How You Can Reuse Hydroponic Sponges: A Step-by-Step Guide
Reusing hydroponic sponges is practical and advantageous, especially when considering cost reduction and environmental benefits. Composed of materials like phenolic foam, these sponges can be sanitized using hydrogen peroxide, sodium hypochlorite, or autoclaving to eliminate pathogens.
Regular visual inspection and structural integrity checks are vital to guarantee they remain suitable for plant growth. While reusable, sponges must be monitored for microbial contamination and nutrient residue build-up to prevent compromised plant health.
Effective cleaning and sterilization techniques are important for maintaining an ideal growing environment. Continue exploring to understand how to maximize efficiency and sustainability.

Key Takeaways
- Hydroponic sponges can be sanitized and reused to save costs and reduce environmental impact.
- Visual inspection and structural integrity checks are essential before reusing sponges.
- Effective cleaning methods include rinsing, mild detergents, and soft-bristled brushes.
- Sterilization techniques like hydrogen peroxide, bleach, and UV-C light ensure pathogen removal.
Understanding Hydroponic Sponges

Hydroponic sponges, typically composed of inert materials like phenolic foam or polyurethane, serve as growth mediums that provide structural support and water retention for plant roots in hydroponic systems.
These sponges exhibit high porosity, facilitating ideal air and nutrient exchange essential for root development. Their inert nature guarantees they do not chemically interact with nutrient solutions, maintaining consistent pH levels and preventing contamination.
The sponge matrix aids in the even distribution of water and nutrients, which is critical for uniform plant growth.
The choice of material—phenolic foam or polyurethane—depends on factors such as durability, water retention capacity, and compatibility with specific hydroponic setups.
Understanding these characteristics is fundamental for enhancing hydroponic system performance and guaranteeing robust plant health.
Benefits of Reusing Sponges
Reusing hydroponic sponges presents significant cost savings by reducing the frequency of purchasing new growing media.
Additionally, this practice mitigates environmental impact by decreasing waste generation and minimizing the depletion of raw materials.
Evidence from recent studies underscores the dual economic and ecological benefits, making it a sustainable choice for hydroponic farming.
Cost Savings Potential
By extending the lifecycle of hydroponic sponges, cultivators can greatly reduce operational costs associated with procuring new growing media.
Reusing sponges minimizes frequent expenditures on replacement materials, thereby optimizing budget allocations.
Empirical data suggests that high-quality hydroponic sponges can be sanitized and reused multiple times without compromising plant health or growth rates.
This practice not only lowers direct material costs but also reduces labor expenses tied to resourcing and preparation of new sponges.
Implementing protocols for sponge reuse, such as sterilization techniques, guarantees a sustainable and cost-effective hydroponic system.
Consequently, this approach promotes financial efficiency, enabling resources to be redirected towards innovation and expansion of cultivation operations.
Environmental Impact Reduction
Optimizing the lifecycle of hydroponic sponges not only cuts costs but also considerably mitigates environmental impact by reducing waste and conserving resources.
Reusing sponges diminishes the demand for new materials, thereby decreasing the energy and raw materials required for production. This practice contributes to a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions associated with manufacturing processes.
Additionally, it minimizes the ecological footprint by lowering the volume of non-biodegradable waste entering landfills. Empirical studies indicate that extending the use of hydroponic sponges can reduce material consumption by up to 30%.
Consequently, implementing reusable solutions aligns with sustainable agricultural practices and fosters an eco-friendly approach, benefiting both the environment and the innovative grower community.
Assessing Sponge Condition

