Diy Hydroponics System in 3 Steps from Builders Guide 3rd Edition
The 'DIY Hydroponics System Builders Guide 3rd Edition' offers an in-depth, methodical approach to constructing hydroponic systems tailored to specific plant requirements and environmental conditions. It covers fundamental hydroponics principles, including optimizing nutrient solutions, managing pH levels, and selecting appropriate materials like pH meters, submersible pumps, and grow lights.
Detailed guidance is provided on various systems like Nutrient Film Technique (NFT) and Deep Water Culture (DWC). The guide also emphasizes regular maintenance practices such as water quality checks and pH monitoring, and offers solutions to common issues like nutrient imbalances and pest infestations.
Dive further to master these advanced techniques and cost-saving strategies for efficient hydroponic farming.

Key Takeaways
- Hydroponics systems grow plants without soil using nutrient-rich water, reducing water use by up to 90% compared to traditional farming.
- Essential tools for building a hydroponics system include pH meters, submersible pumps, grow lights, and air stones for optimal plant growth.
- Nutrient solutions require precise mixing of macronutrients, micronutrients, and pH adjusters, with regular monitoring for balanced plant nourishment.
- Selecting appropriate containers and growing mediums like Rockwool or clay pebbles is crucial for moisture retention and root aeration.
Understanding Hydroponics
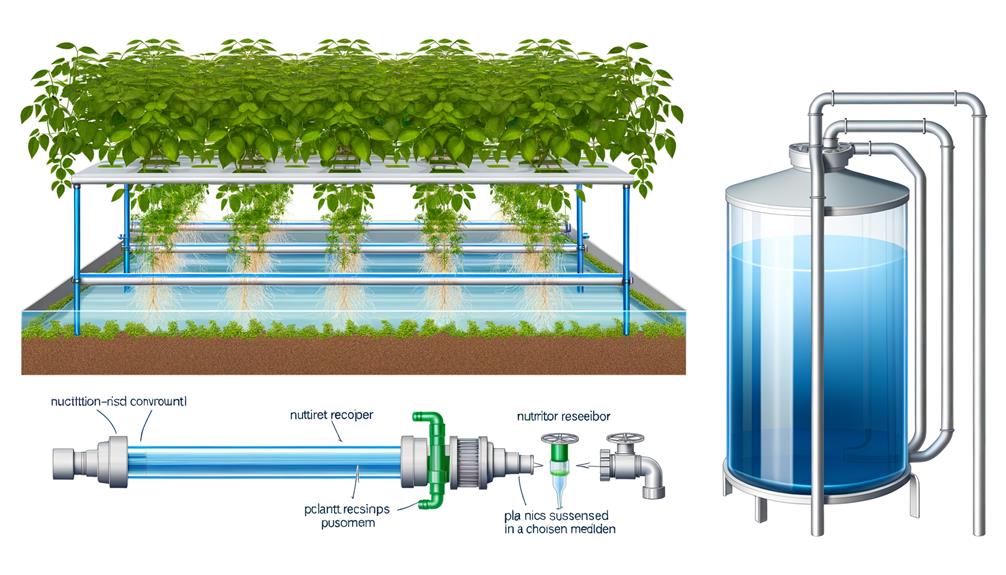
Hydroponics, a method of growing plants without soil, utilizes nutrient-rich water solutions to deliver essential minerals directly to plant roots. This technique offers several advantages over traditional soil-based agriculture.
By controlling nutrient concentrations and pH levels, hydroponic systems can optimize plant growth conditions, leading to faster growth rates and higher yields.
In addition, hydroponics reduces water consumption by up to 90% compared to conventional farming, making it an environmentally sustainable option. The absence of soil also eliminates soil-borne diseases and pests, reducing the need for chemical pesticides.
Systems such as nutrient film technique (NFT), deep water culture (DWC), and aeroponics each offer unique mechanisms for nutrient delivery. Understanding these principles is vital for designing efficient, high-performance hydroponic systems.
Required Materials
To construct an efficient hydroponics system, a precise understanding of the required materials is essential.
This section will outline the essential tools, enumerate the specific ingredients for nutrient solutions, and discuss the selection criteria for containers and growth mediums.
