7 Steps to Adjust pH in Your Hydroponic System
Adjusting pH in a hydroponic system is crucial for nutrient solubility and plant health. Aim for a pH range of 5.5 to 6.5.
Use a calibrated pH meter for accurate readings, checking levels daily. To raise pH, add potassium hydroxide slowly; for lowering, use phosphoric acid.
Thoroughly mix solutions and allow time for equilibration before retesting. Utilize acids and bases carefully, following safety protocols.
For long-term stability, consider automated pH control systems. Regular monitoring and precise adjustments guarantee ideal growth conditions, avoiding nutrient lockout or toxicity.
For a deeper understanding, there are additional techniques and tools to explore further.

Key Takeaways
- Regularly measure pH levels with a calibrated pH meter to maintain the ideal range of 5.5 to 6.5.
- Use pH adjusters like phosphoric acid (pH Down) or potassium hydroxide (pH Up) for precise pH control.
- Gradually add pH adjusters to avoid overshooting the target pH level and thoroughly mix the solution.
- Choose between chemical or natural pH adjusters based on system scale and sustainability preferences.
Understanding Ph Levels
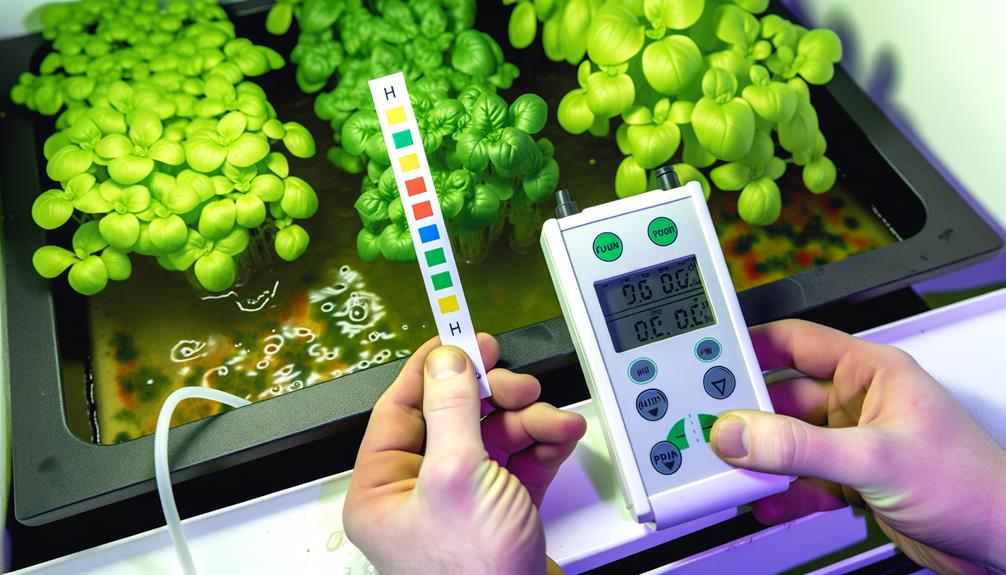