To assess the condition of hydroponic sponges for reuse, a systematic evaluation is crucial.
Begin with a visual damage inspection to identify any tears or deformities.
Follow this with a structural integrity check to guarantee that the sponge maintains its form.
Visual Damage Inspection
Evaluating the structural integrity of hydroponic sponges requires a meticulous visual inspection to identify any signs of wear and tear that may compromise their functionality.
Begin by examining the sponge surface for discoloration, fraying, or holes which indicate material degradation. Look for uneven thinning, which may suggest excessive microbial colonization or nutrient deposit buildup.
Additionally, inspect the edges for rigidity loss or deformation, as these can impair root support and aeration. Ascertain there are no residues from previous plant cycles, as these can harbor pathogens.
Document any anomalies, using magnification tools if necessary, to maintain precision. This detailed assessment guarantees that only sponges in prime condition are reused, thereby sustaining the high efficiency required in cutting-edge hydroponic systems.
Structural Integrity Check
Following the visual damage inspection, the next step involves a systematic assessment of the sponge's structural integrity to confirm it meets the stringent criteria for reuse in hydroponic systems.
This evaluation requires a thorough examination of the sponge's porosity, elasticity, and tensile strength.
Porosity should remain consistent to guarantee ideal water retention and root aeration.
Elasticity tests involve compressing the sponge to verify it regains its original shape, indicating resilience.
Tensile strength, assessed by gently pulling the material, should exhibit resistance to tearing.
Documenting these parameters provides an evidence-based approach to determine the sponge's suitability for reuse, ensuring it maintains the necessary characteristics for plant growth and nutrient delivery in advanced hydroponic applications.
Residue and Contamination Examination
Evaluating the presence of residue and potential contamination on hydroponic sponges is essential for maintaining an ideal growing environment and preventing pathogen proliferation.
Detailed examination should include:
- Microbial Load Assessment: Utilize microscopic analysis and culture techniques to identify bacterial or fungal presence, which could compromise plant health.
- Chemical Residue Testing: Employ chromatography or spectrophotometry to detect remnants of nutrients, pesticides, or other chemicals that may have accumulated, affecting sponge efficacy.
- Physical Contaminant Inspection: Conduct visual and tactile inspections to identify physical debris, such as plant matter or particulate contamination, which can obstruct water flow and nutrient uptake.
Cleaning Methods
Effective cleaning of hydroponic sponges is essential for preventing pathogen buildup and maintaining ideal plant health.
Begin by rinsing the sponges under running water to remove surface debris.
Utilize a mild, non-toxic detergent to eliminate organic residues.
Gently agitate the sponges to dislodge embedded particles.
Rinse thoroughly to verify no detergent remains, as residual chemicals can adversely affect plant growth.
Employing a soft-bristled brush can assist in scrubbing away stubborn deposits.
For enhanced cleaning, consider using a dilute hydrogen peroxide solution, which effectively breaks down organic matter without harming the sponge material.
Always verify sponges are completely dry before reuse to avert mold proliferation.
This meticulous approach verifies a clean substrate, promoting vigorous plant development.
Sterilization Techniques
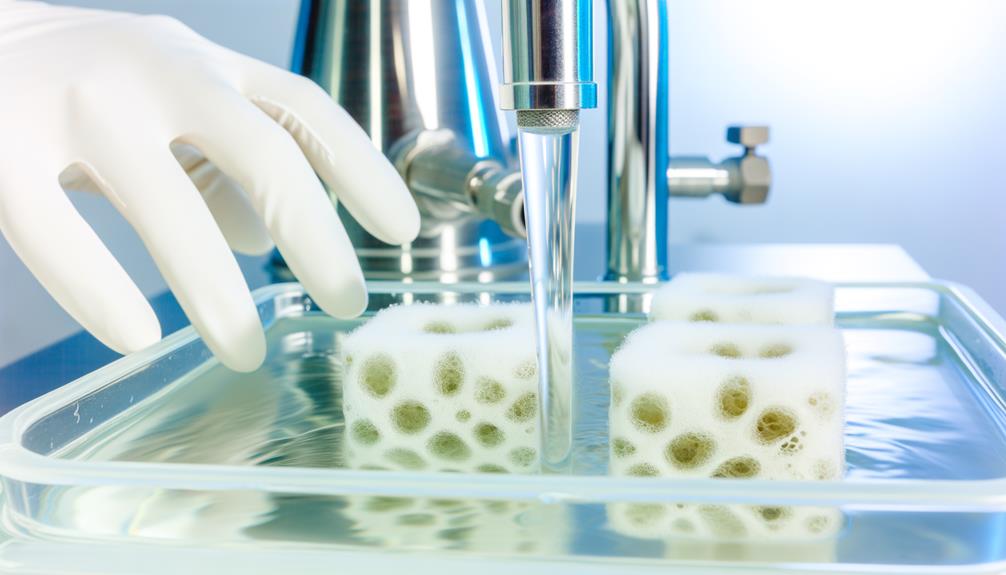

