How You Can Grow Sweet Potatoes Hydroponically: A Step-by-Step Guide
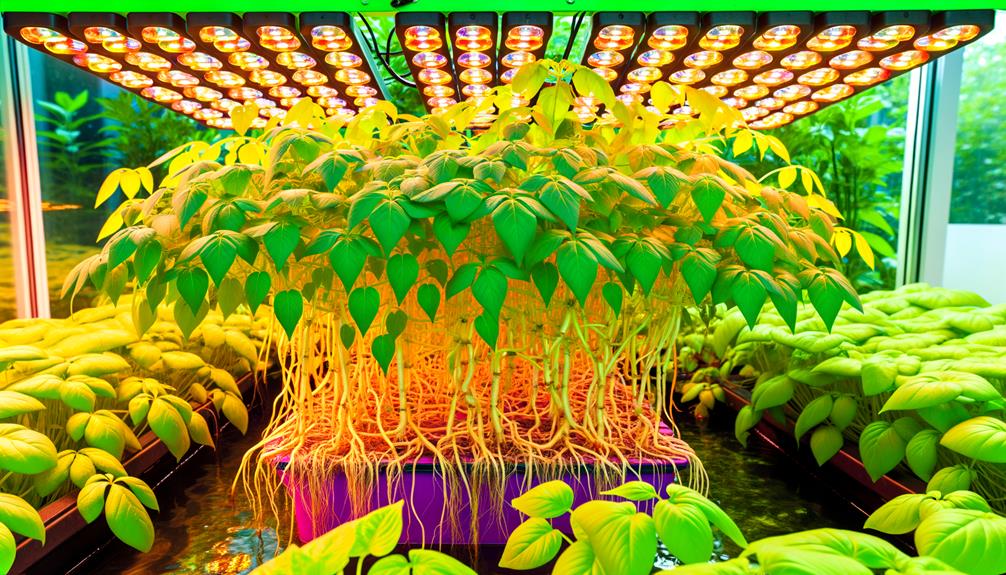
Sweet potatoes can indeed be grown hydroponically using controlled environments that maximize nutrient uptake and growth rates. Employing systems like Nutrient Film Technique (NFT) or Deep Water Culture (DWC) allows for ideal oxygenation and nutrient delivery.
Proper preparation of disease-free sweet potato slips is essential for successful rooting. A balanced nutrient solution with an N-P-K ratio of 10-10-20 and precise lighting conditions of 14-16 hours per day are necessary.
Regular monitoring of pH (5.5-6.5), electrical conductivity (1.8-2.4 mS/cm), and oxygen levels (6-8 ppm) guarantees healthy growth. Learn more about the specific steps and benefits for effective hydroponic sweet potato cultivation.
Key Takeaways
- Yes, sweet potatoes can be successfully grown hydroponically using various systems like NFT, DWC, and aeroponics.
- Hydroponics ensures faster growth and higher yields compared to traditional soil cultivation methods.
- Controlled environment and balanced nutrient solutions enhance plant growth and nutrient uptake efficiency.
- Sweet potato slips require careful preparation, including sprouting and rooting, before hydroponic transplantation.
Understanding Hydroponics

Hydroponics, the method of cultivating plants without soil by using mineral nutrient solutions in an aqueous solvent, offers a controlled environment for maximizing plant growth and yield. This innovative agricultural technique leverages water as the primary growth medium, supplemented with essential macro and micronutrients directly available to the plant roots.
The absence of soil minimizes pathogen risks while enhancing nutrient uptake efficiency. Critical parameters such as pH, electrical conductivity (EC), and dissolved oxygen are meticulously regulated to create an ideal growth environment.
Advanced hydroponic systems also employ artificial lighting, enabling year-round cultivation irrespective of external climatic conditions. By eliminating soil variability, hydroponics guarantees uniformity in nutrient delivery, fostering faster growth rates and higher yields, essential for sustainable and efficient agricultural practices.
Best Hydroponic Systems
Several hydroponic systems, including nutrient film technique (NFT), deep water culture (DWC), and aeroponics, have been identified as highly efficient for optimizing the growth and yield of sweet potatoes.
NFT systems provide a continuous flow of nutrient solution over the roots, ensuring consistent nutrient uptake.
DWC employs oxygen-rich water reservoirs to immerse the roots, facilitating robust growth and increased tuber production.
Aeroponics, which involves suspending roots in air and misting them with nutrient solutions, maximizes oxygen availability and nutrient absorption, thereby enhancing root and tuber development.
Each system offers unique advantages, such as improved nutrient delivery, oxygenation, and reduced risk of soil-borne diseases, making them ideal for innovative hydroponic sweet potato cultivation.
Preparing Sweet Potato Slips
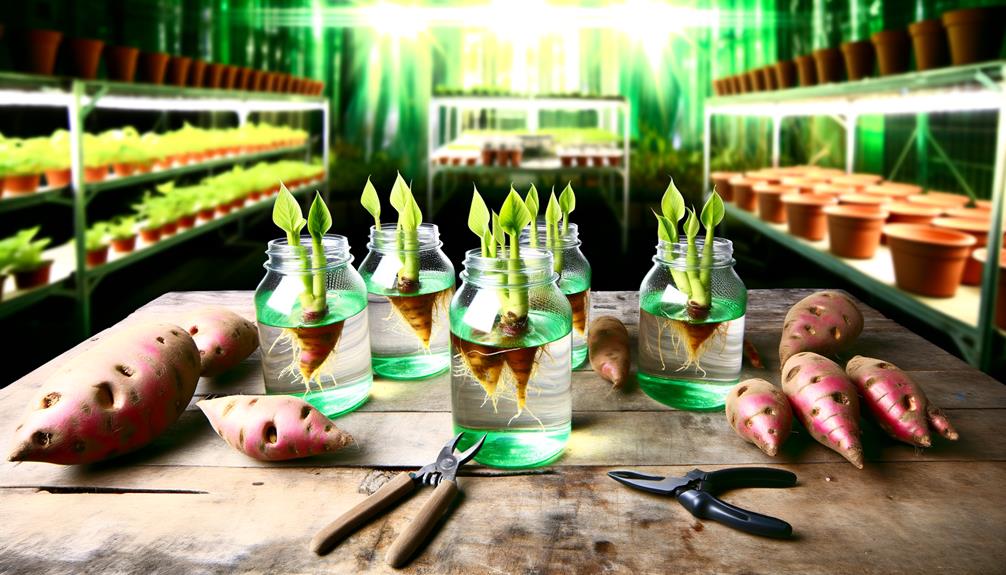