Essential Tools List
A thorough hydroponics system necessitates a precise collection of tools and materials to guarantee peak functionality and efficiency. Each tool plays a critical role in making certain the system operates seamlessly, from construction to maintenance. Below is a detailed list of essential tools required for building a hydroponics system.
| Tool | Purpose | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| pH Meter | Measures nutrient solution acidity | Essential for nutrient balance |
| Submersible Pump | Circulates water and nutrients | Choose appropriate flow rate |
| Grow Lights | Provides artificial sunlight | LED recommended for efficiency |
| Air Stones | Aerates nutrient solution | Enhances root oxygenation |
Accurate use of these tools guarantees peak plant growth, fostering an environment that supports innovative agricultural practices. Each item is integral to maintaining the system's stability and productivity, making it essential for any serious hydroponics enthusiast.
Nutrient Solution Ingredients
After guaranteeing the proper tools are ready and available, the next step involves understanding the specific ingredients needed for an ideal nutrient solution.
The nutrient solution is essential for providing plants with important minerals and nutrients, enabling peak growth within a hydroponic system.
The primary ingredients include:
- Macronutrients: Elements like nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K) are fundamental for plant development, promoting foliage, root growth, and overall health.
- Micronutrients: Trace elements such as iron (Fe), manganese (Mn), and zinc (Zn) are critical for enzymatic functions and metabolic processes.
- pH Adjusters: Compounds like phosphoric acid or potassium hydroxide guarantee the nutrient solution remains within the ideal pH range of 5.5 to 6.5.
- Chelating Agents: These compounds, such as EDTA, help maintain nutrient solubility and prevent precipitation, guaranteeing nutrients are readily available for plant uptake.
Container and Medium Selection
Selecting the appropriate container and growing medium is essential for establishing a successful hydroponic system, as they directly influence plant support, nutrient delivery, and root aeration.
Containers should be non-reactive and opaque to prevent algae growth, with sufficient drainage and aeration holes. Popular choices include food-grade plastic bins and specialized hydroponic trays.
The growing medium must be inert, stable, and capable of retaining moisture while allowing adequate oxygen flow. Rockwool, clay pebbles, and perlite are favored for their balanced moisture retention and aeration properties.
Each medium has unique characteristics; for instance, Rockwool provides excellent support and moisture retention, whereas clay pebbles enhance root aeration.
Selecting the best combination of container and medium is pivotal for maximizing plant health and yield.
Choosing a System

Determining the most suitable hydroponic system involves analyzing factors such as plant type, available space, budget, and the desired complexity of the setup.
Each system offers unique benefits and potential limitations, necessitating a strategic approach to selection.
To aid in decision-making, consider the following systems:
- Nutrient Film Technique (NFT) – Ideal for small, lightweight plants; requires continuous nutrient flow.
- Deep Water Culture (DWC) – Perfect for larger plants; involves submerging roots in oxygenated nutrient solution.
- Ebb and Flow (Flood and Drain) – Versatile; periodically floods the grow tray with nutrient solution.
- Drip System – Provides precise nutrient delivery; suited for a variety of plant types.
Analyzing these systems in the context of your specific needs will facilitate a successful hydroponic venture.
Building Basics
To construct an effective hydroponics system, it is vital to understand the fundamental components and their respective roles in supporting plant growth.
The primary elements include a reservoir for nutrient solution storage, a pump for nutrient delivery, grow trays, and a lighting system.
The reservoir must be constructed from durable, non-reactive materials to prevent contamination.
The pump must deliver nutrients consistently, guaranteeing even distribution.
Grow trays, often made from food-grade plastic, support root systems and facilitate water drainage.
High-efficiency LED grow lights mimic solar energy, fostering ideal photosynthesis.
Additionally, an air stone and air pump guarantee oxygenation, critical for root respiration.
Mastery of these components enhances system reliability and plant yield, driving innovation in hydroponic cultivation.
Nutrient Solutions

Understanding nutrient solutions is critical for the success of any hydroponics system, as they provide the essential minerals required for plant growth.
