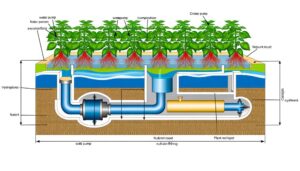
3 Simple Steps to Building a Fish Tank Hydroponic System
To build an aquaponic system using a fish tank, start by selecting a durable, non-toxic tank with a minimum depth of 18 inches. Choose fish like tilapia or goldfish that thrive in your environmental conditions.
Install a high-efficiency filtration system and verify pH and temperature levels are ideal. Position grow beds above the fish tank to utilize gravity for nutrient circulation.
Regularly monitor water quality parameters including pH, ammonia, nitrite, and nitrate levels, and introduce beneficial bacteria for efficient nutrient cycling. Consistent maintenance and adjustments are key to sustaining the ecosystem.
Further details will guide you to perfecting this system.

Key Takeaways
- Choose a non-toxic, durable fish tank with a minimum depth of 18 inches.
- Select fast-growing fish species like tilapia or hardy ones like goldfish.
- Install a high-efficiency filtration system and an adjustable water heater.
- Position grow beds above the fish tank for effective nutrient flow using gravity.
Understanding Aquaponics
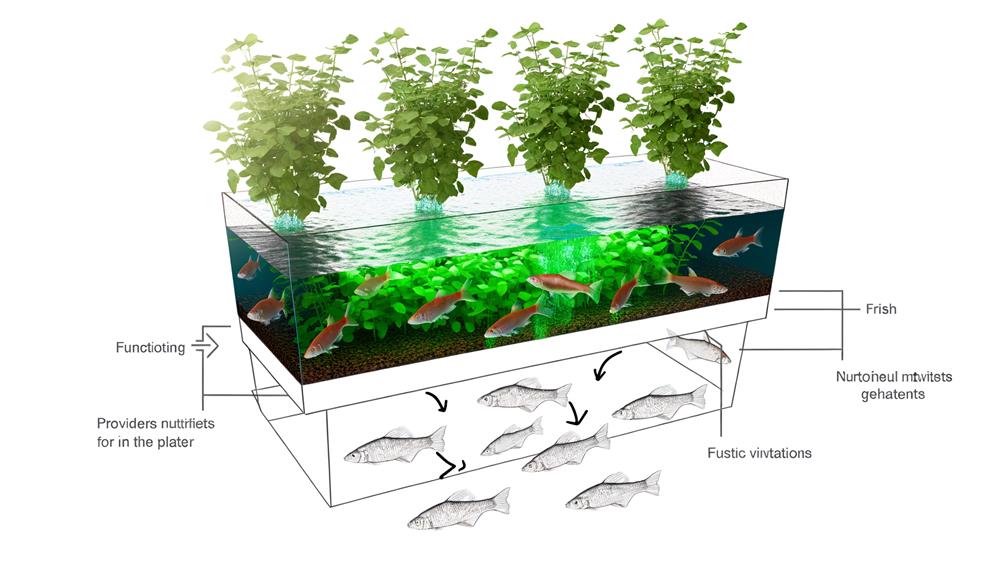
Contrary to hydroponics, aquaponics integrates aquaculture and hydroponics to create a symbiotic environment where fish and plants coexist and thrive.
This innovative system leverages the natural biological cycles of fish and plants to maintain an efficient, self-sustaining ecosystem.
Fish waste provides essential nutrients for plant growth, while plants, in turn, filter and purify the water for fish.
Key components include a fish tank, grow beds, a water pump, and bio-filtration to convert ammonia into nitrates.
Precision in monitoring pH levels, temperature, and dissolved oxygen is vital to maintain balance.
Aquaponics offers a sustainable solution for high-yield food production, leveraging natural processes to minimize resource consumption and environmental impact.
Choosing the Right Fish Tank
Selecting an appropriate fish tank is essential for maintaining a balanced and efficient aquaponic system.
The tank should be constructed from non-toxic, durable materials such as food-grade plastic or fiberglass to guarantee longevity and safety.
Capacity is critical; a larger volume provides a more stable environment by diluting waste and minimizing temperature fluctuations.
Consider a tank with a minimum depth of 18 inches to accommodate fish comfortably.
Opt for a dark-colored tank to inhibit algae growth and maintain water quality.
Accessibility for routine maintenance, including water changes and fish health checks, is paramount.
Verify the tank is positioned to support ideal water flow and integration with the hydroponic components, fostering a symbiotic relationship between fish and plants.
