5 Simple Steps to Grow with Hydroponics
Growing with hydroponics involves cultivating plants using nutrient-rich water solutions rather than soil, ensuring ideal nutrient uptake and growth efficiency. Essential components include a suitable growing medium, a well-balanced nutrient solution, a reliable water reservoir, air pump, nutrient delivery system, and appropriate grow lights.
Choose a hydroponic system that aligns with your space and plant type, such as NFT, DWC, or aeroponics. Consistent monitoring of pH and electrical conductivity (EC) levels is critical for maintaining plant health.
With proper setup and maintenance, hydroponics can yield high-quality, resource-efficient crops. There are additional strategies to enhance your hydroponic gardening further.

Key Takeaways
- Select a hydroponic system (NFT, DWC, Aeroponics) based on your crop type, space, and growth goals.
- Use nutrient-rich water solutions to deliver essential minerals directly to plant roots.
- Monitor pH levels (5.5-6.5) and electrical conductivity (EC) for optimal nutrient absorption.
- Ensure proper oxygenation with air pumps and maintain water temperatures (65-75°F).
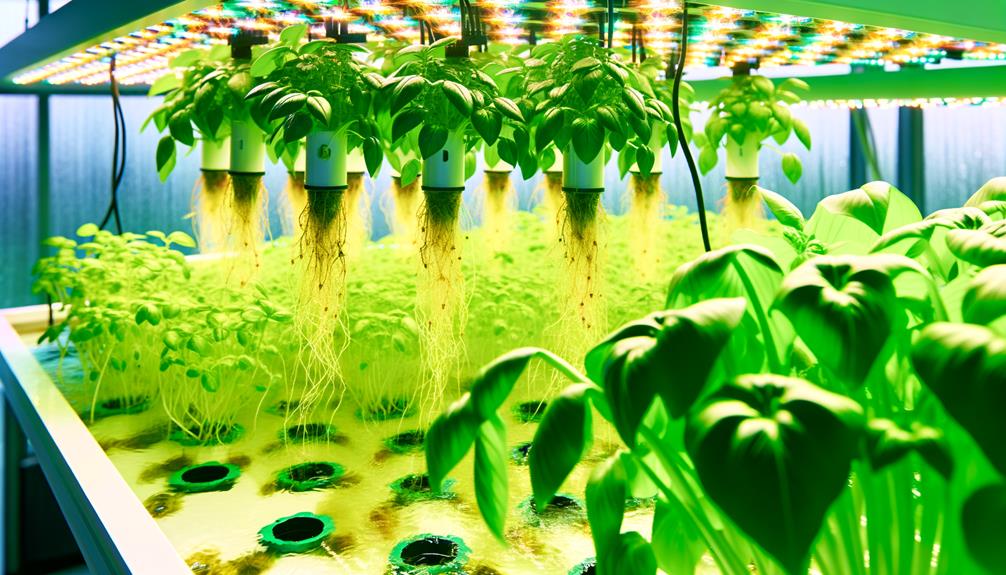
Understanding Hydroponics

Hydroponics, a method of growing plants without soil, utilizes nutrient-rich water solutions to deliver essential minerals directly to plant roots. This system guarantees optimal nutrient uptake, resulting in faster growth and higher yields.
Central to hydroponics are six core components: a growing medium (e.g., perlite, coconut coir), a nutrient solution, a water reservoir, an air pump, a delivery system (e.g., drip irrigation), and adequate lighting. Each component plays a vital role in maintaining the ideal environment for plant growth.
Precision in monitoring pH levels and electrical conductivity (EC) is essential, as these parameters influence nutrient availability. By mastering these technical aspects, growers can achieve unparalleled control over plant health and development, paving the way for innovative agricultural practices.
Benefits of Hydroponics
One of the most significant advantages of hydroponic systems is their ability to enhance resource efficiency, leading to higher crop yields with reduced water and nutrient usage.
