DIY Hydroponic System for Strawberries in 3 Simple Steps
For a DIY hydroponic system tailored to strawberries, consider the Nutrient Film Technique (NFT) due to its ideal nutrient delivery. Essential components include nutrient solutions rich in macro and micronutrients, pH meters to maintain a range of 5.5-6.5, and full-spectrum LED grow lights.
Substrates such as coco coir or perlite provide aeration and water retention. Reservoirs should be airtight and lightproof, with high-efficiency pumps ensuring nutrient flow.
Regular monitoring of pH and Electrical Conductivity (EC) levels is critical for nutrient uptake. To gain thorough insights into setup, planting, and maintenance, further guidance is available.
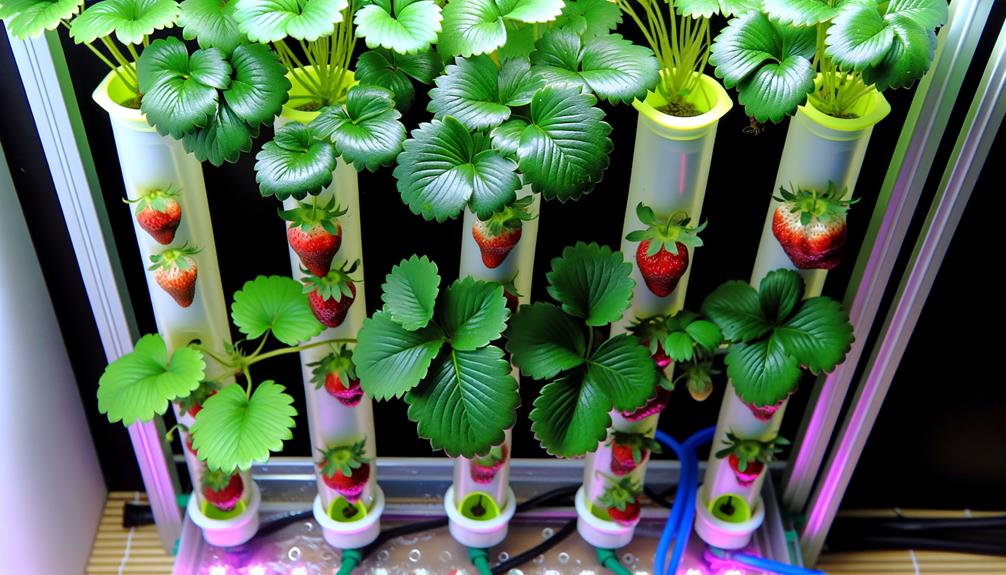

Key Takeaways
- Choose the Nutrient Film Technique (NFT) for efficient nutrient delivery and ideal growth conditions for strawberries.
- Use balanced nutrient solutions and maintain a pH range of 5.5-6.5 for optimal nutrient uptake.
- Install full-spectrum LED grow lights to simulate natural sunlight and enhance photosynthesis.
- Ensure proper aeration with air stones and efficient pumps to prevent root rot.
Choosing the Right System
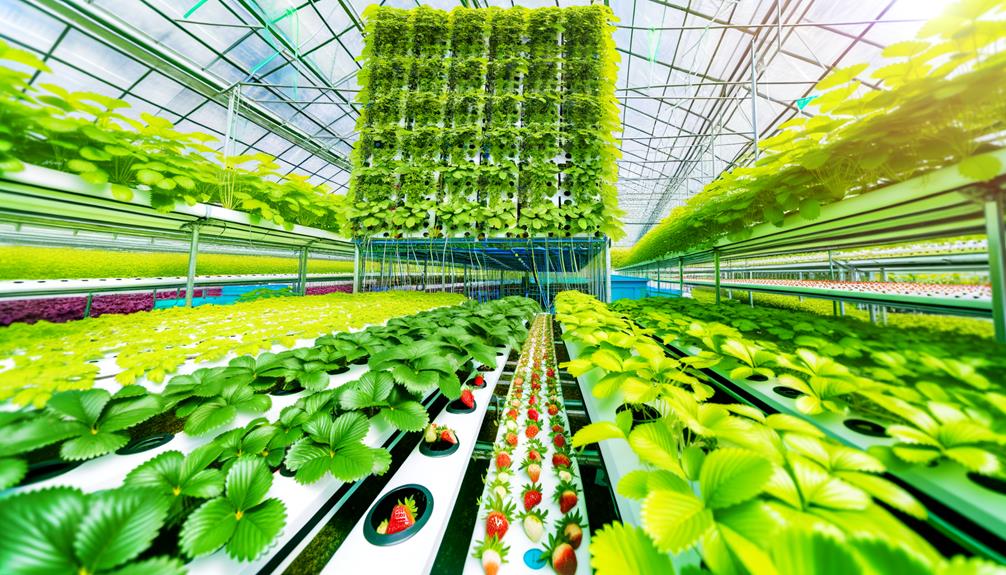

Selecting an appropriate hydroponic system for cultivating strawberries requires a detailed evaluation of various factors, including system types, spatial constraints, and resource availability.
