7 Ways Hydroponics Does Grow Faster Than Soil
Empirical studies have shown that hydroponic systems can enhance plant growth rates by 25-30% compared to soil-based cultivation. This accelerated growth is largely due to the precision nutrient delivery and the controlled environmental conditions inherent to hydroponic setups.
Utilizing nutrient-rich water solutions, hydroponics guarantees ideal nutrient absorption by plant roots, free from soil-borne pathogens. Additionally, the ability to regulate light intensity, humidity, and temperature further boosts growth efficiency.
Advanced systems also incorporate real-time monitoring to maintain stable growing conditions, considerably reducing water and nutrient waste. Greater insights into this agricultural innovation reveal further benefits and applications.

Key Takeaways
- Hydroponics enhances plant growth rates by 25-30% over soil cultivation due to optimized nutrient delivery and absence of soil pathogens.
- Controlled environmental conditions in hydroponics, such as precise regulation of light, humidity, and temperature, support faster growth.
- Continuous and precise nutrient supply in hydroponics maintains stable growing conditions, leading to better nutrient absorption and faster plant development.
- Automated systems in hydroponics extend photoperiods beyond natural daylight, boosting photosynthetic efficiency and accelerating growth.
Understanding Hydroponics

Hydroponics, a method of growing plants without soil, utilizes nutrient-rich water solutions to deliver essential minerals directly to plant roots. This soilless system guarantees ideal nutrient uptake, reduces water usage by up to 90%, and minimizes the risk of soil-borne diseases.
Key components include water reservoirs, aeration systems, and pH control mechanisms, all of which contribute to accelerated growth rates and higher yields. Empirical studies indicate that hydroponic systems can produce crops 25-30% faster compared to traditional soil cultivation, owing to precise control over environmental variables.
Innovations such as vertical farming and automated nutrient delivery systems further enhance the efficiency and scalability of hydroponic agriculture, making it a viable solution for sustainable, high-density urban farming.
Soil-Based Cultivation Basics
Soil-based cultivation relies on the natural nutrient availability within the soil matrix, which varies considerably depending on soil composition and organic matter content.
The water retention capacity of soil is another critical factor, influencing both plant hydration and root aeration.
Understanding these parameters is essential for optimizing plant growth and maximizing agricultural yield in soil-based systems.
Soil Nutrient Availability
Nutrient availability in soil is fundamentally influenced by factors such as pH levels, organic matter content, and microbial activity. These variables are essential in determining the efficacy of nutrient uptake by plants.
Here are four key factors that impact soil nutrient availability:
- pH Levels: Soil pH affects the solubility of nutrients and their availability to plants. Most nutrients are ideally available in a pH range of 6.0 to 7.0.
- Organic Matter: Decomposed organic matter enhances soil structure and nutrient content, providing a sustained release of essential minerals.
- Microbial Activity: Soil microorganisms decompose organic matter, releasing nutrients in forms readily accessible to plants.
- Cation Exchange Capacity (CEC): This measure of soil's ability to hold and exchange cations directly correlates with nutrient retention and availability.
Understanding these factors is vital for improving soil-based cultivation practices.
Water Retention Capacity
A vital aspect of soil-based cultivation, the water retention capacity of soil, directly influences plant water availability and overall growth performance.
The soil's ability to retain water depends on its texture, structure, and organic matter content; loamy soils, for instance, exhibit ideal retention due to balanced sand, silt, and clay proportions.
High water retention mitigates drought stress and promotes consistent nutrient uptake, essential for robust plant development.
However, excessive retention can lead to waterlogging, hindering root respiration and microbial activity.
Quantitative metrics such as field capacity and permanent wilting point are employed to evaluate soil water retention properties.
Understanding these parameters allows for precision irrigation strategies, fostering innovation in sustainable soil-based agricultural practices.
