How You Can Grow Green Beans Hydroponically – A Step-by-Step Guide
Yes, green beans can be grown hydroponically with remarkable efficiency and sustainability. This soilless cultivation method utilizes nutrient-rich water solutions in controlled environments, considerably reducing growth cycles and water usage by up to 90%.
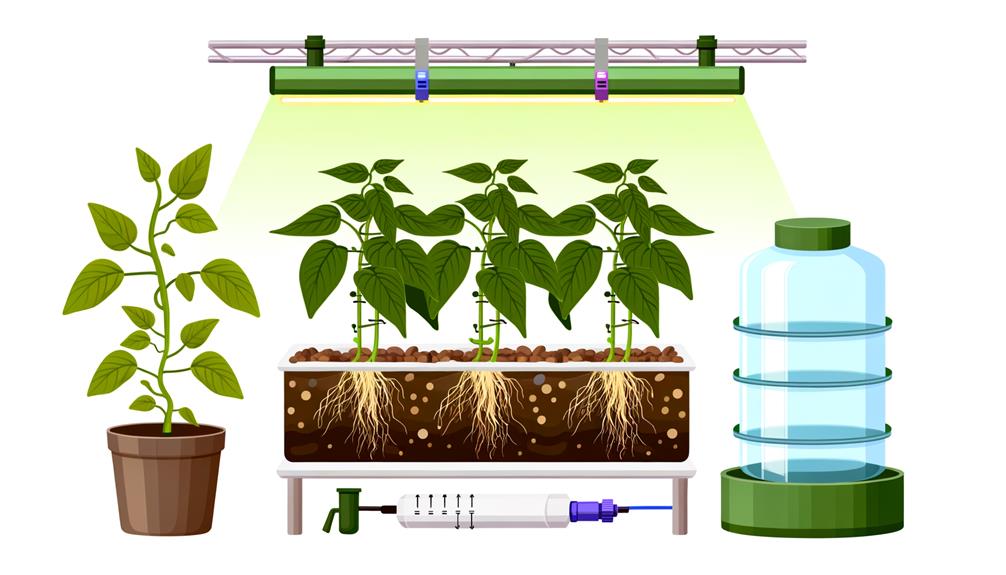
Ideal growth conditions are maintained using systems like Deep Water Culture (DWC) and Nutrient Film Technique (NFT), ensuring enhanced nutrient absorption and minimized exposure to soil-borne pathogens. Key variables such as pH levels, nutrient ratios, and light exposure require precise regulation for successful growth.
Advanced techniques and equipment further contribute to this highly productive farming system. There are more specific insights that can further enhance your understanding.

Key Takeaways
- Yes, green beans can be grown hydroponically using systems like DWC, NFT, and Aeroponics.
- Hydroponic green beans benefit from accelerated growth cycles and reduced water usage by up to 90%.
- Tailored nutrient solutions and pH control between 5.5-6.5 optimize green bean growth and yield.
- Vertical farming techniques in hydroponics maximize space utilization for higher productivity.
What Is Hydroponics?

Hydroponics is a soilless cultivation method where nutrient-rich water solutions are used to provide essential minerals directly to plant roots. This technique leverages a controlled environment to optimize growth conditions, enhancing plant health and yield.
Utilizing substrates such as perlite or rock wool, hydroponic systems guarantee root support while facilitating efficient nutrient uptake. Key systems include Deep Water Culture (DWC), Nutrient Film Technique (NFT), and Aeroponics, each offering unique advantages for specific crop types.
Precision in pH balance, electrical conductivity, and dissolved oxygen levels is critical to maintaining ideal growth conditions. By eliminating soil, hydroponics mitigates pest and disease risks, paving the way for innovative agricultural practices that promise higher efficiency and sustainability.
Benefits of Hydroponic Green Beans
Cultivating green beans hydroponically offers a multitude of benefits, including accelerated growth rates, enhanced nutrient absorption, and reduced vulnerability to soil-borne diseases.
This method leverages precise control over the growing environment, optimizing conditions for plant health and productivity. Hydroponic systems provide consistent access to water and nutrients, which can result in higher yields and superior quality produce.
- Accelerated Growth: Hydroponic systems can reduce the growth cycle by up to 25%.
- Optimal Nutrient Delivery: Nutrient solutions are tailored for maximum absorption efficiency.
- Water Conservation: Utilizes up to 90% less water compared to traditional soil farming.
- Pest and Disease Control: Minimizes exposure to soil-borne pathogens and pests.
