How Do You Grow Garlic Hydroponically?
Yes, garlic can be successfully grown hydroponically by utilizing nutrient-rich solutions and controlled environment systems. Selecting appropriate garlic varieties—hardneck for cooler climates and softneck for warmer conditions—enhances adaptability and yield.
Best growth is achieved through systems like Deep Water Culture (DWC) or Nutrient Film Technique (NFT), with balanced nutrient solutions and high-efficiency LED grow lights providing the necessary conditions. Managing pH levels, electrical conductivity, light cycles, and humidity guarantees ideal nutrient uptake and minimizes disease risk.
Understanding these methodologies can lead to consistent, high-quality garlic production. Further insights into each step guarantee a thorough grasp of the process.

Key Takeaways
- Yes, garlic can be successfully grown hydroponically with accelerated growth rates and precise nutrient control.
- Hydroponic systems like Deep Water Culture (DWC) or Nutrient Film Technique (NFT) are ideal for garlic.
- Disease-resistant garlic varieties enhance crop health and reduce the risk of soil-borne diseases.
- Full-spectrum LED grow lights and controlled environments ensure optimal light, temperature, and humidity for growth.
Benefits of Hydroponic Garlic

Hydroponically grown garlic offers several benefits, including accelerated growth rates, ideal nutrient absorption, and reduced risk of soil-borne diseases.
In hydroponic systems, garlic is cultivated using nutrient-rich water solutions, allowing precise control over essential elements such as nitrogen, potassium, and phosphorus. This meticulous nutrient management guarantees peak plant health and vigor, leading to faster growth cycles compared to traditional soil-based methods.
Additionally, the absence of soil eliminates exposure to pathogens like Fusarium and nematodes, greatly reducing disease incidence. Controlled environments, such as greenhouses, further enhance growth conditions by regulating temperature, humidity, and light.
Consequently, hydroponic garlic cultivation not only maximizes yield but also guarantees a consistent, high-quality product, meeting the demands of modern agricultural innovation.
Choosing the Right Garlic Variety
When selecting a garlic variety for hydroponic cultivation, it is essential to take into account the distinctions between hardneck and softneck types, particularly regarding climate adaptability and bulb formation.
Hardneck varieties are generally more suited to cooler climates and produce a central scape, whereas softneck varieties thrive in warmer conditions and are known for their superior storage capabilities.
Additionally, evaluating each variety's resistance to common diseases such as white rot and nematodes will enhance crop success and sustainability in a controlled hydroponic system.
Hardneck Vs. Softneck
Selecting the appropriate garlic variety for hydroponic cultivation necessitates an understanding of the distinct physiological and horticultural differences between hardneck and softneck types.
Hardneck garlic (Allium sativum var. ophioscorodon) typically features a central flowering stalk known as a scape, which requires specific nutrient solutions to optimize bulb development.
Conversely, softneck garlic (Allium sativum var. sativum) lacks a scape, making it potentially more adaptable for hydroponic systems due to its less rigid growth requirements.
Key factors to evaluate include:
- Bulb Structure: Hardneck varieties typically produce larger, more uniform cloves, beneficial for culinary applications.
- Storage Life: Softneck garlic generally offers extended shelf life, advantageous for commercial scalability.
Understanding these distinctions is paramount for successful hydroponic garlic cultivation.
Climate Suitability
Understanding the climatic requirements of garlic varieties is essential for improving hydroponic growth conditions and ensuring robust yield.
Hardneck varieties, such as Rocambole and Porcelain, generally favor cooler climates and require vernalization—exposure to prolonged cold temperatures for bulb development.
Softneck varieties, like Artichoke and Silverskin, thrive in milder climates and do not necessitate vernalization.
To simulate ideal conditions in a hydroponic setup, control temperature ranges between 12-15°C for hardneck and 18-24°C for softneck varieties.
Additionally, maintaining relative humidity levels at 60-70% and ensuring adequate light exposure (14-16 hours/day) can replicate natural climatic conditions, fostering optimal growth.
Select garlic varieties based on these climatic prerequisites to enhance adaptability and maximize hydroponic yield.
Disease Resistance
To further optimize hydroponic garlic cultivation, it is imperative to contemplate the disease resistance of various garlic varieties, as this considerably impacts overall plant health and yield. Selecting cultivars with inherent resistance to common pathogens mitigates the risk of disease outbreaks, thereby ensuring robust growth and higher productivity.
Critical considerations include:
- Fusarium Basal Rot Resistance: Opt for varieties with genetic resistance to Fusarium oxysporum to prevent root and bulb decay.