Initiating the preparation of sweet potato slips involves selecting disease-free, healthy sweet potatoes and placing them in a controlled environment to encourage sprouting.
Begin by immersing the lower half of the tuber in water, ensuring the top half remains exposed to air. Utilize a glass jar or container to facilitate this process, positioning toothpicks to stabilize the tuber.
Maintain temperatures between 70-80°F (21-27°C) and provide indirect sunlight or artificial lighting to induce sprouting within 2-4 weeks.
Once sprouts reach approximately 6 inches (15 cm), sever them from the parent tuber at the base.
Submerge the cuttings in water until roots develop, typically within 7-10 days, ensuring they are primed for hydroponic transplantation.
Nutrient Solutions and Lighting
After successfully rooting the sweet potato slips, it is imperative to formulate a balanced nutrient solution tailored to the specific needs of hydroponically grown sweet potatoes, ensuring ideal growth and development.
A nutrient solution with a suitable ratio of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium (N-P-K) is essential, typically in the range of 10-10-20. Additionally, micronutrients such as magnesium, calcium, and iron must be meticulously calibrated to prevent deficiencies.
Adequate lighting is another vital factor; a combination of blue and red spectrum LED lights, providing 14 to 16 hours of light per day, can greatly enhance photosynthesis and tuber formation.
Harvesting and Maintenance
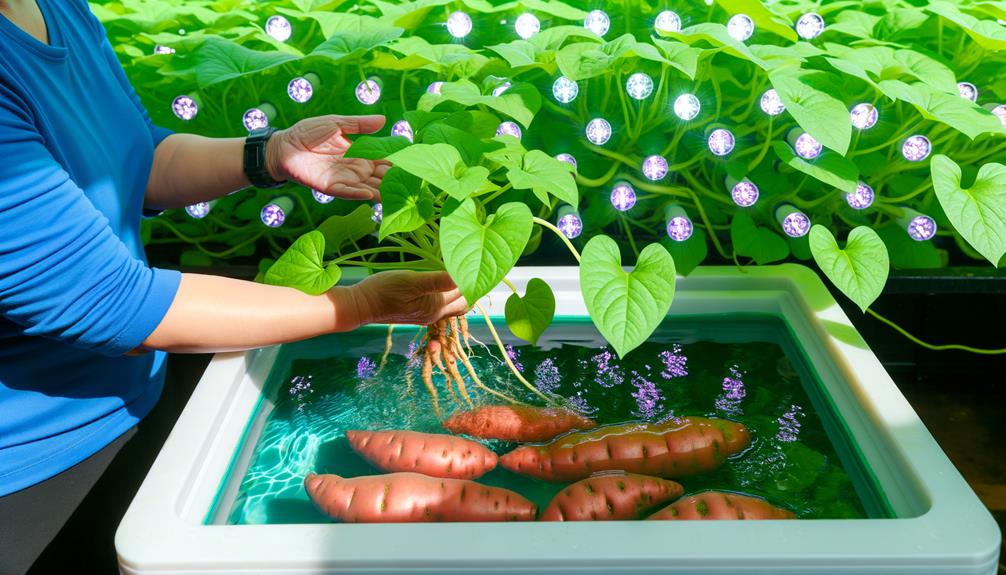

Properly timing the harvesting of hydroponically grown sweet potatoes is essential for optimizing tuber quality and maximizing yield. Typically, sweet potatoes reach maturity within 90 to 120 days. Monitoring indicators such as foliage yellowing and reduced growth rates can signal readiness. Maintenance involves regular inspection for root health, nutrient solution stability, and pH balance. Key parameters include:
| Parameter | Ideal Range | Maintenance Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| pH Levels | 5.5 – 6.5 | Weekly |
| EC (Electrical Conductivity) | 1.8 – 2.4 mS/cm | Bi-weekly |
| Water Temperature | 20 – 25°C | Daily |
| Oxygen Levels | 6-8 ppm | Continuous Monitoring |
Adhering to these guidelines guarantees sustainable growth and high-quality yields, essential for advancing hydroponic sweet potato cultivation. By carefully managing nutrient solutions and monitoring environmental conditions, farmers can optimize plant health and productivity. Understanding how to grow potatoes hydroponically allows growers to maximize space efficiency while reducing water consumption compared to traditional soil farming. Implementing these best practices ensures a consistent and profitable harvest.
Conclusion
Hydroponically grown sweet potatoes exhibit significant potential, with yields surpassing traditional soil methods by up to 30%.
This method necessitates precise control over nutrient solutions and lighting, ensuring ideal growing conditions.
Utilizing systems such as nutrient film technique (NFT) or deep water culture (DWC) can maximize efficiency.
The preparation of sweet potato slips and diligent maintenance are critical for success, illustrating the intersection of advanced agricultural techniques and innovative horticultural practices.
This underscores the future of sustainable crop production.






