Do 5 Steps to Start Your Own Hydroponic Farming
Hydroponic farming employs soilless cultivation techniques using nutrient-rich solutions tailored to plant needs. Systems like Nutrient Film Technique (NFT) and Deep Water Culture (DWC) are selected based on space, crop type, and resource management, often achieving crop yields up to 25% higher while using 90% less water.
Essential equipment includes grow lights, nutrient delivery systems, and climate controls for precise regulation of growth conditions. Nutrient solutions require constant monitoring with pH and EC meters to maintain ideal plant health.
Advanced strategies, such as vertical farming and real-time data analytics, further enhance productivity and sustainability. Discovering these detailed approaches can greatly improve modern food production.

Key Takeaways
- Choose a hydroponic system (NFT, DWC, Aeroponics) based on your plant type and space availability.
- Set up essential equipment like grow lights, nutrient delivery systems, and climate control devices.
- Mix and monitor nutrient solutions using pH and EC meters for balanced plant nutrition.
- Select plants with compact root structures and moderate water needs for efficient growth.
Understanding Hydroponics
Understanding hydroponics requires a foundational knowledge of soilless cultivation methods, where nutrient-rich water solutions are employed to grow plants in controlled environments.
This innovative agricultural practice leverages various hydroponic techniques, such as nutrient film technique (NFT), deep water culture (DWC), and aeroponics, to optimize plant growth by delivering precise nutrient formulations.
Research indicates that hydroponic systems can increase crop yields by up to 25%, while utilizing 90% less water compared to traditional soil-based agriculture.
Furthermore, controlled environment agriculture (CEA) within hydroponics allows for year-round production, independent of climatic conditions. This method mitigates soil-borne diseases and pests, facilitating higher biosecurity and reduced pesticide usage.
Consequently, hydroponics represents a sustainable and efficient solution for modern food production challenges.
Choosing a Hydroponic System
Selecting an appropriate hydroponic system necessitates an evaluation of various factors such as plant type, space availability, and resource management to maximize the efficiency and yield of the cultivation process.
Research indicates that nutrient film technique (NFT) and deep water culture (DWC) systems are most effective for leafy greens due to their high oxygenation and nutrient delivery efficiency.
Conversely, aeroponics is recommended for plant species requiring extensive root aeration.
For limited space scenarios, vertical farming systems are increasingly favored, offering up to a 50% increase in yield per square meter.
Data-driven studies show that closed-loop systems, which recycle water and nutrients, can reduce resource usage by up to 90%, making them ideal for sustainable hydroponic operations.
Essential Equipment

A thorough hydroponic system requires several critical pieces of equipment, including grow lights, nutrient delivery systems, pH and EC meters, and climate control devices.
High-intensity discharge (HID) or LED grow lights are essential for photosynthesis, providing ideal light spectra for plant growth.
Nutrient delivery systems, such as drip emitters or nutrient film techniques, guarantee precise distribution of essential minerals.
pH and EC meters enable the monitoring and adjustment of nutrient solutions to maintain ideal plant health, with target pH levels typically ranging from 5.5 to 6.5 and electrical conductivity (EC) levels between 1.2 to 2.4 mS/cm.
Climate control devices, including fans, heaters, and dehumidifiers, regulate temperature and humidity, creating an environment conducive to robust plant development.
Setting Up Your System
To guarantee ideal hydroponic system performance, start by meticulously planning the layout and configuration based on your specific crop requirements and available space. Evaluate the spatial parameters, ensuring optimal light distribution, airflow, and accessibility.
Employ data from scholarly research to select the most efficient hydroponic system type—NFT, DWC, or aeroponics—tailored to your crop's physiological needs. Integrate sensors for real-time monitoring of pH, electrical conductivity (EC), and temperature, ensuring precise environmental control.
Utilize modular designs for scalability, facilitating future expansion without disrupting existing operations. Incorporate automation technologies to streamline water and nutrient delivery, minimizing manual intervention.