This section will examine the key components that constitute an effective nutrient mix and offer practical guidelines for proper blending and ongoing maintenance.
Ensuring the correct balance and regular monitoring of these solutions can greatly impact plant health and yield.
Essential Nutrient Components
A hydroponic system's success hinges critically on the precise formulation and management of nutrient solutions, which supply plants with the essential elements required for ideal growth and development.
These nutrient solutions must encompass a balanced mixture of macro and micronutrients. Essential components include:
- Nitrogen (N): Important for leaf and stem growth, nitrogen is a key component of chlorophyll and amino acids.
- Phosphorus (P): Essential for energy transfer and root development, phosphorus plays a significant role in photosynthesis.
- Potassium (K): Significant for overall plant health, potassium regulates water uptake and enzyme activation.
- Micronutrients: These include iron, manganese, zinc, copper, molybdenum, and boron, which are necessary in trace amounts for various physiological functions.
Attention to these elements guarantees robust plant health and ideal growth conditions.
Mixing and Maintenance Tips
Consistently achieving ideal nutrient balance in your hydroponics system requires meticulous mixing procedures and vigilant maintenance practices. Begin by accurately measuring each nutrient component, guaranteeing proportions align with plant-specific requirements. Utilize high-quality water, ideally deionized or reverse osmosis treated, to prevent contamination. Regularly monitor pH levels, aiming for a range of 5.5 to 6.5, and adjust using pH up or down solutions. Weekly nutrient solution changes are recommended to avert nutrient imbalances and pathogen proliferation.
| Task | Frequency | Tools Required |
|---|---|---|
| Measure nutrient components | Every mixing | Precision scale, beakers |
| Monitor pH levels | Daily | pH meter |
| Adjust pH | As needed | pH up/down solutions |
| Change nutrient solution | Weekly | Fresh nutrient mix, tanks |
| Inspect for pathogens | Weekly | Microscope, test kits |
Implementing these steps guarantees a thriving hydroponic environment.
Lighting Options
Selecting the appropriate lighting options is critical for enhancing plant growth in a hydroponic system. Effective illumination directly influences photosynthesis, impacting both yield and quality.
Several advanced lighting technologies cater to different needs:
- LED Lights: Energy-efficient and customizable, LEDs offer adjustable spectra to match plant growth stages.
- High-Pressure Sodium (HPS) Lights: Ideal for flowering phases due to their high-intensity yellow-red spectrum.
- Metal Halide (MH) Lights: Provide blue spectrum light, beneficial for vegetative growth.
- Fluorescent Lights: Cost-effective and suitable for seedlings and low-light plants.
Each option presents unique advantages, from energy efficiency to specific spectral outputs, making it essential to match the light type with plant requirements and growth phases for maximum results.
Plant Selection
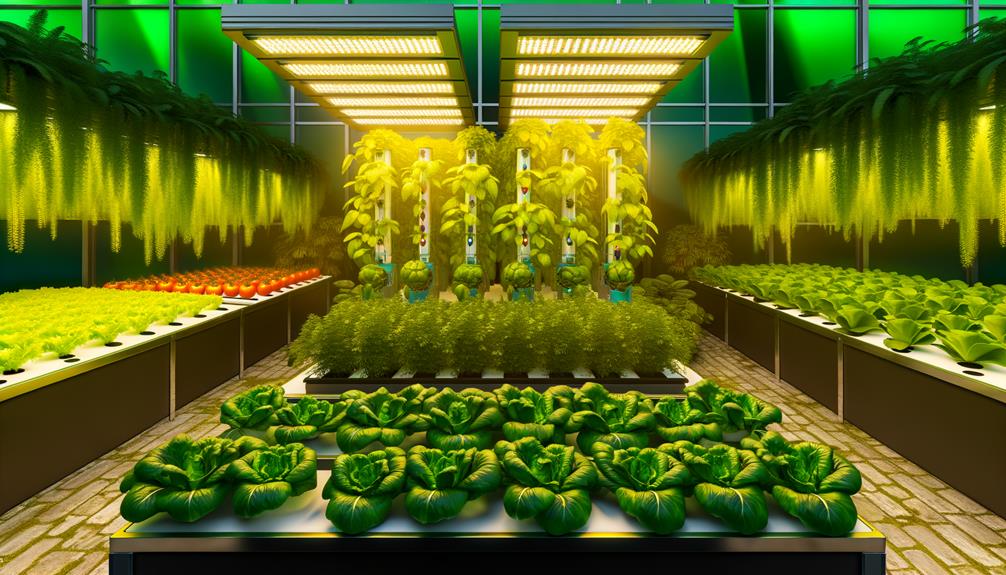

Choosing the right plants for a hydroponic system involves evaluating factors such as growth rate, space requirements, and nutrient needs to guarantee ideal performance and yield.