Nutrient Delivery Systems
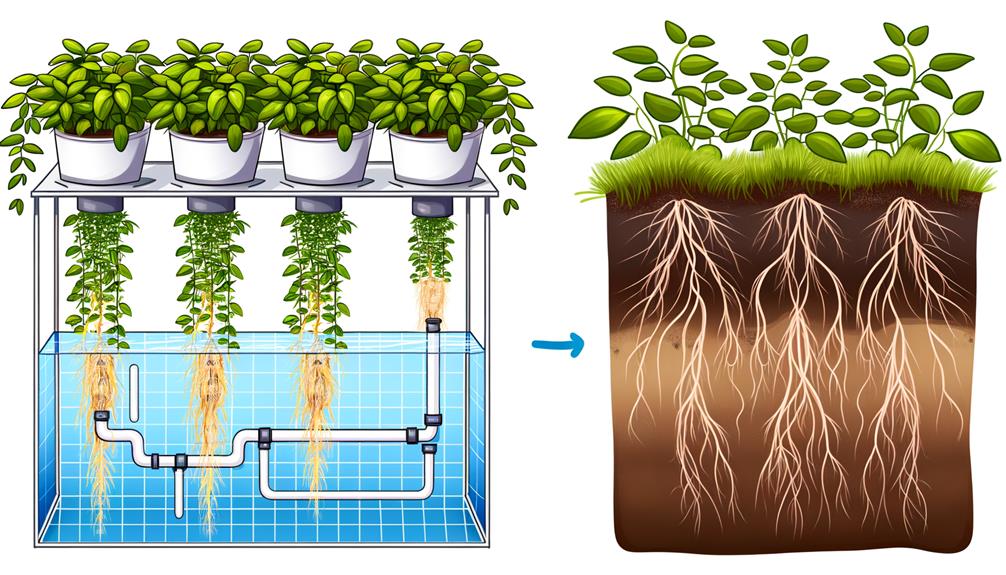
Nutrient delivery systems in hydroponics enable precise control over nutrient availability, allowing for efficient nutrient absorption by plant roots.
Customizable nutrient solutions in hydroponic systems facilitate the tailoring of specific nutrient profiles to meet the unique requirements of different crops.
This technology also minimizes nutrient waste, leading to more sustainable and cost-effective agricultural practices compared to traditional soil-based cultivation.
Efficient Nutrient Absorption
Efficient nutrient absorption in hydroponic systems is achieved through precise control of nutrient solutions, which are directly delivered to plant roots, bypassing the variability and limitations often encountered in soil-based cultivation. This method guarantees ideal nutrient uptake, leading to accelerated growth rates and enhanced crop yields.
Key advantages include:
- Enhanced Bioavailability: Nutrients in hydroponic systems are readily available for absorption, eliminating the need for complex soil interactions.
- Reduced Nutrient Waste: Targeted delivery minimizes nutrient runoff and guarantees efficient usage.
- Consistent Nutrient Supply: Continuous monitoring and adjustment of nutrient levels provide a stable growing environment.
- Ideal Root Zone Conditions: Controlled pH and oxygen levels in the nutrient solution foster healthier root systems.
These attributes collectively contribute to the superior efficiency of hydroponics over traditional soil methods.
Customizable Nutrient Solutions
Building on the foundation of efficient nutrient absorption, customizable nutrient solutions in hydroponic systems allow for precise tailoring of macro and micronutrient ratios to meet the specific needs of different plant species at various growth stages.
This precision is achieved through advanced nutrient delivery systems that utilize sensors and automated controllers to monitor and adjust nutrient concentrations in real-time.
By optimizing nutrient availability, hydroponics minimizes deficiencies and toxicities, thereby promoting faster growth and higher yields.
Research indicates that hydroponic crops receive a balanced nutrient profile, enhancing physiological functions such as photosynthesis and root development.
This data-driven approach guarantees that plants receive the exact nutrients they require, fostering an environment conducive to rapid and healthy growth, surpassing traditional soil cultivation methods.
Reduced Nutrient Waste
Hydroponic systems greatly reduce nutrient waste through the use of sophisticated nutrient delivery technologies that allow for precise control and recycling of nutrient solutions. These systems guarantee ideal nutrient uptake, leading to efficient plant growth and minimal environmental impact.