Choosing the Right Green Bean Varieties

Selecting the right green bean varieties is essential in maximizing the advantages of hydroponic cultivation, ensuring ideal growth and yield outcomes tailored to the controlled environment.
Varieties such as 'Provider' and 'Contender' are highly recommended due to their robust growth traits and resistance to common pathogens. 'Burpee's Stringless Green Pod' is another prime choice, known for its high yield and adaptability to hydroponic systems.
Precision in choosing dwarf or bush types over pole beans is vital, as these varieties better utilize vertical space and nutrient solutions efficiently.
Additionally, selecting seeds with shorter maturation periods can expedite harvest cycles, allowing for more frequent crop turnover.
Detailed cultivar selection can greatly enhance productivity and resource efficiency in hydroponic green bean farming.
Essential Equipment and Supplies
To achieve ideal growth conditions for hydroponic green beans, selecting an appropriate hydroponic system—such as nutrient film technique (NFT), deep water culture (DWC), or drip systems—is vital.
Additionally, the formulation of nutrient solutions must be precisely balanced to guarantee the availability of essential macro and micronutrients.
Proper calibration and monitoring of pH and electrical conductivity (EC) levels are also essential to maintaining plant health and maximizing yield.
Hydroponic System Options
A successful hydroponic system for growing green beans necessitates a precise array of essential equipment and supplies, each contributing to the ideal growth conditions. Guaranteeing optimal light, water, and nutrient delivery is paramount.
The following components are vital for any hydroponic setup aimed at cultivating green beans:
- Grow Lights: High-intensity LED or fluorescent lights to simulate sunlight and guarantee photosynthesis.
- Water Pumps: Reliable pumps to maintain consistent water flow and oxygenation.
- Growing Medium: Alternatives like rockwool or coco coir to support root structure and nutrient absorption.
- pH and EC Meters: Precision instruments to monitor and adjust the nutrient solution's pH and electrical conductivity.
These elements collectively foster a controlled environment, maximizing green bean yield.
Nutrient Solutions Essentials
Understanding the precise composition and balance of nutrient solutions is paramount for the healthy growth and development of hydroponically grown green beans.
Essential macronutrients—nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K)—must be meticulously calibrated to optimize vegetative and reproductive stages.
Complementary micronutrients such as iron (Fe), magnesium (Mg), and calcium (Ca) are also critical, often delivered via chelated compounds to enhance bioavailability.
Accurate pH control (ideally between 5.5 and 6.5) and Electrical Conductivity (EC) monitoring are indispensable, necessitating reliable pH meters and EC sensors.
Advanced hydroponic setups may incorporate automated dosing systems for precision nutrient delivery.
Nutrient reservoirs, air stones for oxygenation, and high-quality water sources complete the array of essential equipment, ensuring robust plant health and maximized yield.
Setting Up Your Hydroponic System

Establishing an efficient hydroponic system for growing green beans requires meticulous planning and precise execution to guarantee perfect plant health and yield. This involves selecting the right nutrient solution, maintaining optimal water pH levels, and ensuring proper lighting conditions for sustained growth. While green beans thrive in hydroponic setups, gardeners can also explore ways to grow rhubarb hydroponically, adjusting factors like temperature and humidity to suit its unique needs. By carefully monitoring these conditions, growers can maximize both the quality and quantity of their harvests.
To achieve the best results, consider the following critical components:
- System Type: Choose a Deep Water Culture (DWC), Nutrient Film Technique (NFT), or Ebb and Flow setup based on space and resources.
- Lighting: Implement full-spectrum LED grow lights to simulate natural sunlight, facilitating robust photosynthesis.
- Aeration: Confirm adequate oxygenation of nutrient solutions using air stones and pumps to support root respiration.
- Temperature Control: Maintain an ambient temperature between 65-75°F to create a conducive growth environment.
This strategic setup forms the foundation for thriving hydroponic green bean cultivation.
Nutrient Solutions for Green Beans
A suitable nutrient solution for hydroponic green beans necessitates a precise balance of essential elements such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, along with trace minerals.
Maintaining pH levels between 5.5 and 6.5 is critical for maximizing nutrient uptake and preventing deficiencies.
In addition, adjusting nutrient ratios according to the plant's growth stages can greatly enhance yield and overall health.
Essential Nutrient Components
Ideal growth of green beans in a hydroponic system requires a meticulously balanced nutrient solution containing essential macro and micronutrients. This precise formulation guarantees peak plant health and productivity. Key elements include nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, which are vital for vegetative growth, root development, and overall plant vigor.
To achieve peak results, the nutrient solution for hydroponic green beans must include:
- Nitrogen (N) for robust foliage and stem development.