Fast-growing plants like lettuce and spinach are excellent for beginners due to their minimal space and nutrient demands. Conversely, fruiting plants such as tomatoes and peppers necessitate precise nutrient management and larger growth areas.
Significantly, selecting plants with similar nutrient profiles can streamline nutrient solution maintenance. Additionally, consider the plant's adaptability to a hydroponic environment; some species may be more resilient to this soilless technique.
Maintenance Tips
Maintenance of a DIY hydroponics system necessitates stringent regular water quality checks and meticulous nutrient solution management to guarantee ideal plant growth.
Regular monitoring of pH levels, electrical conductivity, and temperature is critical for maintaining water quality.
Additionally, precise formulation and periodic adjustment of the nutrient solution are essential to meet the specific nutritional requirements of the plants.
Regular Water Quality Checks
Performing regular water quality checks is vital to guarantee the best growth conditions in a hydroponics system, as it directly influences nutrient availability and plant health.
Consistent monitoring guarantees that parameters remain within ideal ranges, thereby preventing potential issues.
Key aspects to monitor include:
- pH Levels: Maintaining pH between 5.5 and 6.5 is essential for nutrient uptake.
- Electrical Conductivity (EC): Indicates nutrient concentration; ideal levels vary by plant species.
- Dissolved Oxygen (DO): Adequate oxygen levels (5-8 ppm) are necessary for root respiration.
- Temperature: Water temperature should be kept between 65°F and 75°F to avoid bacterial growth and promote nutrient solubility.
Regular checks and adjustments will foster a thriving hydroponic environment, advancing both plant vigor and yield.
Nutrient Solution Management
Effectively managing the nutrient solution in a hydroponics system is paramount for ensuring ideal plant growth and health.
Regularly monitor and adjust the pH levels, aiming for a favorable range of 5.5 to 6.5.
Utilize electrical conductivity (EC) meters to measure nutrient concentration, ensuring it aligns with plant-specific requirements.
Replenish the nutrient solution bi-weekly to prevent imbalances and microbial growth.
Incorporate chelated micronutrients to enhance nutrient uptake.
Implement a recirculation system to maintain consistent nutrient distribution.
Employ water quality tests to detect contaminants and preempt potential issues.
Common Issues
Although hydroponic systems offer numerous advantages, they are not without their challenges, including nutrient imbalances, pH fluctuations, and potential pest infestations. Addressing these issues is critical for ideal plant growth and system efficiency. Proper monitoring and maintenance are essential to prevent these problems and ensure a stable growing environment. For those new to hydroponics, starting with the best hydroponic system for beginners can help minimize complications while allowing them to learn the fundamentals. Selecting a user-friendly setup with automated nutrient and pH regulation can significantly improve success rates and plant health.
Here are some common problems encountered in hydroponics:
- Nutrient Imbalances: Excess or deficiency in essential nutrients can stunt plant growth. Regular monitoring and adjusting of nutrient solutions is crucial.
- pH Fluctuations: Hydroponic systems require a stable pH level to guarantee nutrient availability. Frequent testing and adjustments help maintain the desired pH range.
- Pest Infestations: Despite being soil-free, pests can still invade hydroponic setups. Implementing integrated pest management (IPM) strategies can mitigate this risk.
- Waterborne Diseases: Pathogens can proliferate in nutrient solutions, necessitating regular sterilization and the use of disease-resistant plant varieties.
