Do Drip Hydroponics Systems Run Constantly or Intermittently?
Drip hydroponics systems can operate either continuously or intermittently, tailored to the specific plant's needs. Continuous systems provide constant nutrient delivery, ensuring stable pH levels and ideal growth.
In contrast, intermittent systems enhance root aeration, reducing the risk of root zone saturation and disease. The choice largely depends on plant type and growth stage, with extensive-root plants like tomatoes favoring continuous delivery, while leafy greens benefit from intermittent flow.
Effective management of these systems requires precise control of nutrient delivery and environmental conditions. Advancing your understanding includes exploring maintenance practices, nutrient management, and environmental optimizations for optimal results.

Key Takeaways
- Drip hydroponics systems can run continuously or intermittently depending on plant type and growth stage requirements.
- Continuous drip systems provide steady nutrient delivery, optimizing growth and maintaining stable pH levels.
- Intermittent drip systems improve root aeration and reduce the risk of root diseases by minimizing saturation.
- Both continuous and intermittent systems are used based on specific crop needs and environmental conditions.
Understanding Drip Hydroponics
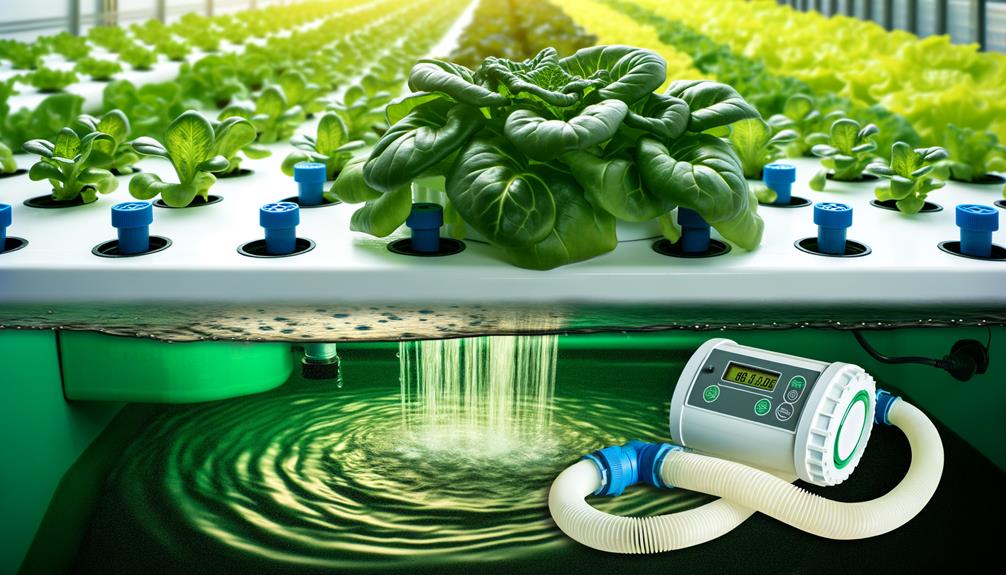

Drip hydroponics is a precise method of nutrient delivery in which a controlled flow of nutrient solution is administered directly to the plant roots through an intricate network of tubes and emitters.
This system offers unparalleled accuracy in nutrient distribution, promoting ideal growth conditions by ensuring each plant receives the necessary nutrients in exact quantities.
The customization of emitter flow rates allows for fine-tuning based on specific plant needs, thereby enhancing efficiency and resource utilization.
In addition, the adoptive flexibility of drip hydroponics supports various plant species, making it a versatile choice for innovative agricultural practices.
Continuous Vs. Intermittent Flow
In evaluating continuous drip versus intermittent flow systems, it is essential to take into account the advantages unique to each method.
Continuous drip systems offer consistent nutrient delivery, optimizing plant growth and reducing the risk of nutrient imbalances.
Conversely, intermittent flow systems provide opportunities for root zone aeration, which can enhance oxygen availability and support robust root development.
Continuous Drip Advantages
By maintaining a consistent nutrient solution delivery, continuous drip systems offer enhanced control over the growing environment compared to intermittent flow systems.