Selecting Suitable Fish

Once the fish tank is in place, it is imperative to choose fish species that are well-suited to the specific conditions and demands of your hydroponic system. The selection of fish should be based on factors such as water temperature tolerance, growth rate, and waste production, which can influence nutrient availability for plants. Below is a table detailing suitable fish species and their key attributes:
| Fish Species | Key Attributes |
|---|---|
| Tilapia | Fast growth, high waste production |
| Goldfish | Hardy, tolerates a wide range of temps |
| Trout | Cold water, high nutrient output |
| Catfish | Tolerates varied water conditions |
Proper selection guarantees a balanced ecosystem where fish thrive, and plants receive prime nutrients, thereby maximizing the efficiency of your hydroponic system.
Picking Your Plants
Choosing the right plants for your hydroponic system is essential for ensuring ideal growth and nutrient uptake.
Prioritize plants that thrive in hydroponic environments, such as leafy greens (lettuce, spinach), herbs (basil, cilantro), and fruiting plants (tomatoes, peppers). These species are known for their rapid growth rates and efficient nutrient absorption.
Consider plant compatibility with your chosen fish species, as their waste will serve as a primary nutrient source. Additionally, assess the space requirements and growth habits of each plant to optimize system layout.
Plants with similar pH and temperature preferences will simplify maintenance.
Employing a diverse selection can enhance system resilience and yield.
Make informed choices to maximize productivity and ecological balance within your aquaponic ecosystem.
Setting Up the Tank
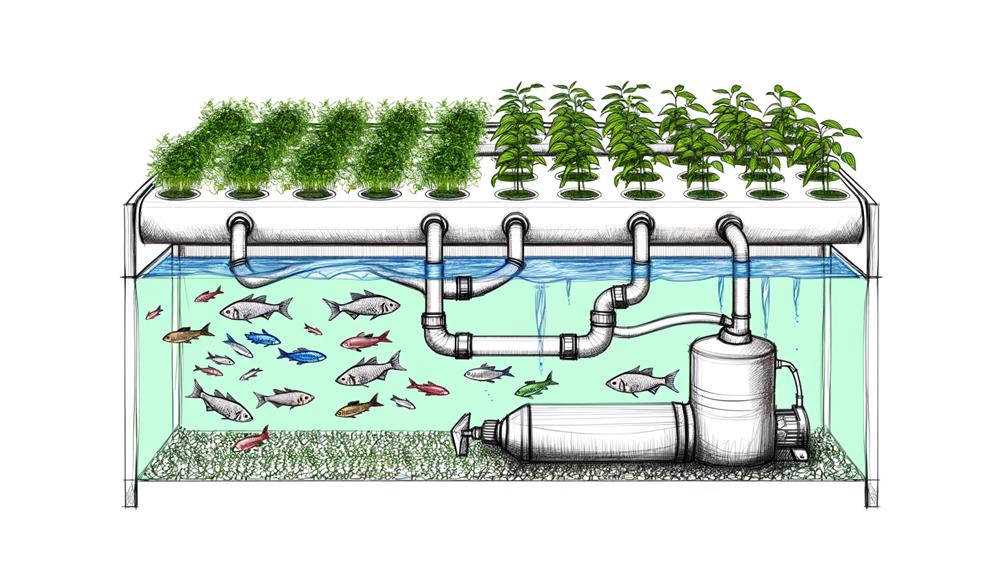
Establishing a robust tank setup is fundamental for the success of your hydroponic system, guaranteeing ideal conditions for plant growth and nutrient cycling. Begin by selecting a tank that provides ample space for both fish and plant roots. Confirm the tank is made of non-toxic materials to maintain a safe environment. Install a reliable filtration system to keep the water clean and oxygenated.
| Component | Specification | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Tank Material | Non-toxic, durable | Safe environment |
| Filtration System | High-efficiency, adjustable | Clean, oxygenated water |
| Water Heater | Adjustable thermostat | Maintain best temperature |
| Lighting | Full-spectrum LED | Support plant photosynthesis |
Regularly monitor pH and nutrient levels, making adjustments as necessary to maintain balance. This precision guarantees a thriving hydroponic ecosystem.
Installing the Hydroponic System
To begin installing your hydroponic system, first, verify that the grow bed is positioned securely and at the correct height relative to the reservoir.
Next, connect the pump to facilitate efficient nutrient solution circulation.
Positioning the Grow Bed
Properly positioning the grow bed is essential for optimizing plant health and system efficiency in a hydroponic setup. The grow bed must be placed above the fish tank, guaranteeing gravity can assist in nutrient flow. Secure the grow bed to prevent shifting or tilting, which could disrupt plant roots. Consider the following factors for ideal placement:
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Light Exposure | Guarantee adequate sunlight or artificial lighting |
| Accessibility | Easy reach for maintenance and harvesting |
| Stability | Securely fixed to prevent movement |
| Drainage | Sufficient slope for effective water flow |
| Space Utilization | Maximize available area efficiently |
Connecting the Pump
After positioning the grow bed, the next step involves connecting the pump, which is critical for maintaining the nutrient solution's circulation throughout the hydroponic system.