Nutrient Solutions

Nutrient solutions are the cornerstone of hydroponic farming, providing plants with essential macro and micronutrients.
Effective nutrient management requires precise mixing and ongoing monitoring to maintain ideal pH and electrical conductivity (EC) levels.
Research indicates that imbalances in nutrient concentrations can greatly affect plant growth rates and yield quality.
Essential Nutrient Components
In hydroponic farming, the composition of nutrient solutions is critical, comprising essential macro and micronutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium, iron, and trace elements.
All of these nutrients are meticulously balanced based on plant-specific requirements and growth stages.
Research indicates that ideal nitrogen levels enhance vegetative growth, while phosphorus and potassium are pivotal during reproductive phases.
Calcium and magnesium prevent physiological disorders and bolster cellular function.
Iron and trace elements such as manganese, zinc, and copper are indispensable for enzymatic activities and photosynthesis.
Empirical studies underscore the importance of precise nutrient ratios, as imbalances can lead to suboptimal growth or nutrient toxicity.
Consequently, hydroponic systems demand rigorous formulation based on empirical data and plant phenology to maximize yield and quality.
Mixing and Monitoring
Properly mixing and meticulously monitoring nutrient solutions are pivotal tasks in hydroponic farming that greatly influence plant health and yield outcomes.
The precise formulation of nutrient solutions, incorporating macro and micronutrients, is essential for optimizing growth conditions.
Employing Electrical Conductivity (EC) meters and pH sensors guarantees the solution remains within ideal ranges, typically 1.2-2.0 mS/cm for EC and 5.5-6.5 for pH.
Real-time data analytics can further refine nutrient delivery, leveraging algorithms to adjust concentrations dynamically based on plant growth stages and environmental variables.
Automated dosing systems are recommended to enhance consistency and reduce human error.
Continuous monitoring via IoT-enabled devices provides actionable insights, promoting sustainable and high-efficiency farming practices.
Selecting Plants
When selecting plants for hydroponic systems, it is crucial to assess species that have demonstrated ideal growth rates and yield under controlled environments. Research indicates that certain cultivars adapt more efficiently to hydroponic conditions, optimizing resource utilization and production cycles.
Key factors to take into account include:
- Root structure: Species with compact root systems minimize space usage.
- Nutrient uptake efficiency: Plants with high nutrient absorption rates enhance growth.
- Water requirements: Opt for species with moderate water needs to balance system sustainability.
- Light tolerance: Select plants that thrive under artificial lighting conditions.
Assessing these parameters guarantees the selection of plants that maximize productivity and align with the operational goals of hydroponic farming.
Germination and Transplanting
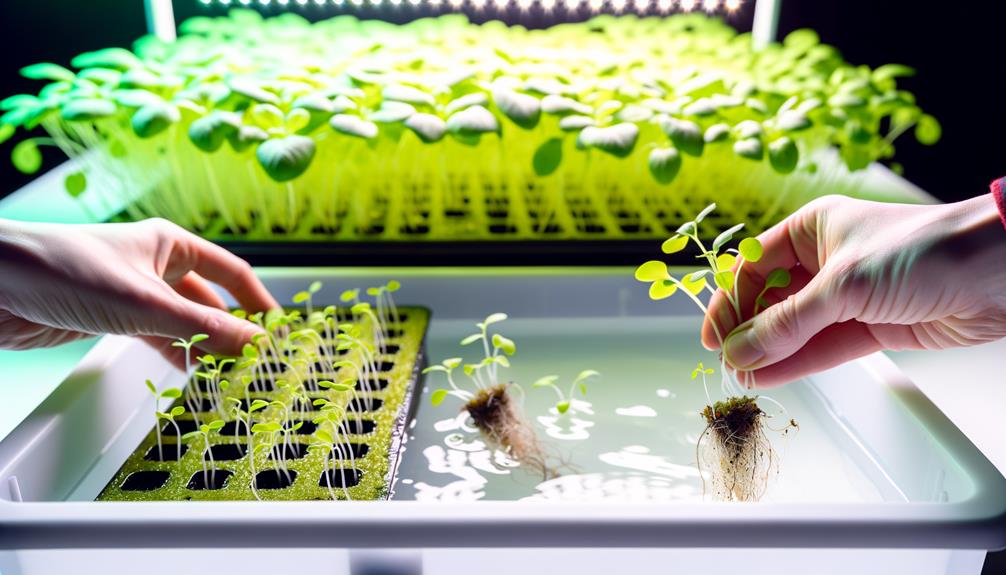

The germination phase in hydroponic farming necessitates precise seed selection based on germination rates and vigor, ensuring peak plant performance.