Hydroponics allows for precise control over the growing environment, ensuring that plants receive ideal levels of nutrients and light, thereby enhancing growth rates and yields.
Additionally, hydroponic systems eliminate the need for soil, reducing the risk of soil-borne diseases and pests.
This method also supports year-round cultivation, irrespective of external weather conditions, providing consistent and predictable crop production.
Furthermore, the vertical stacking capability of hydroponic setups maximizes space utilization, making it ideal for urban farming and areas with limited arable land.
Ultimately, hydroponics represents a sustainable and innovative approach to modern agriculture.
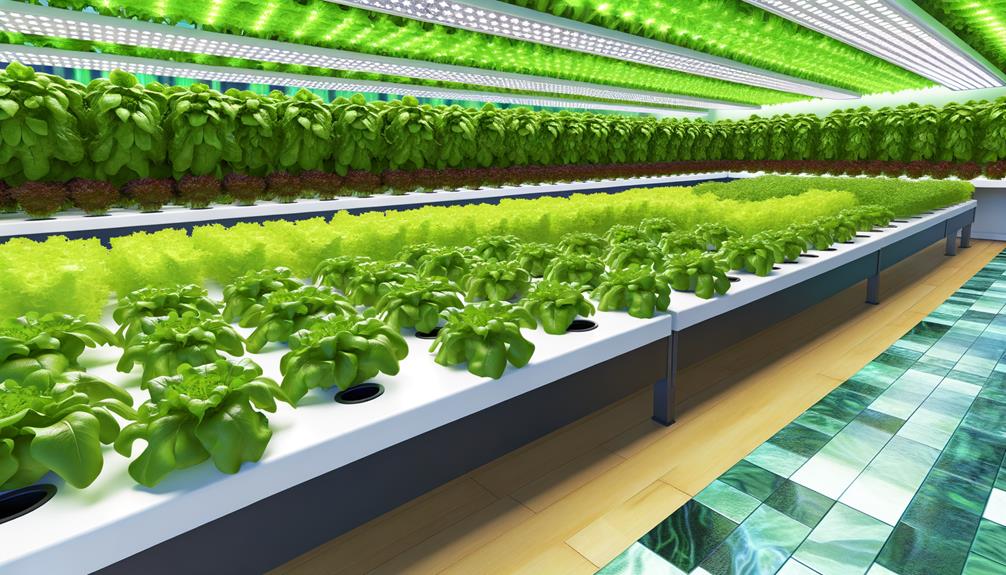
Types of Hydroponic Systems
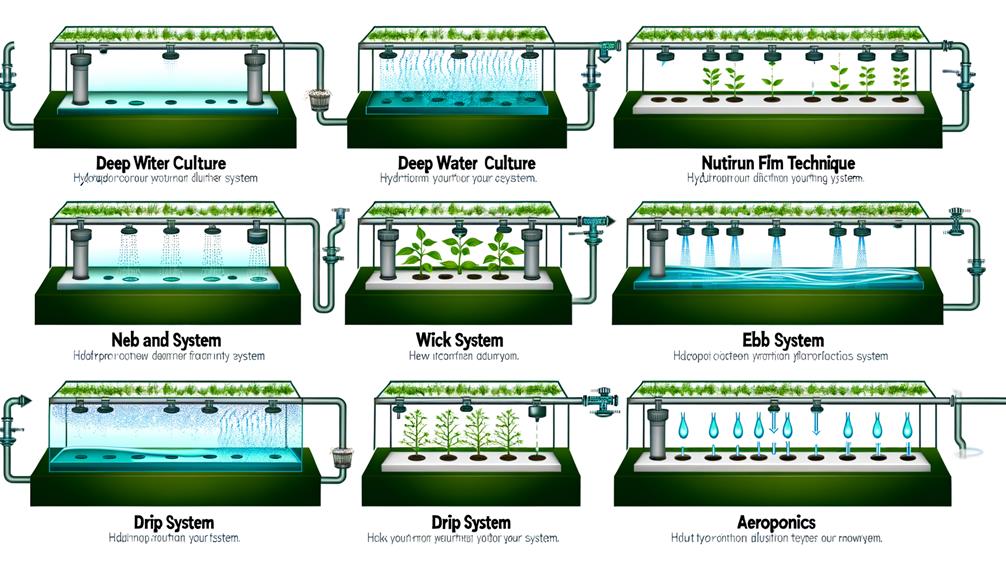
Understanding the various types of hydroponic systems is essential for optimizing plant growth and resource efficiency.
