What Hydroponics System Was Used by the Egyptians
Ancient Egyptians innovatively employed hydroponic techniques to sustain agriculture in their arid climate. Utilizing nutrient-rich water from the Nile, they developed systems like basin irrigation, shaduf water lifting, and floating rafts that allowed plant roots to absorb essential minerals directly from water.
They cultivated crops such as leafy greens and herbs without soil, optimizing water and nutrient use. These advanced methods not only bolstered food security but also laid the groundwork for modern hydroponics, demonstrating a profound understanding of sustainable farming practices.
To grasp how these ancient innovations continue to resonate in today's agricultural techniques offers a fascinating perspective on enduring agricultural wisdom.

Key Takeaways
- Egyptians used floating rafts with nutrient-absorbent materials to support plant growth in hydroponic systems.
- Controlled water channels ensured a steady flow of nutrient-rich water to crops.
- Clay pot systems were employed to regulate water and nutrient absorption effectively.
- Shaduf irrigation systems provided precise water lifting from the Nile for hydroponic cultivation.
Historical Context

While the ancient Egyptians are often celebrated for their architectural and engineering marvels, their innovative agricultural practices, including early forms of hydroponics, provide an essential context for understanding their ability to sustain large, urban populations in a mainly arid environment.
Utilizing the fertile banks of the Nile River, they developed sophisticated irrigation techniques that maximized agricultural yield. This ingenuity was not only vital for feeding their populace but also allowed for the cultivation of a diverse array of crops.
Early Agricultural Techniques
The ancient Egyptians employed a variety of early agricultural techniques, leveraging the predictable inundation cycles of the Nile River to irrigate and fertilize their fields, thereby ensuring consistent crop production.
Their primary method, basin irrigation, involved creating a network of embankments and dykes to control the flow of floodwaters. This allowed for the distribution of nutrient-rich silt across the fields, enriching the soil and enhancing crop yields.
Additionally, they developed shaduf systems for lifting water from the Nile into irrigation channels, enabling precise water management.
These innovations not only maximized agricultural productivity but also laid the groundwork for more advanced agrarian techniques. Such strategic manipulation of natural resources underscores their profound understanding of sustainable farming practices.
Understanding Hydroponics

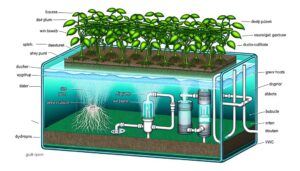
Building on the innovative spirit of ancient agricultural practices, modern hydroponics represents a sophisticated evolution in farming techniques, allowing for soil-less cultivation through nutrient-rich water solutions. This method offers a controlled environment that maximizes plant growth while minimizing resource consumption. By eliminating the need for traditional soil, this approach reduces the risks of pests and soil-borne diseases, leading to healthier crops with higher yields. Many growers choose to build a recirculating hydroponic system, which continuously cycles nutrient solutions, conserving water and essential minerals. This sustainable method not only supports food production in urban areas but also helps address challenges posed by climate change and limited arable land.
Key components include:
- Nutrient solutions: Precisely balanced mixtures tailored for ideal plant health.
- Growing media: Substrates like coconut coir and perlite support root structures.
- Lighting systems: Artificial lights that mimic sunlight, enabling year-round cultivation.
- Water management: Efficient systems for water recirculation and conservation.
These elements collectively enable hydroponics to surpass traditional agriculture in yield and sustainability, underscoring its potential to revolutionize food production.
Evidence of Soil-less Farming
Historical records and archaeological findings have revealed substantial evidence of ancient civilizations, including the Egyptians, engaging in soil-less farming practices. Textual references from ancient Egyptian manuscripts point to the cultivation of crops in nutrient-rich waters, suggesting an early understanding of hydroponic principles.
Additionally, the remnants of ancient gardens, particularly in the arid regions of Egypt, hint at innovative agricultural techniques designed to optimize water usage. Hieroglyphics depicting plant roots suspended in water further substantiate these claims.
These historical insights highlight the ingenuity of the Egyptians, who leveraged their environmental constraints to develop early forms of hydroponics. Such evidence underscores a sophisticated grasp of agricultural science, emphasizing the timeless human pursuit of sustainable farming solutions.
Methods Employed