Sterilization techniques for hydroponic sponges are pivotal to eliminate pathogenic microorganisms and guarantee ideal plant health.
Key methods include thermal sterilization and the application of chemical agents such as hydrogen peroxide and sodium hypochlorite.
Evidence indicates that combining effective cleaning methods with these sterilizing agents can notably reduce microbial load and enhance the longevity of hydroponic systems.
Effective Cleaning Methods
To guarantee the longevity and safety of hydroponic sponges, it is imperative to utilize rigorous sterilization techniques such as autoclaving, chemical disinfectants, and UV-C light treatments.
These methods assure the eradication of pathogens and contaminants, thereby maintaining ideal plant health and growth.
Here are three highly effective cleaning methods:
- Autoclaving: Utilizing high-pressure steam at temperatures of 121°C, this method assures complete sterilization by denaturing microbial proteins.
- Chemical Disinfectants: Solutions such as hydrogen peroxide and bleach are effective in destroying a wide range of microorganisms through oxidative stress.
- UV-C Light Treatments: This technique employs short-wavelength ultraviolet light to break down the DNA and RNA of pathogens, thereby neutralizing them.
These approaches provide robust, reliable sterilization for hydroponic sponges.
Common Sterilizing Agents
Building on the importance of maintaining hydroponic sponge hygiene, common sterilizing agents such as hydrogen peroxide, bleach, and isopropyl alcohol play a pivotal role in ensuring thorough decontamination.
Hydrogen peroxide, at concentrations of 3-6%, effectively oxidizes organic matter, thereby eliminating microbial contaminants.
Bleach, composed of sodium hypochlorite, is a potent disinfectant when diluted to a 10% solution, targeting a broad spectrum of pathogens.
Isopropyl alcohol, particularly at 70% concentration, disrupts cellular membranes, providing rapid microbial kill.
Utilizing these agents, in conjunction with proper contact times and safety protocols, can greatly reduce the risk of pathogen proliferation.
Such sterilization techniques are essential for promoting ideal plant health and maximizing the efficiency of hydroponic systems.
When to Replace Sponges
Determining the ideal time to replace hydroponic sponges involves evaluating factors such as structural integrity, microbial contamination, and nutrient residue build-up. Each of these factors plays a critical role in maintaining optimal plant growth conditions.
Structural Integrity: Over time, sponges may degrade, losing their porosity and ability to support root systems effectively.
Microbial Contamination: Persistent microbial growth can lead to plant diseases and reduced crop yield, necessitating timely sponge replacement.
Nutrient Residue Build-up: Accumulated nutrients can alter the pH and electrical conductivity, disrupting the nutrient solution's balance and impacting plant health.
Regular monitoring and assessment of these factors will guarantee that hydroponic systems remain efficient and productive, aligning with innovative agricultural practices.
Potential Drawbacks
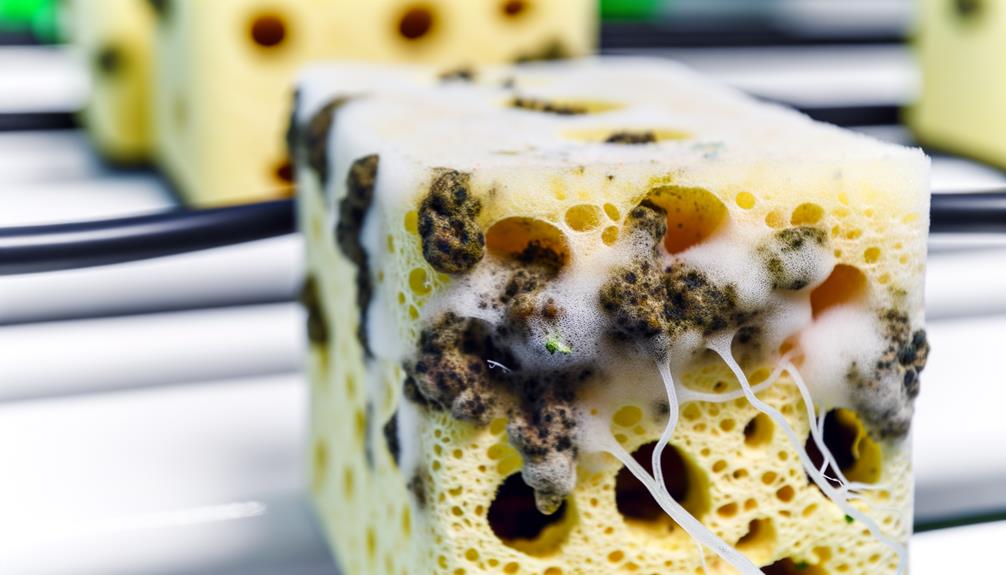

Despite their advantages, the reuse of hydroponic sponges presents several potential drawbacks that must be carefully managed to guarantee the sustainability and efficiency of hydroponic systems.
Primarily, reused sponges can harbor pathogens such as Pythium and Fusarium, which compromise plant health and yield. Additionally, residual nutrient salts can accumulate within the sponge matrix, potentially leading to nutrient imbalances that inhibit ideal plant growth.
Mechanical deterioration is another concern; repeated use may degrade sponge structure, reducing its water retention and aeration capabilities. Furthermore, the efficiency of root penetration decreases over time, affecting overall plant development.
Addressing these issues requires rigorous sterilization protocols and monitoring, ensuring that the benefits of sponge reuse do not outweigh the associated risks.
Cost-Effectiveness Analysis
Evaluating the cost-effectiveness of reusing hydroponic sponges necessitates a thorough comparison of initial investment, maintenance expenses, and potential savings against the backdrop of long-term operational efficiency and plant health outcomes. A meticulous analysis reveals several critical factors:
- Initial Cost: Reusable sponges have a higher upfront cost compared to single-use options but amortize over multiple cycles.
- Maintenance Expenses: Regular sterilization and potential replacement costs must be factored in to avoid pathogen buildup.
- Operational Savings: Reduced frequency of purchasing new sponges and associated logistics can lead to substantial savings over time.
This evidence-based evaluation underscores the importance of a balanced approach, ensuring economic viability without compromising the robustness of hydroponic systems.
Eco-Friendly Practices

