What Size Air Pump for Hydroponics
When selecting an air pump for hydroponics, we need to optimize oxygenation. Generally, we'd recommend 0.5 to 1 LPM (liters per minute) per gallon of water.
For instance, a 20-gallon system would require a minimum of 10 LPM. Diaphragm pumps provide consistent airflow, ideal for large systems, while piston pumps handle high pressures excellently in deep water culture setups.
Efficiency, noise levels, and energy consumption are essential considerations as well. It's significant to match the pump's capacity with our specific hydroponic needs to maximize plant growth.
For precise guidelines and deeper insight into pump selection, let's move forward.
Key Takeaways
- Calculate the total water volume of your hydroponic system to determine the required pump capacity.
- Aim for an airflow rate of 0.5 – 1 LPM per gallon of water.
- Larger systems over 100 gallons need proportional scaling of air pump capacity.
- Different hydroponic systems (NFT, DWC, etc.) require specific pump configurations for optimal oxygenation.
Importance of Air Pumps

Air pumps play an indispensable role in hydroponics by guaranteeing that nutrient solutions are adequately oxygenated, thereby promoting ideal plant growth and health.
We recognize that oxygenation is vital for root respiration, facilitating optimal nutrient uptake and preventing anaerobic conditions that can lead to root diseases.
By continuously infusing air into the nutrient solution, air pumps maintain dissolved oxygen levels essential for vigorous plant development.
Moreover, efficient oxygenation supports beneficial microbial activity, enhancing nutrient availability and uptake.
In our quest for innovation, leveraging the right air pump guarantees that plants receive a consistent supply of oxygen, which maximizes growth rates and yields.
How Air Pumps Work
To comprehend the mechanics of air pumps, we must explore the principles of gas displacement and pressure dynamics that facilitate oxygen infusion into nutrient solutions.
Air pumps operate by creating a pressure differential, forcing ambient air through tubing into air stones or diffusers submerged in the nutrient solution. This process is crucial for maintaining dissolved oxygen levels, which promotes root respiration and nutrient uptake.
Here's a precise breakdown:
- Diaphragm Movement: A flexible diaphragm oscillates, generating airflow.
- Pressure Regulation: Valves control the flow rate, ensuring consistent pressure.
- Air Diffusion: Air stones break the air into fine bubbles for maximal oxygen dissolution.
- Nutrient Solution Interaction: Oxygen-rich bubbles rise, enriching the solution with essential gases.
Understanding these mechanics aids in optimizing hydroponic system efficiency.
Types of Hydroponic Systems

Diving into the domain of hydroponics, we encounter various system types, each uniquely tailored to optimize plant growth through different methods of nutrient delivery.
Nutrient Film Technique (NFT) systems utilize a thin film of nutrient-rich water flowing over the roots, ensuring constant access to nutrients and oxygen.
Deep Water Culture (DWC) systems submerge roots in oxygenated nutrient solutions, ideal for rapid growth.
Aeroponics suspends plants in air, misting roots with nutrient solutions, maximizing oxygen exposure.
Ebb and Flow systems, or Flood and Drain, periodically flood the plant roots, then drain, simulating natural water cycles.
Finally, Drip Systems deliver nutrient solutions directly to the plant roots via a network of tubes, providing precise control.
Each method offers unique advantages for diverse cultivation needs.
Calculating Air Pump Size
Understanding the specific requirements of each hydroponic system, we can now focus on calculating the appropriate air pump size to guarantee ideal oxygenation for plant roots.
To do so, we need to take into account several precise factors:
- Volume of Water: Calculate the total volume of water in the system, making sure the pump can handle the load.
- Desired Air Flow Rate: Determine the best liters per minute (LPM) of air required, typically aiming for 0.5 – 1 LPM per gallon of water.
- Pump Efficiency: Choose high-efficiency pumps to guarantee consistent oxygenation while conserving energy.
- System Type: Adjust the air pump size based on the specific hydroponic setup, such as NFT, DWC, or Ebb and Flow, each having unique aeration demands.