Key advantages include:
- Precision Nutrient Management: Automated systems deliver exact nutrient concentrations required at various growth stages, minimizing excess.
- Closed-Loop Systems: Nutrient solutions are recaptured and reused, markedly reducing waste.
- Reduced Leaching: Controlled environments prevent nutrient runoff into surrounding ecosystems.
- Data-Driven Adjustments: Real-time monitoring and adjustments based on plant needs enhance nutrient utilization efficiency.
Growth Rate Comparisons
When evaluating the growth rates of plants in hydroponic systems versus traditional soil cultivation, empirical studies consistently highlight a marked acceleration in hydroponic environments. This accelerated growth is primarily attributed to the direct delivery of nutrients to plant roots in hydroponic systems, eliminating the need for extensive root networks to seek out nourishment. Additionally, controlled environmental factors such as pH levels, moisture, and oxygen further optimize plant development. These soil vs hydroponics differences demonstrate why hydroponic methods are becoming increasingly popular for maximizing agricultural efficiency.
Research indicates that hydroponics can enhance plant growth rates by 25-30% compared to soil-based systems. This acceleration is attributed to optimized nutrient delivery, as hydroponic systems provide a direct and controlled supply of essential minerals.
In addition, the absence of soil pathogens and the ability to fine-tune pH levels contribute greatly to this enhanced growth performance.
Data-driven analyses reveal that hydroponically grown plants exhibit faster root development, increased biomass accumulation, and expedited maturation cycles.
Such advancements underscore the efficacy of hydroponics for achieving superior growth metrics, aligning with the innovative aspirations of modern agricultural practices.
Environmental Control Factors
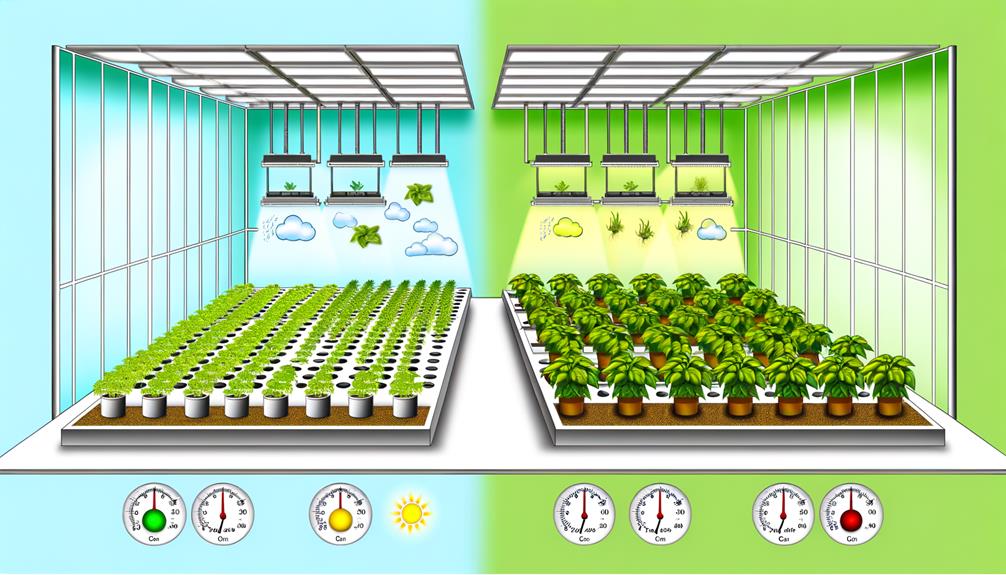
In hydroponic systems, precise environmental control mechanisms allow for the regulation of variables such as light intensity, humidity, and temperature, thereby improving conditions for plant growth. This meticulous control is facilitated by advanced technologies that enable growers to maintain ideal conditions 24/7, mitigating external environmental fluctuations.
Key factors that contribute to the enhanced growth rates in hydroponic systems include:
- Light Intensity: Adjustable LED grow lights provide tailored light spectra, promoting efficient photosynthesis.