- Phosphorus (P) for strong root systems and flowering.
- Potassium (K) for overall plant health and disease resistance.
- Calcium (Ca) to prevent blossom end rot and maintain cell wall integrity.
These nutrients must be administered in precise ratios to meet the specific growth stages of green beans.
Ph Levels Importance
Maintaining the ideal pH range is paramount for guaranteeing that green beans can effectively absorb the meticulously balanced nutrients provided in a hydroponic system. The best pH range for hydroponic green beans typically lies between 5.5 and 6.5. Deviations from this range can lead to nutrient lockout or toxicity, adversely affecting plant growth and productivity. Monitoring and adjusting pH levels are critical for maintaining nutrient solubility and availability. Advanced pH control systems and periodic pH testing are recommended to stabilize the hydroponic environment.
| pH Level | Impact on Green Beans |
|---|---|
| < 5.5 | Nutrient lockout, root damage |
| 5.5-6.5 | Best nutrient absorption |
| > 6.5 | Reduced micronutrient uptake |
Continuous vigilance guarantees the hydroponic system remains conducive to robust green bean cultivation.
Optimal Nutrient Ratios
To achieve ideal growth in hydroponic green beans, precise nutrient ratios must be meticulously formulated and maintained, ensuring an adequate supply of macronutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, as well as essential micronutrients.
A balanced nutrient solution is fundamental for maximizing yield and ensuring plant health.
Key components include:
- Nitrogen (N): Essential for vegetative growth and chlorophyll synthesis.
- Phosphorus (P): Important for root development and energy transfer.
- Potassium (K): Significant for overall plant vigor and disease resistance.
- Calcium (Ca): Crucial for cell wall structure and stability.
Light and Temperature Requirements

Proper light and temperature conditions are critical for maximizing the growth and yield of hydroponically cultivated green beans.
Green beans require a photoperiod of 14-16 hours of light per day, ideally using full-spectrum LED grow lights to mimic natural sunlight. Photosynthetically active radiation (PAR) between 400-700 nm is crucial for enhancing chlorophyll production and promoting robust vegetative growth.
Temperature control is equally important; ideal growth occurs between 70-80°F (21-27°C) during the daytime and 60-70°F (15-21°C) at night. Deviations from these parameters can inhibit enzyme activities, slow metabolic processes, and reduce yield.
Employing precise climate control systems guarantees stable conditions, fostering an environment conducive to vigorous growth and high productivity.
Watering and Maintenance Tips
For ideal growth of hydroponic green beans, adhering to a precise watering schedule is vital to prevent root rot and guarantee adequate oxygenation.
Managing the nutrient solution involves regular monitoring and adjustment of pH and electrical conductivity (EC) to maintain a balanced nutrient profile.
Consistent system checks and timely replenishment of the nutrient solution are fundamental for sustaining plant health and maximizing yield.
Optimal Watering Schedule
An ideal watering schedule for hydroponically grown green beans necessitates precise control over nutrient solution delivery, guaranteeing consistent hydration and nutrient uptake. Achieving maximum growth involves a balance of water availability and oxygenation to the root zone.
Key factors include:
- Frequency: Administer nutrient solution 2-3 times daily, adjusting based on plant maturity and environmental conditions.
- Duration: Each watering session should last 15-20 minutes to guarantee thorough root saturation without waterlogging.
- pH Monitoring: Maintain the nutrient solution at a pH of 5.8-6.2 to enhance nutrient absorption.
- Temperature Control: Keep water temperature between 65-75°F (18-24°C) to prevent root stress.
This meticulous approach underpins successful hydroponic green bean cultivation.
Nutrient Solution Management
Effective nutrient solution management in hydroponic systems is fundamental to guaranteeing ideal growth and development of green beans, requiring meticulous attention to nutrient concentration, solution replacement intervals, and monitoring of electrical conductivity (EC) levels.
Guaranteeing an ideal nutrient concentration—typically a balanced mix of nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and micronutrients—prevents deficiencies and toxicities, thereby promoting healthy plant physiology.
Regularly replacing the nutrient solution, usually every two weeks, mitigates the risk of pathogen build-up and maintains nutrient efficacy.
Monitoring EC levels guarantees nutrient uptake efficiency; for green beans, an EC range of 1.5-2.5 mS/cm is recommended.
Additionally, pH levels should be maintained between 5.5-6.5 for ideal nutrient absorption.
Precision in these parameters fosters robust growth and maximizes yield potential.