Essential hydroponic systems include Nutrient Film Technique (NFT), Deep Water Culture (DWC), and Ebb and Flow systems.
NFT systems, characterized by a thin film of nutrient solution, are ideal for strawberries due to their efficient nutrient delivery.
DWC systems, involving plant roots submerged in nutrient-rich water, offer robust growth but necessitate vigilant oxygenation.
Ebb and Flow systems, which periodically flood and drain the root zone, provide excellent aeration but require precise timing mechanisms.
The choice of system hinges on spatial limitations, resource efficiency, and the grower's technical proficiency, ensuring optimal growth and yield of strawberries.
Essential Materials and Tools
To construct an efficient hydroponic system for strawberries, one must gather specific materials and tools, including high-quality nutrient solutions, pH meters, grow lights, and appropriate substrates such as coco coir or perlite.
The nutrient solution should be meticulously balanced to provide essential macro and micronutrients, optimizing plant growth and fruit yield.
pH meters are essential for maintaining an ideal pH range (typically 5.5-6.5) to guarantee nutrient availability.
Advanced LED grow lights simulate sunlight, promoting photosynthesis and extending the growing season.
Substrates like coco coir or perlite offer excellent aeration and water retention properties, vital for root health.
Additionally, net pots, air stones, and water pumps are indispensable for maintaining a well-aerated and nutrient-rich environment.
Setting Up Your Hydroponic System
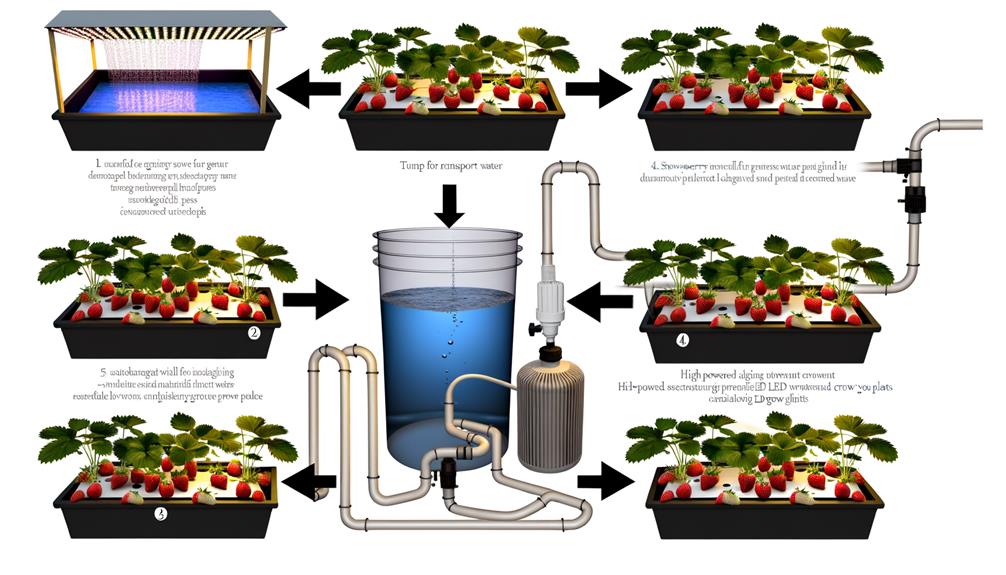
Establishing a hydroponic system for strawberry cultivation necessitates a methodical approach to secure ideal plant health and productivity. Precision in assembling components guarantees robust growth and maximizes yield.
Key steps involve selecting an appropriate hydroponic setup—whether it be NFT (Nutrient Film Technique) or DWC (Deep Water Culture)—and securing proper spacing to avert overcrowding and promote optimal air circulation. Nutrient delivery must be meticulously calibrated with a balanced pH and Electrical Conductivity (EC) levels.