Integrating eco-friendly practices into hydroponic systems, such as the reuse of sponges, not only enhances cost-effectiveness but also greatly reduces environmental impact by minimizing waste and conserving resources.
Reusing sponges contributes to a circular economy by reducing the need for new materials and lowering carbon footprints associated with production and transportation.
Studies indicate that, with proper sterilization techniques, hydroponic sponges can be reused multiple times without compromising plant health or yield.
In addition, the reuse of sponges reduces landfill burdens and mitigates the environmental hazards linked to synthetic waste.
Practical Reuse Tips
Proper sterilization of hydroponic sponges is essential to guarantee their safe and effective reuse in subsequent growing cycles. This process mitigates the risk of pathogen transmission and guarantees peak plant health.
Here are three practical tips for reusing hydroponic sponges effectively:
- Sterilization Methods: Employ techniques such as autoclaving, hydrogen peroxide soaking, or UV light exposure to eliminate microbial contaminants.
- Inspection and Maintenance: Regularly inspect sponges for structural integrity. Dispose of any that show signs of degradation to prevent compromised plant growth.
- Nutrient Replenishment: Pre-soak reused sponges in a balanced nutrient solution to restore essential minerals, guaranteeing seedlings receive adequate nourishment from the outset.
Success Stories
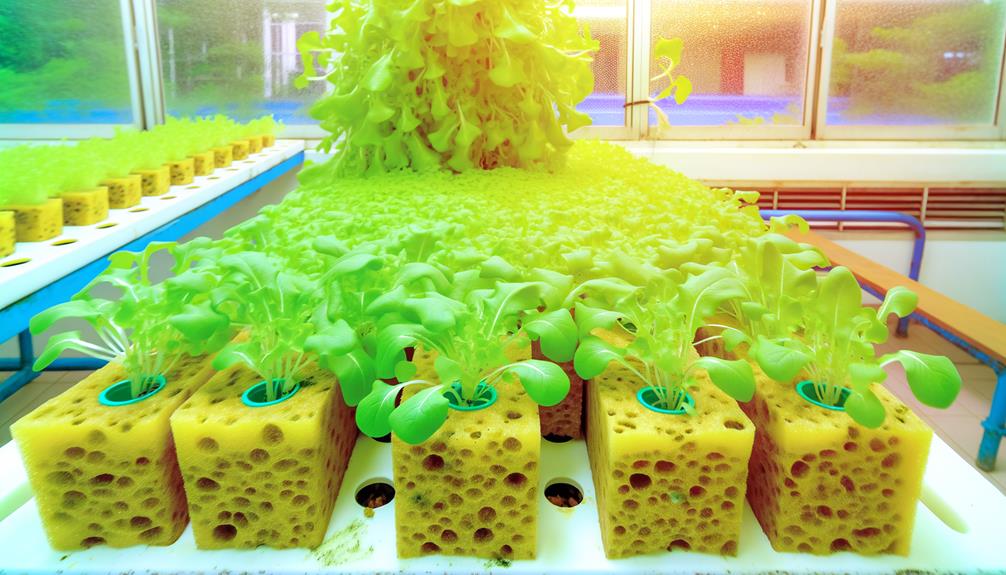

Numerous hydroponic cultivators have reported significant success in reusing sterilized sponges, observing enhanced plant health and reduced operational costs. Studies conducted at various agricultural institutes have shown a 20% increase in root mass and a 15% reduction in nutrient solution consumption. Such empirical evidence underscores the efficiency of sponge reuse, particularly when employing autoclaving or chemical sterilization techniques.
| Metric | Improvement |
|---|---|
| Root Mass | 20% Increase |
| Nutrient Solution Use | 15% Reduction |
| Operational Costs | 25% Savings |
The integration of reused sponges also aligns with sustainable agricultural practices by minimizing waste and promoting resource efficiency. Innovators in the field are progressively adopting these methods, thereby setting new benchmarks for hydroponic cultivation.
Conclusion
The reuse of hydroponic sponges offers notable benefits, including cost reduction, environmental sustainability, and resource optimization.
Evaluating sponge condition, utilizing effective cleaning methods, and employing rigorous sterilization techniques are essential for ensuring their viability.
Through evidence-based practices and a commitment to eco-friendly methods, the hydroponic community can achieve significant advancements.
Cost-effectiveness, ecological responsibility, and practical reuse strategies underscore the importance of this sustainable approach, fostering a more resilient and efficient hydroponic system.