- Humidity Control: Humidity levels are precisely managed to prevent mold and enhance transpiration rates.
- Temperature Regulation: Stable temperatures ensure metabolic processes occur at peak rates, enhancing growth.
- CO2 Enrichment: Controlled CO2 levels can greatly boost photosynthetic efficiency and plant productivity.
These factors collectively create a highly conducive environment for accelerated plant development.
Water Usage Efficiency
Leveraging precise environmental control mechanisms, hydroponic systems also exhibit superior water usage efficiency compared to traditional soil-based methods. This efficiency stems from closed-loop systems that recycle water, minimizing waste. Studies indicate that hydroponics can use up to 90% less water than conventional farming. The absence of soil evaporation and targeted nutrient delivery further enhances conservation. This method is particularly advantageous in arid regions where water scarcity is a critical concern.
| Metric | Hydroponics |
|---|---|
| Water Usage Reduction | Up to 90% |
| Water Recycling | Yes |
| Evaporation Loss | Minimal |
| Nutrient Delivery | Targeted |
| Suitability in Arid Regions | High |
Impact of Light

Ideal light exposure is vital for plant growth, and hydroponic systems offer a superior capacity for precise light management compared to soil-based methods. This advantage stems from the ability to control light intensity, duration, and spectrum, leading to improved photosynthetic activity.
Empirical studies indicate that hydroponics can enhance growth rates through refined light protocols. Key aspects include:
- Light Intensity: Hydroponic setups utilize high-intensity discharge (HID) and LED lighting to deliver consistent, ideal light levels.
- Light Duration: Automated systems can extend photoperiods beyond natural daylight hours, accelerating growth cycles.
- Light Spectrum: Tailored spectral compositions target specific growth phases, from seedling to flowering.
- Uniform Distribution: Even light dispersion ensures all plants receive adequate illumination, minimizing shadowing and promoting uniform growth.
Such precision in light management contributes considerably to faster plant development in hydroponic systems.
Space and Scalability
Hydroponic systems, due to their vertical farming capabilities and modular designs, offer significant advantages in space efficiency and scalability over traditional soil-based agriculture.
Vertical farming leverages multi-tiered setups, maximizing the cubic volume of growth areas, which is particularly beneficial in urban environments with limited ground space.
Modular designs allow for incremental scalability, enabling growers to expand operations without extensive land acquisition.
Data from recent studies indicate that hydroponic farms can produce up to 10 times more yield per square foot compared to soil farms.
This is achieved through optimized nutrient delivery systems and controlled environmental conditions that enhance plant growth rates.
Consequently, hydroponics can meet growing food demands more efficiently, aligning with innovative agricultural practices and urban sustainability goals.
Cost and Accessibility

Despite the technological advancements and efficiency of hydroponic systems, the initial setup costs and accessibility pose significant challenges for widespread adoption. Hydroponic systems often require substantial capital investment in specialized equipment, controlled environment structures, and nutrient solutions.
Key factors impacting cost and accessibility include:
- Initial Setup Costs: On average, hydroponic systems demand an upfront investment of $10,000 to $50,000, depending on scale and complexity.
- Operational Expenses: Continuous monitoring and maintenance of pH levels, electrical conductivity, and nutrient balance incur ongoing costs.
- Technical Expertise: The requirement for specialized knowledge can be a barrier, necessitating training or hiring skilled personnel.
- Geographic Limitations: Accessibility to essential supplies and technologies may vary by region, influencing overall feasibility.
These factors collectively affect the economic viability and practical implementation of hydroponic systems.
Conclusion
In the domain of plant cultivation, hydroponics emerges as a beacon of efficiency, often outpacing soil-based methods in growth rates due to precise nutrient delivery and ideal environmental control.
This technique, akin to a meticulously crafted symphony, harmonizes water usage, light manipulation, and spatial efficiency.
While initial costs may present barriers, the potential for scalability and resource conservation underscores hydroponics as a formidable contender in modern agriculture, transforming traditional paradigms with scientific precision and innovation.