- Reservoir Configuration: Secure an airtight, lightproof nutrient reservoir to prevent algae growth.
- Pump Selection: Utilize high-efficiency pumps for consistent nutrient flow.
- Grow Lights: Implement full-spectrum LED lights to simulate natural sunlight.
This foundation underpins successful hydroponic strawberry cultivation.
Planting and Care Tips
Proper planting and care of strawberries in a hydroponic system necessitate precise attention to plant physiology and environmental control to guarantee optimal growth and fruit production.
Initiate by selecting disease-resistant cultivars and ensuring a suitable pH range of 5.5-6.5 for nutrient solutions.
Maintain an electrical conductivity (EC) of 1.5-2.5 mS/cm to facilitate nutrient uptake.
Implement a photoperiod of 8-12 hours of light to enhance photosynthesis.
Monitor temperature, keeping it within 18-24°C to avoid thermal stress.
Prune runners and decaying leaves to allocate more resources to fruit-bearing structures.
Regularly check for balanced nutrient levels, particularly nitrogen, potassium, and calcium, to prevent deficiencies.
Employ high-efficiency LED grow lights and automated irrigation systems for precision and consistency.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
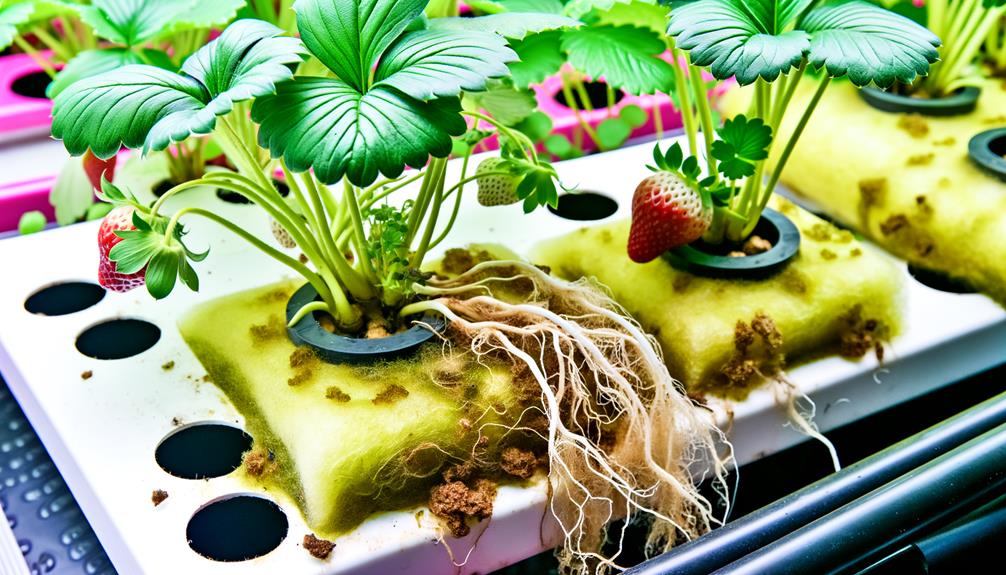

Identifying and addressing common issues in a hydroponic system for strawberries is vital to maintaining plant health and maximizing fruit yield. Monitoring and mitigating these challenges can enhance system efficiency and crop productivity. Regularly checking nutrient levels, pH balance, and water quality helps prevent deficiencies and imbalances that could hinder plant growth. Proper aeration and disease management also contribute to creating the best hydroponic system for strawberries, ensuring optimal conditions for root development. By promptly addressing these factors, growers can achieve higher yields and healthier plants.
- Nutrient Imbalance: Guarantee precise calibration of nutrient solutions to prevent deficiencies or toxicities that can impact plant growth.
- pH Fluctuations: Regularly test and adjust pH levels to maintain an ideal range of 5.5-6.5, essential for nutrient uptake.
- Root Rot: Implement proper aeration and drainage protocols to mitigate the risk of pathogen development in the root zone.
Addressing these issues promptly guarantees robust strawberry production in hydroponic systems.
Conclusion
To sum up, constructing a hydroponic system for strawberries symbolizes the meticulous orchestration of nature and technology, transforming raw materials into a harmonious ecosystem.
This synthesis requires understanding hydroponic principles, precise assembly, and vigilant maintenance.
The successful cultivation of strawberries through this method not only yields bountiful harvests but also represents the triumph of scientific ingenuity over traditional agricultural constraints, embodying the essence of innovative horticultural practices.