This steady supply guarantees optimal nutrient availability, mitigating the risk of nutrient imbalances and fostering uniform plant growth. Continuous drip systems also maintain stable pH levels, reducing the frequency of corrective interventions.
In addition, the perpetual flow minimizes the likelihood of root desiccation, promoting robust root development and overall plant health. This method particularly benefits crops with high water and nutrient demands, assuring they receive a constant and precise supply.
The continuous nature of these systems is conducive to automation and real-time monitoring, making them ideal for innovative growers seeking efficiency and high-yield outcomes.
Intermittent Flow Benefits
While continuous drip systems offer numerous advantages, the intermittent flow approach introduces distinct benefits that cater to different growing needs and conditions. By utilizing scheduled intervals, intermittent flow systems can optimize nutrient uptake and oxygenation, minimizing root zone saturation and reducing the risk of root diseases. This method also promotes more efficient water use, aligning with sustainable practices. The table below contrasts continuous and intermittent flow characteristics:
| Aspect | Continuous Flow | Intermittent Flow |
|---|---|---|
| Nutrient Uptake | Constant | Optimized |
| Root Health | Risk of Saturation | Enhanced Oxygenation |
| Water Efficiency | High Usage | Reduced Consumption |
Intermittent flow systems provide a balanced approach, enhancing overall plant health and resource management, thereby offering innovative solutions for modern horticulture.
Plant Type Considerations

Selecting the appropriate plant types for a drip hydroponics system involves evaluating factors such as root structure, growth cycle, and nutrient requirements to confirm peak performance and yield.
Plants with extensive root systems, like tomatoes or cucumbers, benefit from continuous nutrient delivery and aeration but may require careful monitoring to prevent root clogging.
Conversely, leafy greens such as lettuce and spinach, with less aggressive root growth, adapt well to intermittent drip systems, optimizing water and nutrient efficiency.
Additionally, understanding the specific nutrient profiles and growth rates of chosen plants confirms tailored nutrient solutions, minimizing waste and maximizing growth potential.
Analyzing these variables enables the precise calibration of drip schedules and nutrient formulations, fostering innovative agricultural practices within hydroponic systems.
Growth Stage Requirements
Understanding the specific requirements at each growth stage is critical for enhancing plant development in drip hydroponics systems.
Seedlings necessitate a tailored nutrient profile to guarantee robust initial growth, while the vegetative phase demands precise lighting conditions to promote healthy foliage.
During flowering, the frequency of water delivery must be adjusted to support ideal bud formation and maturation.
Seedling Nutrient Needs
Seedlings in drip hydroponics systems require a carefully balanced nutrient solution to support ideal growth during the initial stages of development.
Essential macronutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium must be precisely calibrated to promote robust root formation and early vegetative growth.
Additionally, micronutrients like calcium, magnesium, and iron are vital in trace amounts to prevent deficiencies and guarantee peak cellular function.
The nutrient solution's pH should be maintained between 5.5 and 6.5 to maximize nutrient uptake efficiency.
Continuous monitoring and adjustments are necessary to prevent nutrient imbalances that could hinder seedling development.
Employing advanced sensors and automated nutrient delivery systems guarantees precise control, fostering an environment conducive to rapid, healthy growth in innovative hydroponic setups.
Vegetative Phase Lighting
Ideal lighting during the vegetative phase is essential for promoting vigorous plant growth and preparing plants for the subsequent flowering stage in a drip hydroponics system.
High-intensity discharge (HID) lamps, such as metal halide (MH) lamps, are typically recommended due to their best spectrum for vegetative growth. Alternatively, energy-efficient LED grow lights can be customized to emit the specific wavelengths required for chlorophyll synthesis and robust development.
A photoperiod of 18 hours of light and 6 hours of darkness is commonly employed to maximize photosynthetic activity. Ensuring proper light intensity, measured in micromoles per square meter per second (µmol/m²/s), is critical to avoid light saturation or deficiency, thereby fostering uniform growth and best plant health during this pivotal phase.