Key systems include the Nutrient Film Technique (NFT), Deep Water Culture (DWC), and Aeroponics, each with distinct methodologies and benefits.
Selecting the appropriate system depends on factors such as crop type, available space, and desired growth outcomes.
Nutrient Film Technique
Among the various hydroponic systems, the Nutrient Film Technique (NFT) stands out for its efficiency and simplicity in delivering nutrients directly to plant roots.
In NFT, a shallow stream of nutrient-rich water flows continuously over the roots, which are supported by an inert medium within a sloped channel. This method guarantees maximum oxygenation and nutrient uptake, fostering rapid growth and high yields.
Key components include a reservoir, pump, and sloped channels to facilitate nutrient flow and return. Precision in maintaining nutrient concentration and flow rate is essential for preventing deficiencies or root drying.
NFT is ideal for smaller plants like leafy greens and herbs, making it a popular choice for innovative, space-constrained urban farming.
Deep Water Culture
Deep Water Culture (DWC) represents another highly effective hydroponic system, where plant roots are fully submerged in a nutrient-rich, oxygenated water solution, promoting robust growth and efficient nutrient absorption.
This system employs air pumps and air stones to guarantee adequate oxygenation, preventing root rot and enhancing nutrient uptake. DWC is particularly suitable for fast-growing plants like lettuce and herbs.
For peak performance, maintain water temperatures between 65-75°F and monitor pH levels closely, aiming for a range of 5.5-6.5. Regularly inspect and clean the system to prevent algae buildup and guarantee continuous oxygen flow.
Aeroponics Systems
Aeroponics systems, a cutting-edge method within hydroponics, suspend plant roots in the air and mist them with a nutrient-rich solution, enabling unparalleled oxygenation and nutrient uptake. This innovative approach maximizes plant growth and efficiency by eliminating the medium between roots and nutrients.
Key components include a misting apparatus, a timer, and a reservoir for the nutrient solution. Precision in misting intervals is essential, typically set between 5-10 minutes, ensuring roots remain moist without oversaturation.
These systems are ideal for environments where space is limited, offering vertical scalability. Maintenance involves regular monitoring of pH levels and nutrient concentrations, as well as ensuring misting nozzles remain unclogged.
Embrace aeroponics for a highly efficient, space-maximizing growing solution.
Choosing the Right Plants
Selecting the appropriate plants for your hydroponic system is crucial for maximizing growth efficiency and yield.
Begin with fast-growing, high-yield crops like lettuce, spinach, and herbs such as basil and mint, which thrive in hydroponic environments due to their shallow root systems and short maturation periods.
For those seeking more diversity, consider fruiting plants like tomatoes, strawberries, and peppers, which perform well with adequate support and nutrient management.
Avoid plants with extensive root systems, such as root vegetables, unless utilizing specialized deep-water culture systems.
Evaluate plant requirements, including light, temperature, and pH levels, to ascertain compatibility with your hydroponic setup.
This strategic selection not only optimizes resource use but also enhances overall productivity and innovation within your cultivation practices.