Controlled environmental parameters, including temperature, humidity, and light intensity, are critical for achieving uniform and rapid seedling growth.
Employing evidence-based transplant techniques minimizes root disturbance and promotes seamless adaptation to hydroponic systems, as demonstrated by recent studies in controlled agricultural settings.
Seed Selection Tips
Selecting high-quality seeds for hydroponic farming is essential for optimizing germination rates and guaranteeing successful transplanting. The selection process should be informed by data-driven research and technical criteria to maximize yield potential.
Key considerations include:
- Genetic Purity: Opt for seeds with a high genetic purity to guarantee uniform growth and predictable performance.
- Germination Rate: Choose seeds with a germination rate of at least 90%, as documented by seed suppliers.
- Disease Resistance: Prioritize seeds bred for resistance to common pathogens to reduce dependency on chemical treatments.
- Seed Size and Uniformity: Select seeds of consistent size to guarantee uniform germination and growth rates.
Implementing these tips will enhance productivity and guarantee robust crop development.
Optimal Growth Conditions
Achieving ideal growth conditions for germination and transplanting in hydroponic farming necessitates a meticulously controlled environment, characterized by precise parameters such as temperature, humidity, light intensity, and nutrient availability.
Best germination generally occurs at temperatures between 68-75°F (20-24°C) and relative humidity levels of 70-90%.
Light intensity should range from 2000-3000 lumens per square foot, utilizing full-spectrum LED lights to replicate natural sunlight.
Nutrient solutions must contain balanced macronutrients (N, P, K) and micronutrients, with electrical conductivity (EC) maintained at 0.5-1.0 mS/cm.
During the transplanting phase, gradual acclimatization to the growing system's environmental conditions is essential to minimize stress and foster robust root development.
Employing real-time monitoring systems guarantees adherence to these stringent parameters, promoting best plant growth.
Safe Transplant Techniques
Consistently employing meticulous techniques during germination and transplanting is essential to guaranteeing plant health and minimizing transplant shock in hydroponic systems. Precision in these early stages establishes a robust foundation for peak growth.
Key practices include:
- Sterilizing Equipment: Prevents pathogenic contamination, essential for seedling vigor.
- Controlled Environment: Maintains ideal humidity (70-80%) and temperature (20-25°C) for germination.
- Nutrient Solution Management: Guarantees seedlings receive balanced nutrition without root burn.
- Gentle Handling: Minimizes root damage during transplantation, reducing stress.
Adhering to these evidence-based methodologies, corroborated by recent agronomic research, greatly enhances the likelihood of successful crop establishment in hydroponic farming.
Lighting Requirements
Proper lighting is a critical factor in hydroponic farming, directly influencing photosynthetic efficiency, plant growth rates, and overall crop yield.
Advanced research indicates that light spectra, intensity, and photoperiod must be meticulously calibrated to enhance plant performance. Utilizing full-spectrum LED grow lights, which mimic natural sunlight, has been shown to improve chlorophyll synthesis and biomass production.
Data-driven studies have established that a light intensity of 400-700 µmol/m²/s and a photoperiod of 16-18 hours daily are ideal for most hydroponic crops.
In addition, the implementation of automated light control systems can maintain consistent environmental conditions, thereby mitigating stress factors and promoting uniform growth.