Advanced Techniques
Implementing advanced techniques in hydroponics can markedly enhance system efficiency and crop yield through precise environmental control and specialized equipment. Key approaches include the utilization of automated nutrient delivery systems, advanced lighting technologies such as LED grow lights, and environmental monitoring via IoT sensors. These technologies allow for real-time adjustments to improve plant growth conditions.
| Technique | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Automated Nutrient Delivery | Guarantees consistent nutrient levels |
| LED Grow Lights | Energy-efficient and spectrum-tuned |
| IoT Environmental Sensors | Real-time monitoring and control |
| pH and EC Monitoring Systems | Precision in nutrient solution management |
| Climate Control Systems | Maintains ideal temperature and humidity |
Incorporating these sophisticated methodologies requires a deep understanding of plant physiology and system dynamics, offering a pathway to maximizing productivity and innovation in hydroponic farming.
Cost-Saving Ideas
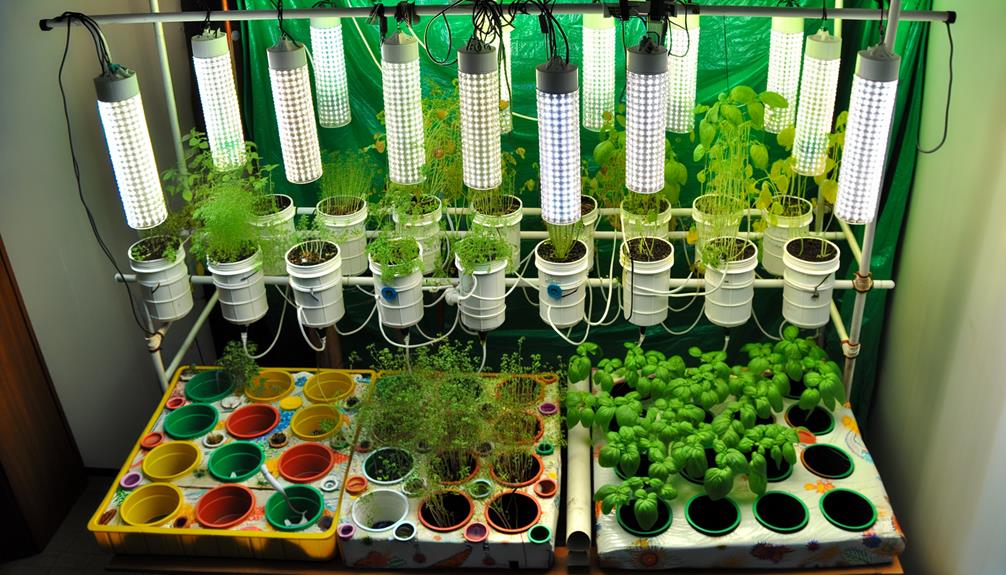

While advanced techniques can greatly enhance a hydroponic system's performance, exploring cost-saving ideas is equally important for maintaining long-term sustainability and profitability. Implementing cost-efficient strategies not only reduces initial investments but also minimizes operational expenses.
Here are some practical cost-saving tips:
- DIY Nutrient Solutions: Formulate your own nutrient mixes using bulk fertilizers. This approach can notably cut costs compared to pre-made solutions.
- Recycled Materials: Utilize recycled containers and materials for constructing grow beds and reservoirs. This reduces waste and saves money.
- Energy-Efficient Lighting: Invest in LED grow lights, which use less electricity and have a longer lifespan compared to traditional lighting.
- Water Reclamation Systems: Install systems to capture and reuse water, reducing water consumption and associated costs.
These strategies guarantee a more economical and sustainable hydroponic operation.
Conclusion
Coincidentally, the mastery of hydroponics—a method of soilless cultivation—necessitates an intricate balance of materials, system selection, construction acumen, precise nutrient solutions, regular maintenance, troubleshooting, advanced methodologies, and cost-effective practices.
The convergence of these elements guarantees the optimization of plant growth and the efficiency of the hydroponic system.
Such thorough understanding and application of hydroponics not only maximizes agricultural productivity but also advances sustainable farming practices, highlighting the critical intersection of innovation and ecological stewardship.