Setting Up Your System
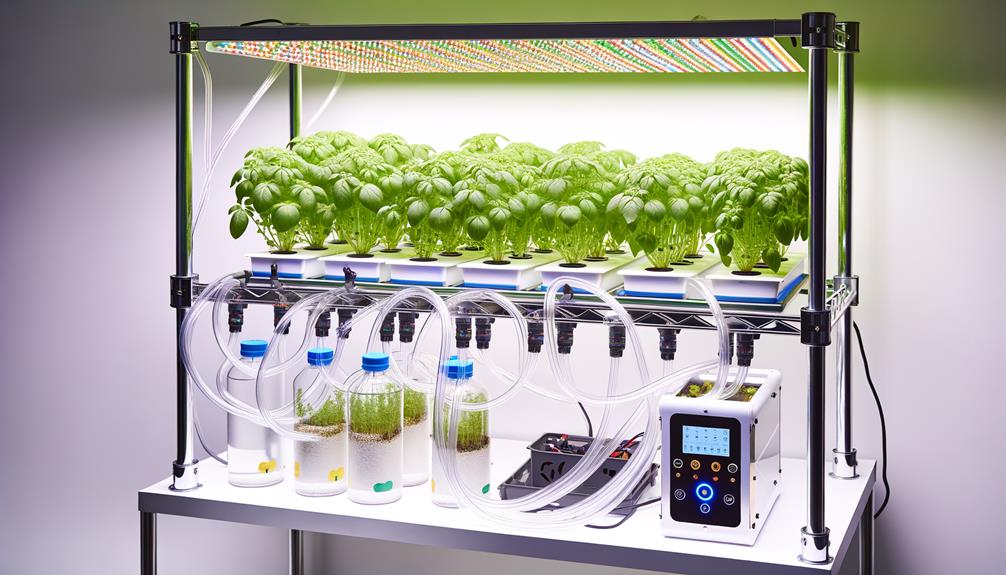

Once you've chosen the ideal plants for your hydroponic garden, the next step is to meticulously set up your system to guarantee peak growth conditions.
Begin by selecting a suitable hydroponic method, such as Deep Water Culture (DWC), Nutrient Film Technique (NFT), or Ebb and Flow, each offering distinct advantages.
Make sure your system includes a reliable water pump, air pump, and grow lights to simulate optimal environmental conditions.
Position your grow lights to provide uniform illumination, and utilize timers for consistent light cycles.
Install a pH and EC meter to monitor water quality, essential for maintaining nutrient uptake.
Secure net pots and growing media to support plant roots, ensuring stability.
Proper setup is vital in achieving a thriving hydroponic garden.
Nutrient Solutions
The cornerstone of successful hydroponic cultivation lies in the precise formulation and management of nutrient solutions.
Essential nutrient components, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, must be meticulously balanced to meet the specific needs of your plants.
Additionally, regular monitoring and maintenance of the nutrient solution are vital for optimizing plant health and growth.
Essential Nutrient Components
Essential nutrient solutions are meticulously formulated to provide hydroponic plants with the precise balance of macro and micronutrients required for ideal growth.
Macroelements such as nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K) are essential for fundamental plant functions including photosynthesis and energy transfer.
Secondary nutrients like calcium (Ca), magnesium (Mg), and sulfur (S) support structural integrity and enzymatic activity.
Micronutrients, including iron (Fe), manganese (Mn), and zinc (Zn), are critical in trace amounts for catalytic and regulatory functions.
Ensuring the correct concentration and ratio of these elements is paramount, as imbalances can impede plant health and productivity.
Advanced hydroponic systems often incorporate automated nutrient delivery technologies, optimizing the nutrient uptake process and fostering robust plant development.
Mixing and Maintenance
Proper mixing and meticulous maintenance of nutrient solutions are vital for achieving ideal hydroponic plant growth and productivity.
To guarantee peak nutrient absorption and plant health, it is essential to measure and adjust the solution's pH and electrical conductivity (EC) accurately. Regular monitoring prevents nutrient imbalances and fosters a stable growing environment.
Key steps include:
- Precise Measurement: Use calibrated pH and EC meters for exact readings.
- Consistent Monitoring: Check pH and EC levels daily to maintain stability.
- Solution Renewal: Replace nutrient solutions every two weeks to prevent nutrient depletion and pathogen buildup.