- White Rot Tolerance: Choose cultivars that exhibit resilience against Sclerotium cepivorum, which can devastate garlic crops.
Setting Up Your Hydroponic System
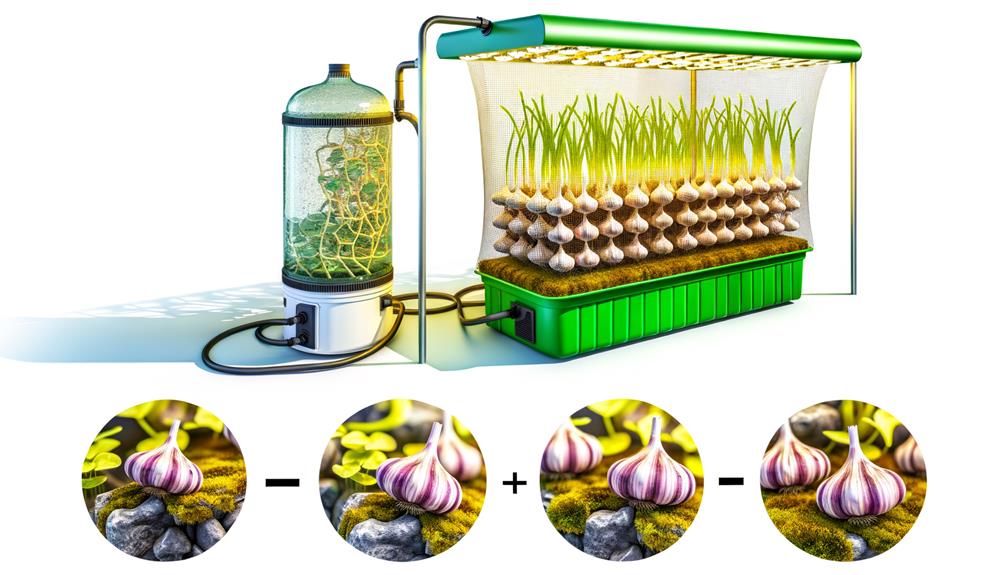
Establishing an efficient hydroponic system for garlic cultivation necessitates careful consideration of system design, nutrient delivery methods, and environmental controls.
Select a system such as Deep Water Culture (DWC) or Nutrient Film Technique (NFT) for ideal root oxygenation and nutrient uptake. Ascertain the system includes a reliable pump for continuous nutrient solution circulation.
Maintain pH levels between 6.0 and 6.5 using precise pH meters and adjusters. Employ high-efficiency LED grow lights to provide a light spectrum conducive to garlic growth, guaranteeing a photoperiod of 12-16 hours.
Implement environmental controls such as humidity regulators and temperature controllers to maintain conditions between 60°F and 75°F.
Consistent monitoring and adjustments are critical for maximizing garlic yield and quality in hydroponic systems.
Nutrient Solutions for Garlic
Selecting the appropriate nutrient solution for hydroponically grown garlic is vital to guaranteeing ideal growth and maximizing yield. Garlic requires a balanced macronutrient profile, emphasizing nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. Additionally, garlic benefits from essential micronutrients to sustain its robust growth and development.
Key considerations include:
- Nutrient Concentration: Maintain Electrical Conductivity (EC) between 1.8-2.2 mS/cm.
- pH Levels: Ideal pH range of 6.0-6.5.
Regular monitoring and adjustments of the nutrient solution are important. Utilizing a high-quality hydroponic nutrient mix tailored for allium species will promote bulb formation and vigorous foliage.
Implementing an automated dosing system can maintain nutrient consistency, reducing human error and enhancing crop performance.
Light Requirements for Growth

When growing garlic hydroponically, it is essential to maintain ideal light intensity, typically around 400-600 µmol/m²/s, to guarantee robust photosynthetic activity.
Additionally, an optimal photoperiod of 14-16 hours per day is recommended to simulate the natural growing conditions and promote bulb development.
These parameters must be carefully monitored and adjusted to achieve maximal growth and yield.
Optimal Light Intensity
To guarantee robust growth and high yields, garlic cultivated hydroponically requires a specific light intensity range of 14 to 16 hours per day, with an ideal photosynthetically active radiation (PAR) value between 400 to 600 µmol/m²/s. This precise light intensity is critical for ensuring peak photosynthesis, which directly influences bulb development and overall plant vigor.
Key considerations for maintaining appropriate light intensity include:
- Light Source: Utilizing full-spectrum LED grow lights to mimic natural sunlight.
- Distance: Positioning lights at a calibrated height to achieve uniform light distribution.