Flowering Water Frequency
As plants enter the flowering stage in a drip hydroponics system, adjusting the water frequency becomes paramount to support the increased nutrient and hydration demands integral to bud development.
During this critical phase, maintaining ideal moisture levels is essential for maximizing floral yield and potency. Typically, the irrigation frequency should be increased to guarantee continuous nutrient delivery while preventing root zone saturation.
Advanced growers often employ automated timers and sensors to fine-tune irrigation schedules, thereby enhancing water use efficiency.
Monitoring electrical conductivity (EC) and pH levels further guarantees that nutrient uptake remains at its peak. Such precision in water management not only fosters robust bloom formation but also mitigates potential issues like nutrient lockout and root rot.
Environmental Factors

Several essential environmental factors must be meticulously controlled to enhance the performance of drip hydroponics systems. These factors include maintaining optimal nutrient concentration, pH levels, and oxygenation to ensure healthy plant growth. Understanding the differences between ebb vs flow vs drip systems helps growers choose the most efficient method for their specific crops and conditions. Proper monitoring and adjustments to temperature, humidity, and light exposure further contribute to maximizing yields in drip hydroponics.
These factors are pivotal in ensuring plant health and maximizing yield. Key environmental parameters include:
- Temperature: Maintaining an ideal temperature range (generally 18-26°C) is essential for nutrient uptake and plant metabolism.
- Humidity: Optimal relative humidity levels (50-70%) help prevent plant stress and diseases while promoting efficient transpiration.
- Light: Adequate light intensity and photoperiods are vital for photosynthesis and growth. Use of LED grow lights can provide precise control over light spectra.
- Air Quality: Ensuring proper ventilation and CO2 levels (around 400-800 ppm) enhances photosynthetic efficiency and overall plant vigor.
Precision in these parameters fosters an environment conducive to robust plant development.
Nutrient Delivery Efficiency
Nutrient delivery efficiency in drip hydroponics systems is pivotal for achieving ideal nutrient absorption by plant roots, thereby enhancing growth and yield.
This method precisely controls water usage, considerably reducing waste while maintaining the necessary hydration levels.
Furthermore, it positively influences root health by providing a consistent supply of nutrients, mitigating the risk of nutrient imbalances and related stress.
Optimal Nutrient Absorption
Achieving ideal nutrient absorption in drip hydroponics systems requires precise control over the delivery rate and concentration of nutrient solutions. This precision guarantees plants receive necessary nutrients without waste or deficiency.
Key factors influencing optimal nutrient uptake include:
- Flow Rate: Maintaining a consistent and appropriate flow rate guarantees uniform distribution of nutrients to all plants.
- Nutrient Concentration: Adjusting the nutrient solution concentration to meet plant growth stages maximizes absorption and minimizes excess.
- pH Levels: Regular monitoring and adjustment of pH levels facilitate efficient nutrient uptake by maintaining the solution within an optimal range (typically 5.5-6.5).
- Timing and Frequency: Implementing a scheduled delivery system synchronizes nutrient availability with plant metabolic cycles, enhancing absorption efficiency.
These factors collectively contribute to a sophisticated nutrient management strategy essential for high-yield hydroponic production.
Water Use Reduction
Implementing precise water management techniques in drip hydroponics systems enhances nutrient delivery efficiency while markedly reducing water waste.
By utilizing controlled irrigation schedules and advanced sensors, these systems deliver nutrients directly to the root zone, minimizing runoff and evaporation. This precision guarantees that plants receive only the necessary amount of water and nutrients at ideal intervals, thereby conserving resources and improving plant health.
Automated monitoring systems enable real-time adjustments based on plant needs and environmental conditions, further maximizing resource use. Additionally, the closed-loop nature of hydroponics allows for the recycling of nutrient solutions, drastically lowering overall water consumption.
Consequently, drip hydroponics systems represent a significant advancement in sustainable agriculture, aligning with the goals of water conservation and maximum nutrient efficacy.
Root Health Impact
Optimizing nutrient delivery efficiency in drip hydroponics systems substantially enhances root health by guaranteeing precise and consistent access to essential nutrients. This methodical approach to nutrient management fosters robust root development, which is crucial for overall plant health.