Understanding pH levels is essential in hydroponic systems because pH levels directly influence nutrient availability and uptake in plants.
Hydroponic systems, unlike soil-based cultivation, rely on nutrient solutions where pH dictates solubility and bioavailability of essential minerals. A pH level between 5.5 and 6.5 is typically ideal, as it guarantees a balanced absorption of macronutrients and micronutrients.
Deviations from this range can lead to nutrient lockout or toxicity, impairing plant growth and yield.
Advanced monitoring tools, such as digital pH meters, provide precise readings, enabling real-time adjustments. Regular calibration of these instruments is critical for accuracy.
Implementing automated pH control systems can further enhance stability, guaranteeing ideal conditions for plant health and maximizing hydroponic system efficiency.
Importance of Ph in Hydroponics
In hydroponics, maintaining the appropriate pH level is crucial as it directly affects the solubility of nutrients and their subsequent uptake by plants. Ideal pH guarantees that nutrients are available in forms that plants can absorb efficiently, preventing deficiencies and toxicities. The pH range for most hydroponic systems is typically between 5.5 and 6.5, facilitating maximum nutrient absorption.
| pH Range | Nutrient Availability Impact |
|---|---|
| < 5.5 | High metal toxicity |
| 5.5-6.5 | Ideal nutrient uptake |
| 6.5-7.0 | Reduced nutrient absorption |
| > 7.0 | Nutrient lockout |
| Variable | Growth inconsistencies |
Consistently monitoring and adjusting pH levels is crucial. Small deviations can negatively impact plant health, growth rates, and yield quality, making precise pH control a cornerstone of successful hydroponic farming.
Measuring Ph Accurately
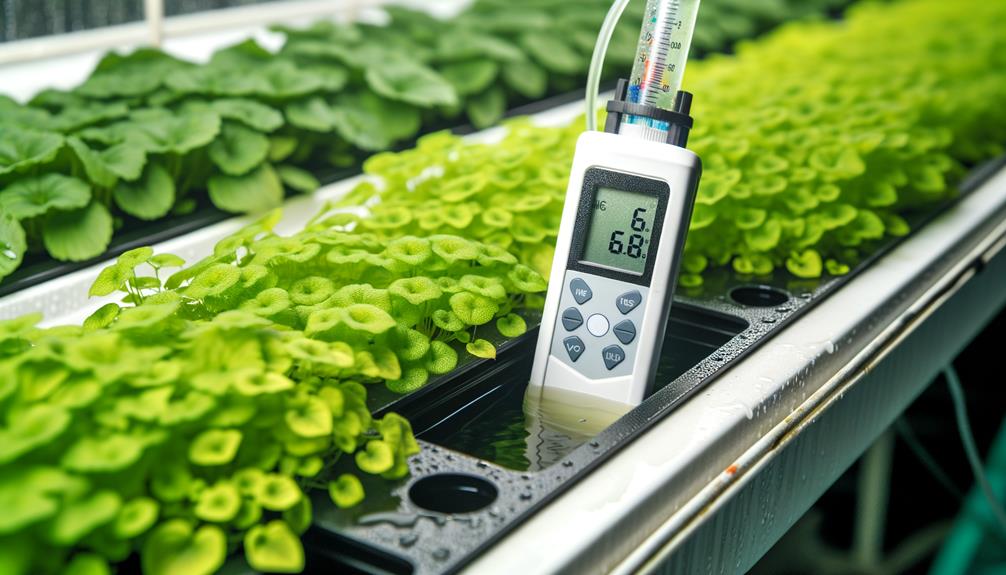

Accurate pH measurement is vital for maintaining ideal conditions in a hydroponic system.
This involves selecting reliable pH meters, ensuring these tools are properly calibrated, and taking representative water samples.
Each of these steps is essential for obtaining precise and consistent pH readings.
Choosing PH Meters
Selecting the right pH meter is essential for ensuring precise pH measurements in a hydroponic system, as it directly impacts plant health and nutrient absorption.
Advanced digital pH meters with automatic temperature compensation (ATC) are recommended for their accuracy and ease of use. Look for meters with a resolution of at least 0.01 pH units and a wide measurement range.
Consider features such as backlit displays for low-light environments, data logging capabilities, and replaceable probes to extend the device's lifespan. Waterproof models are advantageous in humid or wet conditions.
Investing in a high-quality pH meter not only enhances measurement reliability but also optimizes the hydroponic environment, fostering robust plant growth and nutrient uptake.
Calibrating Measurement Tools
To guarantee the effectiveness of your pH meter, regular calibration is necessary to maintain measurement accuracy and reliability in your hydroponic system.
Begin by rinsing the electrode with distilled water and gently dabbing it dry to prevent contamination.
Use fresh calibration solutions, typically pH 4.01, 7.00, and 10.01, to cover the range of your measurements. Submerge the electrode in the calibration solution and adjust the meter according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Ascertain the temperature of the calibration solutions is consistent with the meter's operating range.
Regularly calibrating, ideally before each use, secures precise pH readings, which are essential for nutrient uptake and plant health in hydroponic environments.
Proper calibration fosters innovation by enabling accurate adjustments to optimize growth conditions.
Sampling Water Properly
Properly sampling water in your hydroponic system is essential for obtaining accurate pH measurements that reflect the true conditions affecting plant health. Ascertain to collect water samples from different points within the system to account for any pH variations. Use clean, non-reactive containers to avoid contamination. Measure pH promptly after sampling to prevent changes due to exposure to air.
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Choose Location | Sample from various points in the system to capture representative data. |
| 2. Clean Container | Use a clean, non-reactive container to avoid skewing results. |
| 3. Sample Quickly | Measure pH immediately after sampling to ascertain accuracy. |
| 4. Record Results | Document the pH readings to track changes and make informed adjustments. |
Precise sampling leads to more effective pH management, promoting ideal plant growth.
Choosing Ph Adjusters
Choosing the suitable pH adjusters for your hydroponic system necessitates an understanding of the various types available, including both natural and chemical solutions.
It is vital to evaluate the advantages and disadvantages of each, as well as the safety and handling protocols necessary to guarantee ideal plant health and operator safety.
This section will provide detailed guidance on making informed choices for effective pH management.
Types of Ph Adjusters
Choosing the right pH adjuster for your hydroponic system is vital for maintaining ideal nutrient availability and plant health. pH adjusters can be broadly categorized into acids and bases.
Common acidic solutions include phosphoric acid and nitric acid, which effectively lower pH levels. Conversely, potassium hydroxide and sodium hydroxide are prevalent bases used to raise pH. The selection depends on the system's specific needs; for instance, phosphoric acid also adds phosphorus, a key nutrient.
Precision in measurement and gradual adjustments are important to avoid overcorrection. Innovative growers may also consider buffered solutions, which stabilize pH fluctuations, ensuring a more consistent environment for peak plant growth.
Understanding the chemical properties and effects of each adjuster is indispensable for achieving a balanced hydroponic ecosystem.
Natural Vs. Chemical Solutions
While chemical pH adjusters such as phosphoric acid and potassium hydroxide are widely used for their precision and effectiveness, natural alternatives like vinegar and lemon juice offer a more organic approach to pH management in hydroponic systems.
Chemical adjusters provide rapid, consistent results and are easy to dose accurately, making them ideal for large-scale operations.
However, natural solutions can be advantageous for smaller, eco-conscious setups. Vinegar and lemon juice, though less stable and requiring more frequent monitoring, minimize synthetic inputs and can enhance microbial activity.
When choosing between these options, consider factors such as system scale, desired sustainability, and maintenance capacity.
Balancing precision with environmental impact is key to optimizing hydroponic system performance.
Safety and Handling Tips
Guaranteeing safe and effective handling of pH adjusters in hydroponic systems necessitates a thorough understanding of each substance's properties, appropriate storage methods, and proper usage protocols.
The choice of pH adjusters, whether natural or chemical, should be informed by their impact on plant health and system longevity.
- Understand Chemical Properties: Familiarize with the Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) for each pH adjuster to comprehend hazards, reactivity, and required precautions.
- Storage Guidelines: Store pH adjusters in cool, dry places, away from direct sunlight and incompatible substances, guaranteeing containers are clearly labeled.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Use gloves, goggles, and aprons when handling pH adjusters to prevent skin and eye contact, and guarantee proper ventilation.
Adjusting Ph Upwards