Managing Water and Ph
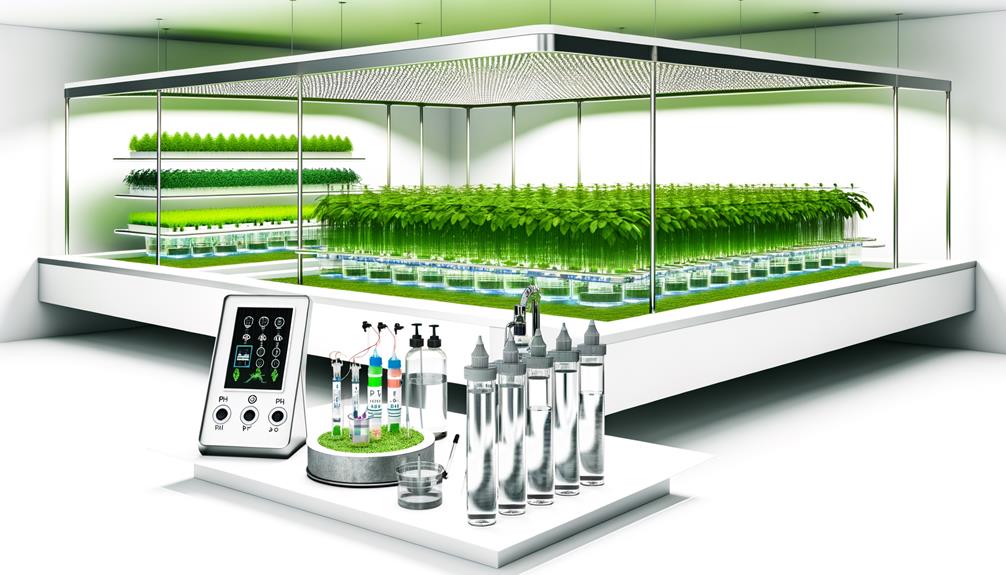

Effective hydroponic farming necessitates precise management of water levels and pH balance to maximize plant growth.
Research indicates that maintaining water levels within 0.5 to 1.0 inches below the root zone can greatly enhance nutrient uptake efficiency.
Concurrently, empirical studies have shown that a pH range of 5.5 to 6.5 is critical for optimal nutrient availability and absorption in hydroponic systems.
Optimal Water Levels
Maintaining ideal water levels and pH balance is essential for maximizing nutrient uptake and guaranteeing the healthy growth of plants in hydroponic systems. Research indicates that precise water management directly influences root oxygenation and nutrient solubility. Ideal water levels can be achieved by monitoring and adjusting the system based on empirical data and specific plant needs.
Key factors include:
- Water Temperature: Maintain between 65°F and 75°F to support ideal root function.
- Dissolved Oxygen (DO): Levels should be kept above 5 mg/L for effective root respiration.
- Water Circulation: Guarantees uniform nutrient distribution and prevents stagnation.
- Evapotranspiration Rates: Monitor and adjust for plant-specific water usage.
These parameters are critical for sustaining an efficient hydroponic environment.
Maintaining Ph Balance
Achieving accurate pH balance in hydroponic systems is essential, as it directly impacts nutrient availability and plant health.
Research indicates that the ideal pH range for most hydroponic crops lies between 5.5 and 6.5. Deviations from this range can cause nutrient lockout, adversely affecting plant growth and yield.
Implementing automated pH monitoring systems, equipped with sensors, guarantees real-time adjustments, maintaining stability. Data from a 2022 study highlights that consistent pH management can enhance nutrient uptake efficiency by up to 30%.
Regular calibration of pH meters and using buffering solutions are critical practices for precision.
Innovators in hydroponic farming should leverage these technologies to achieve superior crop performance and sustainability. By implementing step by step hydroponic farming techniques, growers can optimize nutrient delivery, water conservation, and overall plant health. Advanced automation and data-driven insights further enhance efficiency, allowing for precise environmental control. As a result, these innovations contribute to higher yields while minimizing resource waste.
