Nutrient Management: Develop a detailed nutrient plan to meet the specific requirements of fruit-bearing plants.
These foundational elements are vital for achieving successful hydroponic fruit tree cultivation.
Conclusion
Hydroponic horticulture, when harnessed with high-level expertise, offers outstanding opportunities for cultivating certain fruit trees.
By blending ideal nutrient solutions, strategic pollination practices, and sophisticated systems, successful soilless growth can be achieved.
Although challenges such as root rot and nutrient imbalances exist, meticulous management makes this method a viable alternative to traditional techniques.
Ultimately, hydroponic fruit tree cultivation combines scientific precision with sustainable practices, promising potential for prolific production.