Common Pests and Diseases
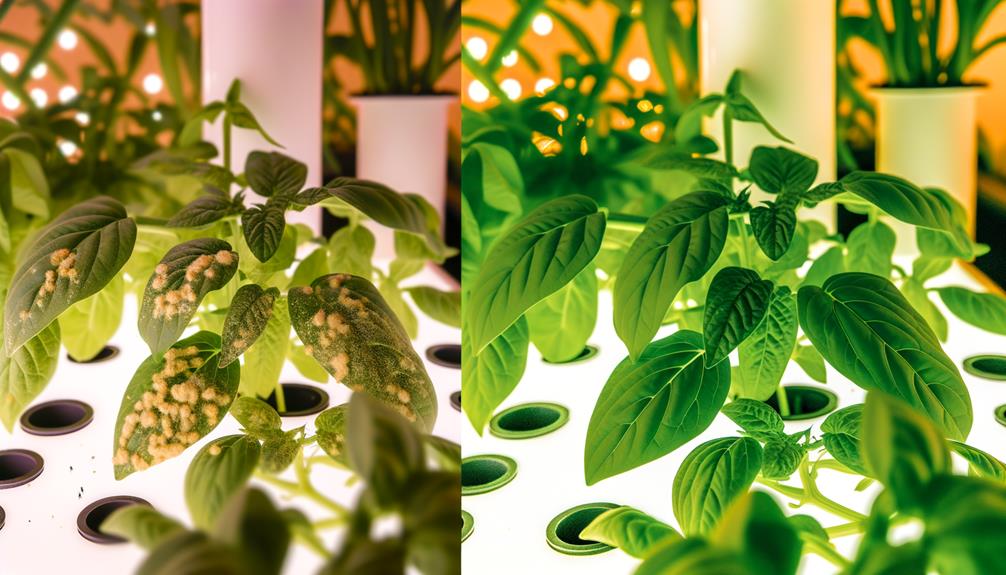

Despite the controlled environment of hydroponic systems, green beans are still susceptible to various pests and diseases that can substantially impact their growth and yield. Recognizing and managing these threats is essential for ideal production.
Common pests and pathogens include:
- Spider Mites: Tiny arachnids causing stippling and yellowing of leaves.
- Aphids: Small insects that excrete honeydew, leading to sooty mold.
- Root Rot: Often caused by Pythium spp., leading to brown, mushy roots.
- Powdery Mildew: Fungus that forms a white powdery coating on leaves.
Implementing integrated pest management (IPM) strategies, such as biological controls and periodic monitoring, can mitigate these challenges effectively.
Harvesting Your Green Beans
Ideal harvesting of hydroponically grown green beans requires close monitoring of pod size and color to guarantee peak flavor and nutritional content.
Typically, ideal harvest time is when pods reach 4-6 inches in length and exhibit a vibrant green hue, indicating chlorophyll concentration. Employing a refractometer can provide insights into sugar content, ensuring maximum sweetness.
It is essential to harvest before seeds visibly bulge, as this can compromise texture and taste. Employ sterile scissors to minimize plant trauma and potential pathogen exposure.
Post-harvest, maintain beans in a controlled environment at 40-45°F to preserve freshness. Regular, staggered harvesting promotes continued pod production, leveraging the plant's inherent growth cycles for sustained yield in hydroponic systems.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Identifying and addressing common issues in hydroponic green bean cultivation requires a methodical approach, leveraging detailed observations and scientific analysis to verify ideal plant health and yield. Factors such as nutrient imbalances, pH fluctuations, and environmental stressors can greatly impact growth.
To effectively troubleshoot:
Nutrient Deficiencies: Monitor for signs like yellowing leaves, indicating nitrogen deficiency, or purpling of leaves, pointing to phosphorus shortages.
pH Levels: Confirm the nutrient solution maintains a pH between 5.5 and 6.5 to optimize nutrient uptake.
Water Quality: Regularly test for contaminants and maintain appropriate Electrical Conductivity (EC) levels.
Pest Control: Implement integrated pest management strategies to mitigate infestations.
Environmental Conditions: Maintain a stable temperature (70-85°F) and confirm adequate light exposure.
These practices are pivotal for thriving hydroponic green beans.
Conclusion
The cultivation of green beans through hydroponic systems represents a fertile intersection of agricultural innovation and scientific precision.
By meticulously controlling environmental variables, one can achieve bountiful yields while minimizing resource wastage.
This method, akin to an orchestra where each instrument must be perfectly tuned, guarantees ideal plant health and productivity.
Understanding the nuances of hydroponic farming can lead to sustainable and efficient crop production, transforming traditional agricultural practices into a symphony of modern horticultural excellence.