Maintenance and Care
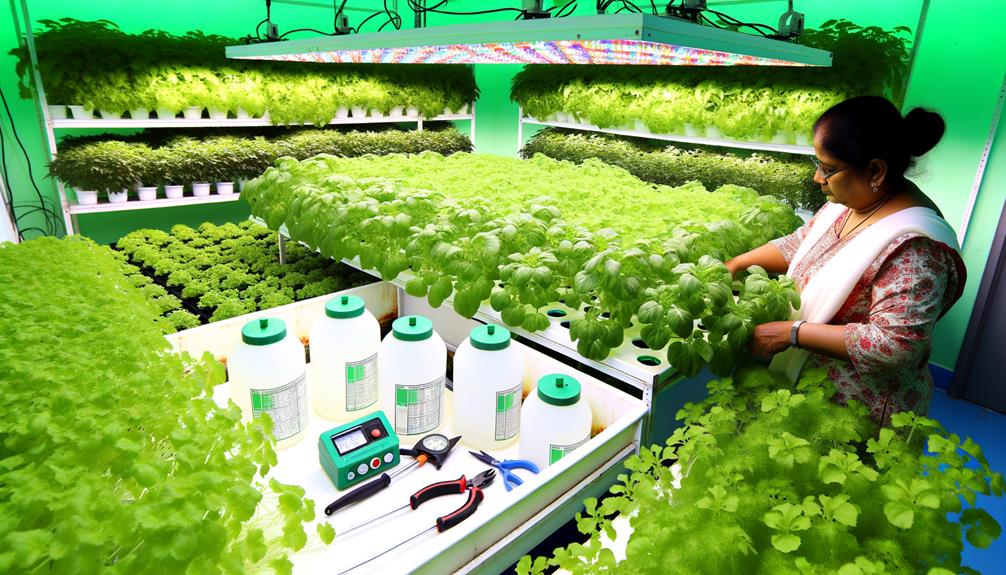

Guaranteeing ideal performance of your hydroponic system requires diligent monitoring and regular maintenance to prevent issues and promote healthy plant growth.
Conduct daily checks on pH and electrical conductivity (EC) levels, as these are critical for nutrient uptake.
Clean and sterilize the system components, such as reservoirs, pumps, and tubing, on a bi-weekly basis to mitigate algae and bacterial growth.
Inspect and adjust light sources to guarantee optimal photoperiod and intensity.
Prune plants regularly to encourage airflow and reduce the risk of mold.
Additionally, replace nutrient solutions every two weeks to maintain balanced chemistry.
Implementing these meticulous practices will support robust plant development and maximize your hydroponic yields, aligning with innovative agricultural techniques.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Identifying and resolving common issues in hydroponic systems is paramount to maintaining plant health and achieving high yields. Innovators in hydroponics must be vigilant in monitoring and addressing typical challenges.
Key issues include:
- Nutrient Imbalances: Regularly check and adjust nutrient solutions to prevent deficiencies or toxicities.
- pH Fluctuations: Maintain a stable pH level, ideally between 5.5 and 6.5, to optimize nutrient uptake.
- Root Rot: Guarantee proper oxygenation and avoid waterlogging to prevent fungal infections.
Conclusion
In summary, hydroponics presents a viable alternative to traditional soil-based agriculture, offering numerous benefits such as increased growth rates and resource efficiency. By eliminating the need for soil, hydroponic systems allow plants to receive nutrients directly through water, leading to faster and more controlled growth. Understanding hydroponic growing basics is essential for optimizing factors like nutrient balance, water quality, and lighting conditions. As a result, this method can help maximize yields while conserving valuable resources such as water and space.
Significantly, hydroponic systems can achieve up to 90% water savings compared to conventional farming methods.
By understanding the types of systems, selecting appropriate plants, and maintaining nutrient solutions, practitioners can optimize crop yields and sustainability.
Effective troubleshooting further guarantees the reliability and productivity of hydroponic setups, making it a promising approach for future agricultural practices.