These elements are instrumental in fostering a controlled environment that maximizes the efficacy of hydroponic garlic cultivation.
Ideal Light Duration
Determining the ideal light duration is essential for maximizing the growth and development of hydroponically cultivated garlic. Research indicates that garlic thrives under a photoperiod of approximately 14 to 16 hours of light per day.
This extended light exposure facilitates robust photosynthetic activity, guaranteeing optimal biomass accumulation and bulb formation. Implementing LED grow lights with customizable spectrums can further enhance growth by delivering specific wavelengths that promote chlorophyll synthesis.
It is critical to maintain a consistent light-dark cycle to prevent photoinhibition and stress responses. Automated timers can guarantee precise control of light duration, thereby enhancing growth conditions.
Such meticulous light management is pivotal in achieving superior yield and quality in hydroponically grown garlic.
Managing Water and Humidity
Proper management of water and humidity is essential for enhancing the growth and development of hydroponically cultivated garlic. A precisely controlled hydroponic environment guarantees that garlic receives adequate hydration and maintains appropriate humidity levels to prevent desiccation or fungal growth.
Key factors to take into account include:
- Water Quality: Utilize nutrient-enriched, pH-balanced water to facilitate ideal nutrient uptake.
- Humidity Levels: Maintain relative humidity between 50-60% to support transpiration and prevent mold.
Employing these strategies guarantees a stable microclimate within the hydroponic system, thereby promoting vigorous root development and robust bulb formation.
Pest and Disease Control

Effective pest and disease control in hydroponic garlic cultivation necessitates a thorough understanding of common pests such as aphids and thrips, as well as implementing strategies for preventing fungal infections like white rot.
Maintaining ideal water quality is essential to inhibit pathogen proliferation, requiring regular monitoring and adjustments to pH and nutrient levels.
Employing integrated pest management (IPM) techniques and utilizing beneficial microorganisms can further enhance the resilience of hydroponically grown garlic.
Common Garlic Pests
Identifying and managing common garlic pests is vital for maintaining the health and productivity of hydroponic garlic systems. Key pests that can impact garlic include aphids, thrips, and nematodes. Effective control strategies involve early detection and integrated pest management techniques.
Aphids: These small sap-sucking insects can cause significant damage by transmitting viruses. Regular monitoring and biological controls such as introducing ladybugs can mitigate infestations.
Thrips: Thrips feed on garlic leaves, causing silvery streaks and reduced photosynthesis. Employing sticky traps and predatory mites can help manage their population.
Nematodes: Soil-dwelling nematodes can attack garlic roots, leading to stunted growth. Utilizing nematode-resistant cultivars and maintaining sterile growing conditions are vital preventive measures.
Scientific vigilance and innovative approaches are essential for pest control in hydroponic garlic cultivation.
Preventing Fungal Infections
In addition to managing pests, preventing fungal infections is vital for sustaining the importance of hydroponic garlic systems.
Implementing stringent sterilization protocols is essential; all equipment should be disinfected with a 10% bleach solution. Utilizing a UV-C light system effectively eradicates airborne fungal spores.
Hydroponic reservoirs must be continuously monitored for pH and nutrient levels, maintaining an ideal pH range of 5.5 to 6.5 to inhibit fungal growth. Incorporating beneficial microbes, such as Trichoderma harzianum, enhances root zone protection.
Consistent air circulation, achieved through high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters, mitigates humidity levels, thereby reducing fungal proliferation.
Maintaining Water Quality
Maintaining ideal water quality is essential for preventing pest infestations and disease outbreaks in hydroponic garlic systems. Rigorous monitoring and adjustment of water parameters are critical. Implementing advanced filtration systems and UV sterilization can mitigate microbial growth.
Key factors to monitor include:
- pH Levels: Maintain a pH range of 5.5-6.5 to optimize nutrient uptake and inhibit pathogen proliferation.
- Electrical Conductivity (EC): Regularly measure EC to guarantee appropriate nutrient concentrations, minimizing the risk of nutrient imbalances that can weaken plant defenses.
Adhering to these practices fosters a robust, pest-free hydroponic environment conducive to vigorous garlic growth.
Harvesting Hydroponic Garlic
To determine the ideal time for harvesting hydroponic garlic, monitor the foliage for signs of yellowing and drying, which indicate bulb maturation.
Employ precise observation techniques, ensuring the majority of leaves exhibit these symptoms.
Carefully lift the garlic bulbs from the hydroponic system, minimizing root disturbance to prevent damage.
Post-extraction, conduct a thorough rinse to eliminate any remaining nutrient solution residues.