Key Factors to Consider
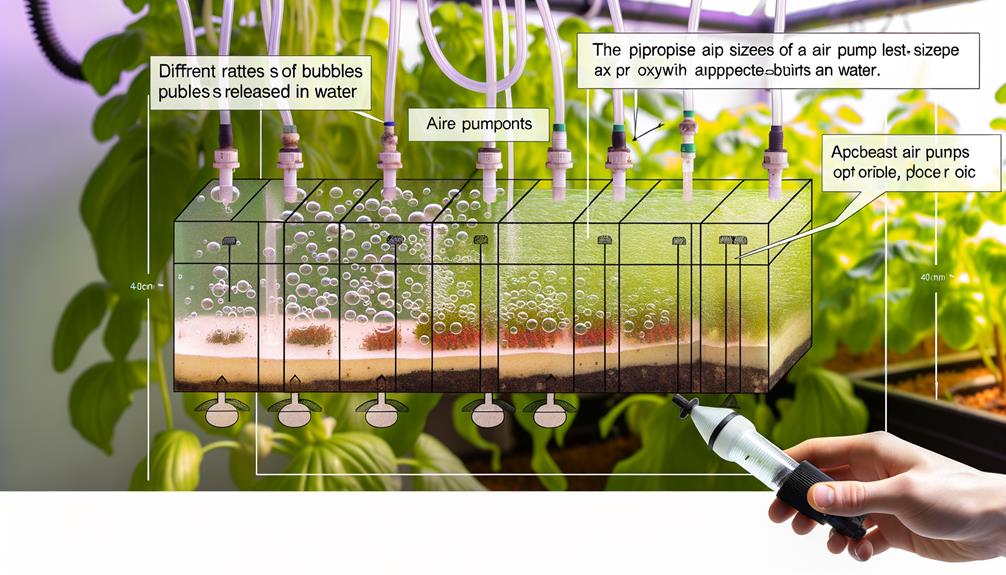
When selecting an air pump for hydroponics, we must consider key factors such as water volume, airflow rate, pump efficiency, and system type to guarantee ideal root oxygenation.
Water volume dictates the necessary pump capacity, guaranteeing sufficient oxygen diffusion throughout the nutrient solution.
The airflow rate, measured in liters per minute (LPM), must match or exceed the system's oxygen demand.
Pump efficiency, including energy consumption and noise levels, affects long-term sustainability and operational costs.
Additionally, different hydroponic systems—whether deep water culture, nutrient film technique, or aeroponics—require specific pump configurations for best performance.
Recommended Pump Sizes
Let's evaluate the recommended air pump sizes by considering plant growth requirements, tank volume, and specific air pump types.
We need to guarantee the pump's capacity aligns with the oxygenation needs of our hydroponic system.
Plant Growth Requirements
Determining the ideal air pump size involves calculating the specific oxygenation needs of your hydroponic system based on plant density and growth stage. We need to guarantee each plant receives adequate dissolved oxygen for peak growth. Here's how to tailor your air pump selection:
- Plant Density: Higher plant densities require more oxygen, necessitating a more powerful pump.
- Growth Stage: Seedlings need less oxygen compared to mature plants in the flowering stage.
- Root Zone: Larger root masses demand increased oxygen to prevent root rot and promote nutrient uptake.
- Pump Efficiency: Evaluate pumps by liters per minute (LPM) output to match the system's oxygenation requirements.
Tank Volume Considerations
To guarantee ideal oxygenation for your hydroponic system, we must consider the tank's volume and select a pump that delivers the appropriate liters per minute (LPM) for that capacity.
For precise aeration, the general rule is to aim for an air pump that provides at least 0.5 LPM per gallon of water.
For instance, a 20-gallon tank requires a pump with a minimum output of 10 LPM.
Larger systems, such as those exceeding 100 gallons, necessitate proportional scaling to maintain peak dissolved oxygen levels.
Air Pump Types
Given the diverse array of air pump types available, selecting the ideal size for hydroponic systems necessitates an understanding of their specific features and recommended output capacities.
We should consider the following air pump types and their most effective uses:
- Diaphragm Pumps: Ideal for larger systems, offering consistent air flow and high output. Recommended for setups needing 1-5 liters per minute (LPM) per gallon.
- Piston Pumps: Suitable for high-pressure needs, best for deep water culture. Aim for 2-6 LPM per gallon.
- Linear Air Pumps: Energy-efficient and quiet, perfect for medium to large systems. Target 1-4 LPM per gallon.