Pests and Diseases
Pests and diseases in hydroponic farming systems pose significant challenges due to the controlled environment and the absence of natural predators, necessitating rigorous monitoring and precise management strategies. Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is essential for maintaining ideal plant health and system efficiency. Data-driven approaches help in early detection and effective intervention.
Regular Monitoring: Weekly inspections using magnifying tools to detect early signs of infestation.
Biological Controls: Introduction of beneficial insects such as predatory mites to manage pest populations.
Sterilization Protocols: Routine sterilization of tools and equipment using UV light or hydrogen peroxide.
Environmental Controls: Adjusting humidity and temperature to deter pathogen proliferation.
Chemical Interventions: Application of targeted, eco-friendly pesticides only when necessary, based on threshold levels.
These strategies guarantee a robust defense against biotic stressors.
Harvesting and Maintenance
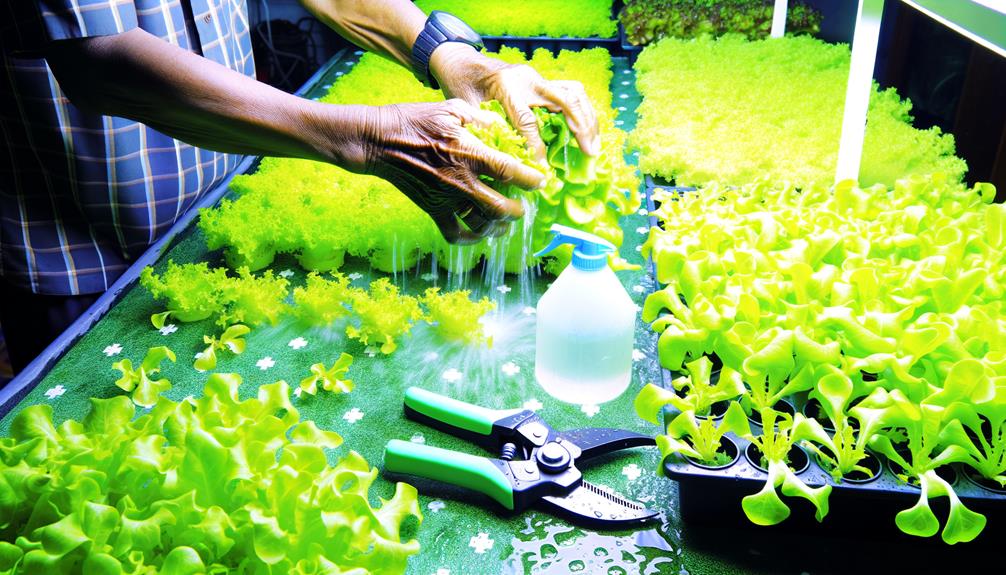

After successfully managing pests and diseases, the next vital phase in hydroponic farming involves optimizing harvesting and system maintenance to secure maximum yield and operational efficiency.
Harvesting at the correct physiological maturity is essential; research indicates that nutrient concentration peaks at specific growth stages. Utilize precision tools to measure parameters such as Brix levels for fruits or chlorophyll content for leafy greens.
Post-harvest, perform system maintenance by sterilizing reservoirs, replacing nutrient solutions, and checking pH and EC levels to prevent biofilm formation and nutrient lockout. Regularly inspect and calibrate sensors and automated systems to guarantee accurate environmental control.
Employing data-driven approaches and cutting-edge technologies can greatly enhance productivity and sustainability in hydroponic farming operations.
Conclusion
Hydroponic farming, akin to a well-orchestrated symphony, requires meticulous attention to each component to achieve ideal growth.
When the harmonious interplay of nutrient solutions, precise lighting, and pH management is achieved, plants thrive in a controlled environment, free from the constraints of traditional soil cultivation.
This method, underpinned by technical precision and scientific principles, offers a robust framework for sustainable agriculture, promising enhanced yields and resource efficiency.
The future of farming consequently lies in mastering this delicate balance.