For best curing, place the bulbs in a well-ventilated area with controlled humidity and temperature, maintaining 70-80°F (21-27°C) and 45-55% humidity.
This curing phase, typically spanning 2-3 weeks, is critical for enhancing flavor intensity and storage longevity.
Comparing Yields: Hydroponic Vs. Soil
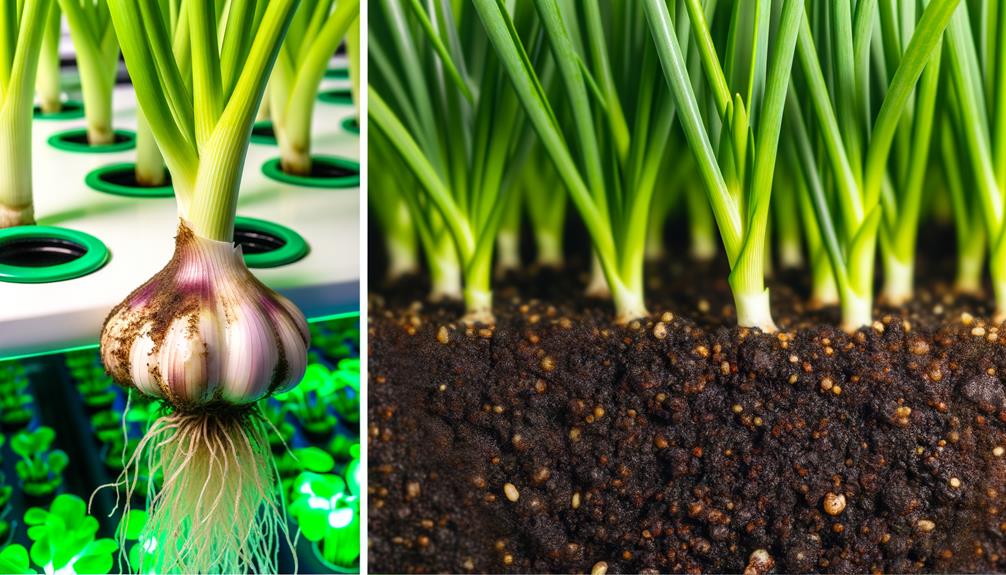

After successfully curing and storing hydroponic garlic, it becomes pertinent to analyze and compare the yield efficiencies of hydroponic systems versus traditional soil cultivation. Empirical studies and controlled experiments offer valuable insights into this comparison. Key factors include nutrient delivery, root oxygenation, and growth rate.
- Nutrient Delivery: Hydroponic systems provide precise nutrient dosing, often resulting in optimized growth.
- Root Oxygenation: Enhanced oxygen availability in hydroponic systems can accelerate metabolic processes in garlic bulbs.
Quantitative data indicate that hydroponic garlic often exhibits superior yield per square meter. However, the initial setup costs and operational complexity must be carefully weighed against these advantages for a thorough assessment.
Tips for Successful Cultivation
Effective cultivation of hydroponic garlic necessitates meticulous attention to nutrient composition, pH levels, and environmental conditions to assure ideal growth and bulb development.
Employ a balanced nutrient solution with a nitrogen-phosphorus-potassium (N-P-K) ratio of 4-3-3, supplemented with essential micronutrients such as calcium, magnesium, and iron.
Maintain a pH range between 6.0 and 6.5 to optimize nutrient uptake. Assure constant monitoring of electrical conductivity (EC) to sustain appropriate salinity levels.
Utilize high-efficiency LED grow lights to replicate the photoperiod and intensity of natural sunlight, aiming for 12-16 hours of light daily.
Implement an aeration system to maintain dissolved oxygen levels, thereby promoting robust root health.
Consistently monitor temperature, ideally between 60-70°F, to prevent thermal stress.
Conclusion
To summarize, hydroponic cultivation of garlic presents a promising alternative to traditional soil-based methods, with potential for higher yields and controlled growth conditions. Additionally, this method minimizes the risk of soil-borne diseases and allows for year-round production in controlled environments. Growers interested in expanding their hydroponic ventures may also explore how to grow rosemary hydroponically, as similar techniques can be applied to various herbs. By optimizing nutrient delivery and environmental factors, hydroponic systems can enhance both the quality and efficiency of garlic and other aromatic crops.
By selecting suitable garlic varieties, optimizing nutrient solutions, and maintaining proper light and pest control, hydroponic systems can notably enhance productivity.
While comparing yields, hydroponic methods often prove to be a cut above the rest.
Consequently, integrating these advanced techniques can lead to more efficient and sustainable garlic production.