To increase the pH level in a hydroponic system, it is crucial to use a pH increaser solution, commonly referred to as pH Up, which is typically composed of potassium hydroxide or potassium carbonate.
Begin by measuring the current pH of your nutrient solution using a reliable pH meter. Gradually add pH Up to your reservoir, in small increments, to avoid overshooting the desired pH range.
Stir the solution thoroughly and allow it to equilibrate for 30 minutes before rechecking the pH. Repeat the process if necessary, guaranteeing precise adjustments.
Employing a controlled approach guarantees ideal nutrient uptake and plant health, thereby fostering a more efficient and productive hydroponic system. This method ensures that essential minerals are delivered in precise amounts, reducing waste and enhancing overall growth. By following the 7 steps to set up hydroponics, growers can establish a well-balanced environment that maximizes yields and minimizes common issues like nutrient deficiencies. Consistently monitoring and adjusting nutrient levels will further support plant vitality and system efficiency.
Adjusting Ph Downwards
Lowering the pH level in a hydroponic system requires the use of a pH decreaser solution, commonly known as pH Down, which typically contains phosphoric acid or citric acid.
To achieve accurate pH adjustment, follow these steps:
- Measure Initial pH: Utilize a digital pH meter to determine the current pH level of the nutrient solution.
- Calculate Dosage: Based on the initial pH and desired pH level, calculate the required amount of pH Down. Begin with a small dose to avoid over-adjustment.
- Mix and Recheck: Add pH Down gradually, stirring the solution thoroughly. Wait 15-30 minutes and remeasure the pH to verify it reaches the target range.
This method guarantees a precise and controlled pH adjustment for peak plant growth.
Monitoring and Maintaining Ph

Regularly monitoring and maintaining the pH levels in a hydroponic system is essential for optimizing nutrient uptake and ensuring plant health.
Utilize a reliable digital pH meter for precise readings, calibrating it frequently with standard buffer solutions. Ideal pH levels typically range from 5.5 to 6.5, depending on the plant species.
Adjustments can be made using pH up or down solutions, added incrementally to avoid drastic changes.
Regularly check pH levels daily or at least several times a week, as factors like nutrient concentration, water quality, and plant uptake can cause fluctuations.
Implementing an automated pH control system can offer real-time adjustments, promoting a stable growing environment and enhancing growth efficiency.
Conclusion
Understanding and managing pH levels in a hydroponic system is fundamental to plant health and nutrient absorption.
Accurate measurement and appropriate adjustment, whether upwards or downwards, guarantee ideal growth conditions.
The selection of suitable pH adjusters and continuous monitoring are pivotal in maintaining these conditions.
Consequently, the juxtaposition of precise measurement and diligent maintenance culminates in a thriving hydroponic environment, demonstrating the critical role of pH management in successful hydroponic cultivation.