Ancient Egyptian farmers employed various advanced techniques to facilitate soil-less farming, capitalizing on their understanding of nutrient-rich water systems to cultivate crops efficiently. These methods were not only innovative but also highly effective, demonstrating a profound grasp of agricultural science.
- Floating Rafts: Wooden rafts layered with nutrient-absorbent materials allowed plants to grow directly on water surfaces.
- Flowing Water Channels: Controlled channels guaranteed a steady flow of nutrient-laden water to support plant growth.
- Clay Pot Systems: Utilized porous clay pots to regulate water and nutrient absorption.
- Shadoof Irrigation: Lever-based systems lifted water from the Nile for precise irrigation.
These techniques underscore the Egyptians' mastery in creating sustainable, efficient agricultural systems.
Nutrient-Rich Water Systems
The Egyptians' hydroponics systems were marked by their innovative use of nutrient-rich water, which was crucial for plant growth.
They employed ancient fertilizer techniques, utilizing organic materials to enrich the water with important minerals and nutrients.
Additionally, their water circulation methods guaranteed consistent distribution of these nutrients, optimizing the conditions for plant health and productivity.
Ancient Fertilizer Techniques
Leveraging the fertile inundation of the Nile, Egyptians developed sophisticated nutrient-rich water systems that served as an early form of hydroponics, demonstrating advanced understanding of plant nutrition and irrigation. Their techniques included the use of silt and organic matter deposited by the river's annual floods to create highly fertile grounds for crop cultivation. This practice guaranteed that essential nutrients were readily available to the plants, fostering robust growth.
The ancient Egyptians' approach to nutrient management included:
- Utilization of river silt rich in minerals.
- Incorporation of decayed plant and animal matter.
- Strategic seasonal planting aligned with flood cycles.
- Construction of irrigation canals for controlled water distribution.
These methods exemplify an early integration of natural resources and agricultural innovation.
Water Circulation Methods
Building upon their mastery of nutrient management, Egyptians also innovated in the domain of water circulation methods to maintain consistently nutrient-rich environments for their crops. They employed various techniques to guarantee ideal hydration and nutrient delivery, leveraging their understanding of hydraulic principles. The table below outlines key methods used:
| Method | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Shaduf | Manual water-lifting device | Efficient for small-scale farming |
| Saqiya | Animal-powered water wheel | Increased irrigation capacity |
| Basin Irrigation | Flooding fields using canal systems | Enhanced soil nutrient absorption |
| Nile Flooding | Seasonal inundation leveraging natural cycles | Natural nutrient replenishment |
These methods exemplify the Egyptians' advanced approach to water management, integrating technology and natural resources. This strategic use of water circulation systems laid a foundational framework for modern hydroponics.
Crop Varieties Grown

Among the diverse crop varieties cultivated using hydroponics systems in ancient Egypt, leafy greens such as lettuce and spinach were particularly prominent due to their rapid growth cycles and high nutritional value.
These crops were strategically chosen for their ability to thrive in nutrient-rich water environments, maximizing the efficiency of the hydroponics system. Additionally, the Egyptians experimented with other crops to optimize their agricultural output.
- Lettuce: Favored for its quick maturation and nutritional benefits.
- Spinach: Valued for its dense nutritional profile and fast growth.
- Herbs: Including mint and basil, used for culinary and medicinal purposes.
- Cucumbers: Cultivated for their high water content and versatility.
This selection demonstrates the Egyptians' innovative approach to sustainable agriculture.
Benefits of Hydroponics
The strategic selection of crop varieties in ancient Egyptian hydroponics highlights the numerous benefits of this innovative agricultural method, including enhanced resource efficiency, faster growth cycles, and the ability to cultivate crops in challenging environments.
By optimizing water and nutrient delivery directly to plant roots, hydroponics minimizes water wastage and eliminates the need for soil, thereby preserving arable land.
Additionally, the controlled environment accelerates plant growth, enabling multiple harvests per year. This method also allows for agriculture in arid regions or areas with poor soil quality, expanding the potential for food production.
These advantages underscore the historical significance and future potential of hydroponics, positioning it as a pivotal technique for sustainable and resilient agricultural practices.
Impact on Society

Ancient Egyptian hydroponics fundamentally transformed societal structures by enabling food production in otherwise inhospitable regions, thereby supporting population growth and fostering economic stability.
This agricultural ingenuity allowed for the cultivation of crops independent of soil quality, facilitating consistent food supplies and reducing famine risks. Consequently, it led to advancements in trade, as surplus produce could be exchanged for other goods and services. The increased food security also permitted greater specialization of labor, fostering advancements in various fields such as engineering and medicine.
- Enhanced agricultural productivity in arid regions
- Increased population growth and urbanization
- Strengthened economic stability and resilience
- Expansion of trade networks and commerce
These societal shifts underscore the profound impact of hydroponic systems in ancient Egypt.
Modern Implications
Hydroponic systems, inspired by ancient innovations, now play a pivotal role in modern agriculture by offering sustainable solutions to contemporary challenges such as food security, resource conservation, and urban farming.
Leveraging controlled environments, hydroponics maximizes crop yields while minimizing water usage and soil dependency. This technology addresses the escalating demand for agricultural productivity in urban settings, where space is limited.
In addition, hydroponics can mitigate the adverse effects of climate change by enabling year-round cultivation, independent of external weather conditions.
The integration of IoT and AI in hydroponic systems also allows for precision farming, optimizing nutrient delivery and reducing waste.
Consequently, hydroponics stands as a demonstration of how ancient agricultural practices can be adapted to meet modern needs, fostering innovative food production solutions.
Conclusion
Historical hydroponics harnessed by the Egyptians highlights humanity's ingenious ingenuity.
Evidence elucidates early engineering and agricultural acumen, showcasing soil-less systems that supported sustenance.
These methods, meticulously managed, maximized crop yields of various vegetables and herbs.
Benefits blossomed, bolstering societal stability and sustainability.
Insights into ancient innovations offer intriguing implications for modern agricultural advancements.
The Egyptians' early employment of hydroponics underscores a sophisticated understanding of efficient farming techniques, fostering future food security and environmental harmony.