- Vane Pumps: High durability and suited for commercial applications. Most effective at 3-7 LPM per gallon.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
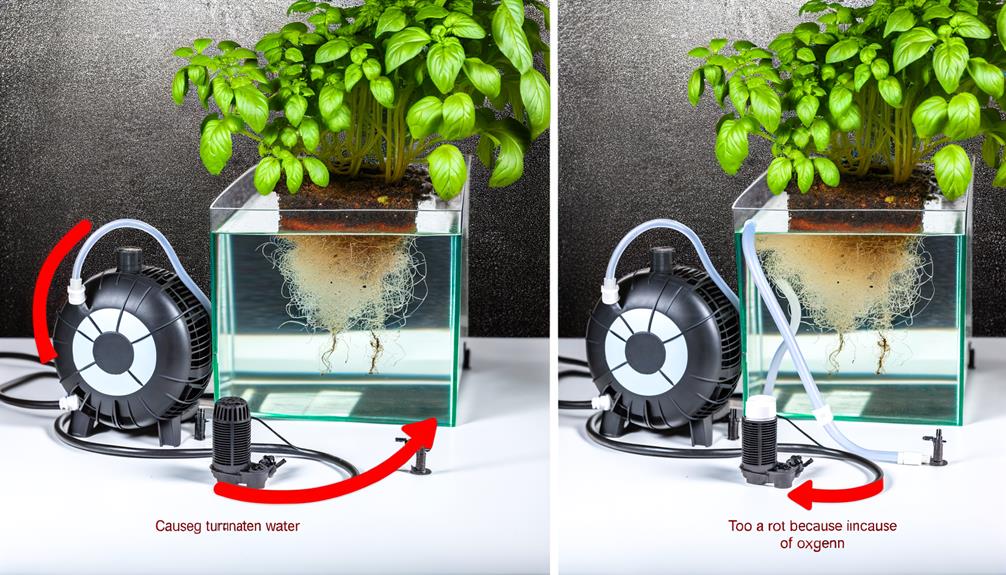

One common mistake we often encounter is selecting an air pump without considering the specific oxygen requirements of different hydroponic systems.
Each system, whether it's deep water culture, nutrient film technique, or aeroponics, demands precise dissolved oxygen levels for ideal root health.
We must avoid the pitfall of underestimating the pump's capacity, as inadequate aeration can lead to root rot and stunted plant growth.
Oversizing the pump can also cause turbulence, stressing the roots and wasting energy.
It's essential to evaluate the system's volume and the number of air stones used.
Additionally, ignoring the pump's noise level and energy efficiency can compromise the operational environment and sustainability.
Let's innovate by making informed, precise choices for our hydroponics systems.
Maintenance Tips
For ideal performance, we must implement a regular cleaning schedule for our air pumps.
Let's not forget to check the air stones for blockages and inspect tubing connections for any leaks or wear.
Consistent maintenance guarantees efficient oxygenation and prolongs the lifespan of our hydroponic systems.
Regular Cleaning Schedule
To guarantee the ideal performance of your hydroponic air pump, we must adhere to a rigorous and regular cleaning schedule. Consistent maintenance guarantees maximum oxygen delivery and longevity of the system.
Here's a precise cleaning regimen:
- Weekly Inspection: Examine the pump for debris accumulation and check for unusual noises.
- Bi-weekly Cleaning: Disassemble the pump and clean each component using a mild detergent solution to remove any biofilm buildup.
- Monthly Deep Clean: Soak pump parts in a 10% bleach solution for 15 minutes, followed by a thorough rinse to eradicate microbial growth.
- Quarterly Maintenance: Replace worn-out diaphragms and seals to maintain efficiency and prevent air leakage.
Implementing this schedule will sustain the pump's efficiency and support our innovative hydroponic systems.
Check Air Stones
Regularly monitoring and cleaning air stones is essential to maintaining ideal oxygen levels and preventing clogging in our hydroponic systems.
We should inspect air stones weekly for any buildup of biofilm, mineral deposits, or algae. Using a soft brush or a mild acid solution, we can effectively clean these obstructions.
By soaking air stones in a diluted hydrogen peroxide solution, we guarantee thorough sterilization, which minimizes pathogenic risks.
Additionally, replacing air stones every 6-12 months prevents performance degradation. This routine not only maximizes oxygen diffusion efficiency but also promotes optimal root health and nutrient absorption.
Let's prioritize these maintenance practices to sustain the innovative edge of our hydroponic cultivation systems.
Inspect Tubing Connections
While maintaining our air stones, we must also guarantee that tubing connections are secure and free from blockages to maintain consistent airflow in our hydroponic systems.
Confirming ideal performance involves scrutinizing every aspect of the tubing.
Here are four essential steps:
- Examine Tubing Integrity: Regularly check for cracks or wear that could compromise air delivery.
- Verify Connections: Confirm all joints are tightly sealed to prevent air leakage.
- Clean Inside Tubing: Periodically flush the tubing with water to remove any algae or mineral buildup.
- Inspect for Kinks: Confirm the tubing is free from bends or kinks that could impede airflow.
Conclusion
In summary, selecting the right air pump for your hydroponic system is essential, much like finding the perfect gear for a cyclist.
By understanding the importance of aeration, calculating the required pump size, and considering key factors such as system type and tank volume, we can optimize plant health and growth.
Let's avoid common pitfalls, stay diligent with maintenance, and guarantee our hydroponic gardens thrive.
With precision and care, we'll achieve a flourishing, oxygen-rich environment.