Begin by placing the submersible pump into the fish tank, making certain it is fully submerged to prevent damage.
Attach the pump's outlet to flexible tubing, which will carry the nutrient-rich water to the grow bed.
Secure the tubing to prevent leaks and guarantee an unobstructed flow.
Route the tubing so that it delivers water evenly across the grow bed, promoting uniform nutrient distribution.
Finally, plug in the pump and test its operation.
Adjust the flow rate to match the plant requirements, making sure that the nutrient solution is efficiently cycled through the system.
Ensuring Proper Lighting
Ensuring adequate lighting is essential for the ideal growth of plants in a hydroponic system, as it directly influences photosynthesis and overall plant health.
When selecting lighting, opt for full-spectrum LED lights, as they offer a balanced range of wavelengths similar to natural sunlight. Position the lights 12-18 inches above the plants to prevent light burn while ensuring optimal light penetration.
Employ a timer to automate a 16-hour light cycle, mimicking natural daylight conditions. Regularly adjust the light height as plants grow to maintain consistent intensity.
For innovative efficiency, consider integrating reflective surfaces around the grow area to maximize light utilization.
This precision in lighting setup will considerably enhance plant development and yield in your hydroponic system.
Cycling and Balancing the System

Cycling and balancing the system are critical for maintaining ideal plant health.
Start by establishing a nitrogen cycle to guarantee beneficial bacteria convert harmful ammonia into nitrates.
Concurrently, monitor water quality parameters such as pH, electrical conductivity, and nutrient concentrations to maintain a stable and productive hydroponic environment.
Establishing Nitrogen Cycle
Establishing a balanced nitrogen cycle is vital for maintaining ideal plant health and productivity in a hydroponic system.
Begin by introducing beneficial bacteria, such as Nitrosomonas and Nitrobacter, which facilitate the conversion of ammonia into nitrites and subsequently into nitrates. This process, known as nitrification, is essential for providing plants with accessible nitrogen.
Regularly monitor ammonia and nitrite levels, guaranteeing they remain minimal to avoid toxicity. Gradually introduce fish to the system to produce waste, which serves as the ammonia source.
Utilize biofilters to house bacterial colonies and support efficient nutrient cycling. Allow the system to cycle for 4-6 weeks before adding plants to guarantee stable nitrate levels, promoting a balanced, thriving environment for both fish and plants.
Monitoring Water Quality
Regularly monitoring water quality is essential for maintaining a balanced and healthy hydroponic system.
The primary parameters to measure include pH, ammonia, nitrite, and nitrate levels.
Aim for a pH range of 6.0 to 6.5 to optimize nutrient uptake and fish health.
Ammonia and nitrite levels should be near zero, as elevated concentrations can be toxic to both fish and plants.
Nitrate levels, while safer, should still be kept in check to prevent nutrient imbalances.
Utilize reliable water testing kits to conduct regular assessments, and make necessary adjustments using buffers or water changes.
Consistent monitoring and timely intervention guarantee a thriving hydroponic ecosystem, promoting innovation and sustainability in your aquatic gardening endeavors.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Effective maintenance and troubleshooting are essential to guarantee the ideal performance and longevity of your hydroponic system. Regular attention to key components guarantees optimal plant growth and fish health.
Here are three critical tasks:
- Check pH and Nutrient Levels: Regularly test and adjust pH and nutrient concentrations to maintain a balanced aquatic environment. Imbalances can inhibit plant growth and harm fish.
- Inspect Equipment: Verify all pumps, filters, and aeration systems are functioning correctly. Malfunctioning equipment can disrupt water flow and oxygen levels, endangering both plants and fish.
- Monitor for Pests and Diseases: Conduct routine inspections for signs of pests or diseases. Early detection and intervention are vital to prevent widespread damage.
Adhering to these practices will enhance system efficiency and sustainability.
Conclusion
Ironically, while constructing a hydroponic system with a fish tank may initially appear intimidating, it is the meticulous attention to detail in each step that guarantees success. By carefully monitoring water quality, nutrient levels, and fish health, enthusiasts can create a thriving, self-sustaining ecosystem. A DIY hydroponic system with fish not only maximizes plant growth but also reduces waste by naturally cycling nutrients. With patience and regular maintenance, this innovative approach can yield impressive results for both beginners and experienced hobbyists alike.
From selecting the appropriate tank and fish to establishing a balanced ecosystem, every element requires technical expertise and precision.
However, the irony lies in the simplicity of the maintenance required once the system stabilizes, highlighting the practicality and long-term benefits of aquaponics for sustainable cultivation.