Key benefits include:
- Balanced Nutrient Uptake: Roots receive an ideal mix of macro and micronutrients, reducing deficiencies.
- Improved Oxygenation: Intermittent dripping guarantees that roots are sufficiently aerated, mitigating the risk of root rot.
- Minimized Waste: Precise delivery minimizes nutrient leaching and runoff, enhancing sustainability.
- Scalability: Nutrient delivery can be fine-tuned for various growth stages, promoting uniform development.
These factors collectively contribute to a healthier root system, driving higher yields and improved plant resilience in hydroponic environments.
Water Conservation Techniques

Leveraging advanced irrigation methods, drip hydroponics systems effectively minimize water usage while maintaining ideal plant hydration levels.
This precision is achieved through the use of emitters that deliver nutrients and water directly to the root zone, greatly reducing evaporation and runoff. The system's closed-loop design recirculates excess nutrient solution, further enhancing water efficiency.
Additionally, automated sensors and controllers monitor and adjust flow rates, ensuring optimal moisture levels without waste. By employing these sophisticated techniques, drip hydroponics systems can use up to 90% less water than traditional soil-based agriculture.
Consequently, they represent a highly sustainable choice for water conservation, especially in regions facing water scarcity. This innovative approach underscores the commitment to resource-efficient agriculture in the 21st century.
Common System Timers
Common system timers in drip hydroponics are essential for regulating the intervals and duration of nutrient solution delivery to the plants.
These timers guarantee precise control over hydration cycles, optimizing plant growth and resource efficiency.
The types of timers commonly used include:
- Mechanical Timers: Simple, cost-effective devices that use clockwork mechanisms to control cycles but lack fine-tuning capabilities.
- Digital Timers: Offer high precision and flexibility, allowing users to set multiple on/off cycles per day with minute accuracy.
- Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs): Advanced systems that provide extensive customization, integrating with sensors for real-time adjustments.
- Wi-Fi Enabled Smart Timers: These allow remote monitoring and adjustments via smartphones, offering unparalleled convenience and control.
Each type of timer serves a specific purpose and can be selected based on the complexity and requirements of the hydroponic system.
Troubleshooting Overwatering

Understanding the role of system timers brings us to the critical issue of troubleshooting overwatering in drip hydroponics systems.
Overwatering is often signaled by symptoms such as root rot, yellowing leaves, and stunted growth. To diagnose and correct this, first inspect the frequency and duration settings of your system timer. Excessive irrigation cycles can saturate the growing medium, leading to poor oxygenation.
Evaluate the drainage efficiency and guarantee that the medium allows for proper aeration. Additionally, consider utilizing moisture sensors to provide real-time data, helping to fine-tune watering schedules.
Implementing these measures can prevent overwatering, thereby optimizing plant health and maximizing yield, aligning with the innovative aspirations of hydroponic cultivators.
Best Practices for Maintenance
Routine maintenance is essential for guaranteeing the longevity and peak performance of drip hydroponics systems. Such systems require a disciplined approach to preserve their efficiency and avoid potential malfunctions.
Here are four best practices for maintaining your drip hydroponics system:
- Regular Cleaning: Clean all components, including tubing and emitters, to prevent clogs. Use a mild disinfectant to eliminate pathogens.
- System Inspection: Conduct weekly inspections to identify wear and tear or leaks. Replace any malfunctioning parts immediately.
- Nutrient Solution Management: Monitor and adjust the pH and nutrient levels regularly. Replenish the solution every two weeks to maintain balance.
- Pump Maintenance: Inspect and clean the pump monthly to guarantee it operates efficiently, preventing unexpected system failures.
Adhering to these practices fosters reliable and efficient system performance.
Conclusion
In summary, the operational schedule of drip hydroponics systems hinges on various factors, including plant type, growth stage, and environmental conditions.
Is it not vital to balance continuous and intermittent flow to enhance water usage and prevent overwatering?
Implementing water conservation techniques and utilizing effective timers are fundamental for efficient system maintenance.
By adhering to best practices, one can guarantee the ideal growth and health of hydroponically cultivated plants.